Summary
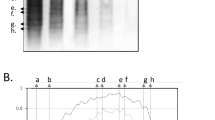
Isoelectric focusing of CSF and serum IgG followed by crossed immuno isoelectric focusing and direct immunofixation as well as quantitative assay of IgG and albumin were performed in 64 clinically definite multiple sclerosis patients. Intrathecal IgG synthesis was calculated according to the CSF IgG index and de novo CNS IgGsyn. Isoelectric focusing showed abnormal IgG fractions in CSF indicating increased intrathecal synthesis of oligoclonal IgG in 99% of patients. Only 62% and 70% of multiple sclerosis patients showed values of CSF IgG indices and de novo CNS IgGsyn higher than in controls. Increased intrathecal IgG synthesis was indicated more frequently by de novo CNS IgGsyn in patients with a normal CSF IgG index than by the CSF IgG index in patients with normal de novo CNS IgGsyn. All patients with blood CSF barrier damage had increased de novo CNS IgGsyn, but only 40% had an increased CSF IgG index. Isoelectric focusing seemed to be a more sensitive method to detect an increased intrathecal oligoclonal IgG synthesis than quantitative methods. Identification of abnormal IgG fractions can be performed easily and with more reproducible results by direct immunofixation than by crossed immuno isoelectric focusing. The formula for de novo CNS IgGsyn seemed more sensitive and less influenced by blood-CSF barrier damage than the CSF IgG index to detect increased intrathecal IgG synthesis in multiple sclerosis patients. No correlation was found between the CSF IgG pattern or amounts and age, duration, clinical course or therapy of the disease.
Zusammenfassung
Bei 64 klinisch bestimmten Fällen von multipler Sklerose wurde die isoelektrische Fokussierung von CSF und Serum-IgG, gefolgt von „crossed“ immuno-isoelektrischer Fokussierung und direkter Immunofixierung, sowohl bei der quantitativen Bestimmung als auch bei Albumin, durchgeführt. Die IgG-intrathekal-Synthese wurde entsprechend dem CSF-IgG-Index und de-novo-CNS-IgGsyn berechnet. Bei 99% der Patienten zeigte die isoelektrische Fokussierung abnorme Fraktionen im CSF an, ein Hinweis auf eine erhöhte intrathekale Synthese von oligoklonalem IgG. Nur bei 62–70% der Multiple-Sklerose-Fälle waren die Werte des CSF-IgG-Index und de-novo-CNS-IgGsyn höher als bei Vergleichskontrollen. Eine erhöhte intrathekale Synthese wurde häufiger von de-novo-CNS-IgGsyn bei Patienten mit normalem CSF-IgG-Index als von CSF-IgG-Index bei Patienten mit normalem de-novo-CNS-IgGsyn angezeigt. Bei allen Patienten mit Störung der Blut-CSF-Schranke war de-novo-CNS-IgGsyn erhöht, dagegen wurde bei nur 40% eine Erhöhung des CSF-IgG-Index festgestellt. Im Vergleich zu den quantitativen Verfahren scheint die isoelektrische Fokussierung die genauere Methode zur Feststellung einer erhöhten Intrathekal-oligoklonal-IgG-Synthese zu sein. Abnorme IgG-Fraktionen werden eher durch direkte Immunofixierung einfacher und mit wenig voneinander abweichenden Resultaten festgestellt als durch immunoisoelektrische Fokussierung. Die Formel für die de-novo-CNS-IgGsyn scheint sensibler und weniger durch Störungen der Blut-CSF-Schranke beeinflußbar zu sein als der CSF-IgG-Index bei der Bestimmung erhöhter Intrathekal-IgG-Synthese bei Fällen von multipler Sklerose. Es wurde kein Zusammenhang zwischen der CSF-IgG-Zusammensetzung und den Werten zum Alter, der Krankheitsdauer, dem klinischen Verlauf und der Behandlungstherapie des Kranken gefunden.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumhefner RW, Mendez M, Ma BI, Tourtellotte WW (1979) Modulation of the de novo central nervous system (CNS) IgG synthesis with preservation of oligoclonal IgG in multiple sclerosis (MS). Neurology 29:549
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Christensen O, Clausen J, Fog T (1978) Relationships between abnormal IgG index, oligoclonal bands, acute phase reactants and some clinical data in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 218:237–244
Cwynarski MT, Watkins J, Jonson PM (1975) Isoelectric pattern in IgG myeloma proteins: possible biochemical and clinical inferences. In: Arbuthnott JP, Beeley JA (eds) Isoelectric focusing. Butterworths, London, pp 319–326
Davies H (1975) Thin layer isoelectric focusing. In: Arbuthnott JP, Beeley JA (eds) Isoelectric focusing. Butterworths, London, pp 97–113
