Summary
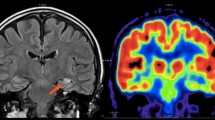
A patient with medically intractable complex partial epilepsy was evaluated for epilepsy surgery by electroencephalograph recording with depth electrodes and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET). A small calcified arteriovenous malformation was excised from the left parietal lobe, and the patient became seizure free. Baseline and language stimulation PET scans were obtained preoperatively and 10 months postoperatively. There was a significant increase in glucose metabolism of the left temporal lobe postoperatively, which we interpret as evidence of improved neuronal function. We suggest that this case represents evidence for a functional, and reversible, inhibition of neuronal metabolism by epileptic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borowski JG, Benton AL, Spreen O (1967) Word fluency and brain damage. Neuropsychologia 5:135–140
Delgado-Escueta AV, Walsh GO (1985) Type I complex partial seizures of hippocampal origin: excellent results of anterior temporal lobectomy. Neurology 35:143–154
DeRenzi E, Vignolo LA (1962) The Token test. A sensitive test to detect receptive disturbances in aphasia. Brain 85:665–678
Engel J Jr, Kuhl DE, Phelps ME, Rausch R, Nuwer M (1983) Local cerebral metabolism during partial seizures. Neurology 33:400–413
Goodglass H, Kaplan E (1983) Boston naming test. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia
Gur RC, Sussman NM, Alavi A, Gur RE, Rosen AD, O'Connor M, Goldberg HI, Greenberg JH, Reivich M (1982) Positron emission tomography in two cases of childhood epileptic encephalopathy (Lennox-Gastaut syndrome). Neurology 32:1191–1194
Hutchins GD, Holden JE, Koeppe RA, Halama JR, Gatley SJ, Nickles RJ (1984) Alternative approach to single-scan estimation of cerebral glucose metabolic rate using glucose analogs with particular application to ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:35–40
La Pointe LL, Horner J (1979) Reading comprehension battery for aphasia. CC Publications, Tigard, Oregon
Mazziotta JC, Engel J Jr (1984) The use and impact of positron computed tomography scanning in epilepsy. Epilepsia 25 [Suppl 2]:S86-S104
Mazziotta JC, Phelps ME, Carson RE, Kuhl DE (1982) Tomographic mapping of human cerebral metabolism: auditory stimulation. Neurology 32:921–937
Penfield W, Jasper H (1954) Epilepsy and the functional anatomy of the human brain. Little Brown, Boston
Raven JC (1962) Coloured progressive matrices. Lewis, London
Schuell P (1957) A short examination for aphasia. Neurology 7:625–635
Spencer SS, Spencer DD, Williamson PD, Mattson RH (1983) Sexual automatisms in complex partial seizures. Neurology 33:527–533
Tewson TJ (1983) Cyclic sulfur esters as substrates for nucleophilic-substitution. A new synthesis of 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose. J Org Chem 48:3507–3510
Walsh GO, Delgado-Escuta AV (1984) Type II complex partial seizures: poor results of anterior temporal lobectomy. Neurology 34:1–13
Ward AA Jr (1983) Perspectives for surgical therapy of epilepsy. In: Ward AA, Penry JK, Purpura D (eds) Epilepsy (ARNMD, vol 61). Raven Press, New York, pp 371–390
Werz RT, Rosenbek JC (1981) Appraising apraxia of speech. J Colo Speech Hear Assoc 5:18–33
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dasheiff, R.M., Rosenbek, J., Matthews, C. et al. Epilepsy surgery improves regional glucose metabolism on PET scan. J Neurol 234, 283–288 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314281
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314281