Delmotte P (1972) Results comparatifs de l'electrophorèse en agar et de l'examen par electrofocalisation des gammaglobulines du liquide cephalo-rachidien. Acta Neurol Belg 72:226–234
Delmotte P, Gonsette R (1977) Biochemical findings in multiple sclerosis. IV: Isoelectric focusing of the CSF gamma globulins in multiple sclerosis (262 cases) and other neurological diseases (272 cases). J Neurol 215:27–37
Delpech B, Lichtblau E (1972) Etude quantitative des immunoglobulines G et de l'albumine du liquide cephalo-rachidien. Clin Chim Acta 37:15–23
Elsner W, Tourtellotte WW, Murthy KN, Ma BI, Potvin AR, Syndulko K (1978) Multiple sclerosis: effect of dexamethasone on in situ central nervous system (CNS) IgG synthesis. Neurology 28:403
Hershey LA, Trotter JL, Banks G (1979) Isoelectric focusing (IF) in the evaluation of CSF IgG in multiple sclerosis (MS). Neurology 29:538
Kabat EA, Glusman M, Knaub V (1948) Quantitative estimation of the albumin and gammaglobulin in normal and pathological cerebrospinal fluid by immunochemical methods. Amer J Med 4:653–662
Kjellin KG, Vesterberg O (1974) Isoelectric focusing of CSF proteins in neurological diseases. J Neurol Sci 23:199–213
Kjellin KG, Siden Å (1977) Aberrant CSF protein fractions found by electrofocusing in multiple sclerosis. A study of 26 cases with clinically verified or probable multiple sclerosis and 2 cases with optic neuritis. Eur Neurol 15:40–50
Laterre EC, Callawaert A, Heremans JF, Sfaello Z (1970) Electrophoretic morphology of gamma-globulin in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system. Neurology 20:982–990
Laurenzi MA, Link H (1978) Comparison between agarose gel electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing of CSF for demonstration of oligoclonal immunoglobulin bands in neurological disorders. Acta neurol Scand 58:148–156
Link H, Müller R (1972) Immunoglobulins in multiple sclerosis and infections of the nervous system. Arch Neurol 25:320–344
Link H (1972) Oligoclonal immunoglobulin G in multiple sclerosis brains. J Neurol Sci 16:103–114
Link H (1973) Comparison of electrophoresis on agar gel and agarose gel in the evaluation of gamma globulin abnormalities in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in multiple sclerosis. Clin Chim Acta 46:383–389
Link H (1975) The value of cerebrospinal fluid analysis in clinical neurology. Proc XIX National Congress of Neurology, Genova (Italy)
Link H, Tibbling G (1977) Principles of albumin and IgG anaysis in neurological disorders. Evaluation of IgG synthesis within the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37:397–401
Link H, Möller E, Müller R, Norrby E, Olsson JE, Stendahal L, Tibbling G (1977) Immunoglobulin abnormalities in spinal fluid in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 55, suppl 63:173–191
Livrea P, Zimatore GB, Simone IL, Lepore V, Trojano M, Loreto M, De Blasi A, Gennarini GF (1978) Isoelectric focusing and crossed immunoisoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid proteins in neurological disorders. Acta Neurol 33:501–517
Livrea P, Zimatore GB, Simone IL, Trojano M, Lepore V, Ferrara V, Lupo FA, Pedone D (1980) Isoelectric focusing and quantitative estimation of cerebrospinal fluid and serum IgG in idiopathic polyneuropathy. J Neurol 223:1–12
Lowenthal A (1964) Agar gel electrophoresis in neurology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurements with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mancini G, Vaerman JP, Carbonara AO, Heremans JF (1964) A single radial diffusion method for the immunological quantification of proteins. In: Peeters H (ed) XI Colloquium on protides of the biological fluids. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 370–373
McAlpine D, Lumsden CE, Acheson ED (1972) Multiple sclerosis: a reappraisal. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
McDonald WI, Halliday AM (1977) Diagnosis and classification of multiple sclerosis. Brit Med Bull 33:4–8
Mattson DH, Roos RP, Arnason BGW (1979) Comparison of agar gel electrophoresis (AGE) and isoelectric focusing (IEF) in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE), multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating diseases. Neurology 29, abs MSI 7:549
Muller R (1949) Studies on multiple sclerosis. Acta Med Scand 133, suppl 222:1–214
Nilsson K, Olsson JE (1978) Analysis for cerebrospinal fluid proteins by isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gel: methodological aspects and normal values with special reference to the alkaline region. Clin Chem 24:1134–1139
Olsson JE, Petterson B (1976) A comparison between agar gel electrophoresis and CSF and serum quotients of IgG and albumin in neurological diseases. Acta Neurol Scand 53:308–322
Olsson JE, Link H, Muller R (1976) Immunoglobulin abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. Relation to clinical parameters: disability, duration and age of onset. J Neurol Sci 27:233–345
Olsson JE, Nilsson K (1979) Gamma globulins of CSF and serum in multiple sclerosis: isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gel and agar gel electrophoresis. Neurology 29:1383–1391
Poloni M, Rocchelli B, Scelsi R, Pinelli P (1979) Intrathecal IgG synthesis in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. A comparative evaluation by IgG index and isoelectric focusing. J Neurol 221:245–255
Reiber H (1979) Quantitative Bestimmung der lokal im Zentralnervensystem synthetisierten Immunoglobulin G-Fraktion des Liquors. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 17:587–591
Sandberg Wollheim M (1974) Immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro by cerebrospinal fluid cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. Scand J Immunol 3:717–730
Schliep G, Felgennauer K (1978) Serum-CSF protein gradient, the blood-CSF barrier and the local immune response. J Neurol 218:77–96
Schuller E, Deloche G,Delasnerie N, Loridan M (1977) Oligoclonal aspect in the CSF of the multiple sclerosis patients: a statistical and physiological study. Acta Neurol Scand 55, suppl 63:207–216
Siden Å (1977) Crossed immunoelectrofocusing of cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulins. J Neurol 217:103–109
Siden Å, Kjellin KG (1977) Isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid proteins in multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis. In: Proc of the 11th World Congress of Neurology, Excerpta Medica, International Congress Series, abs 427. Amsterdam, p 136
Siden Å, Kjellin KG (1978) CSF protein examination with thin layer isoelectric focusing in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 39:131–146
Stibler H (1978) Isoelectric focusing of the cerebrospinal fluid proteins in degenerative diseases of the central nervous system. Ph D thesis, Karolinska Hospital, Stockholm
Stibler H (1979) Direct immunofixation after isoelectric focusing. J Neurol Sci 42:275–281
Tourtellotte WW, Parker JA (1967) Multiple sclerosis: brain immunoglobulin G and albumin. Nature 214:683–686
Tourtellotte WW (1970) On cerebrospinal fluid IgG quotients in multiple sclerosis and other diseases. A review and a new formula to estimate the amount of IgG synthesized per day by central nervous system. J Neurol Sci 10:279–304
Tourtellotte WW, Murthy K, Brandes D, Sajben N, Ma B, Cosimo P, Potvin A, Costanza A, Korelitz J (1976) Schemes to eradicate the multiple sclerosis central nervous system immune reaction. Neurology [Suppl] 26:59–61
Tourtellotte WW, Booe I (1978) Multiple sclerosis: the blood brain barrier and the measurement of the de novo central nervous system IgG synthesis. Neurology 28:76–83
Trotter JL, Garuey WF (1979) Prolonged suppression of CNS IgG synthesis (IgG syn) after large dose “pulse” methylprednisolone therapy in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 29:549
Vandvik B, Skrede S (1973) Electrophoretic examination of cerebrospinal fluid proteins in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. Eur Neurol 9:224–241
Vesterberg O (1972) Isoelectric focusing of proteins in polyacrylamide gel. Biochem Biophys Acta 257:11–19
Vesterberg O (1973) Isoelectric focusing of proteins in thin layer of polyacrylamide gel. Sci Tools 20:22–29
Williamson AR (1975) Antibody isoelectric spectra. In: Arbuthnott JP, Beeley JA (eds) Isoelectric focusing. Butterworths, London, pp 291–305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Livrea, P., Trojano, M., Simone, I.L. et al. Intrathecal IgG synthesis in multiple sclerosis: Comparison between isoelectric focusing and quantitative estimation of cerebrospinal fluid IgG. J Neurol 224, 159–169 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313278
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313278