Summary
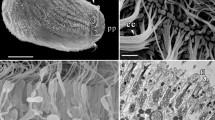
Specimens of Haliclona elegans (Bowerbank, 1866) are covered by a thin, double layered dermal membrane extending over large subdermal spaces. The pores in the dermal membrane are formed by single porocytes with one or sometimes several pores in the center of the cell. The subjacent tissue shows a faintly developed mesenchyme and numerous big choanocyte chambers projecting into lacunar spaces of the incurrent canal system. The outer surface of the chambers is directly covered by the pinacocyte epithelium of the incurrent canal wall, which also separates them completely from the mesenchyme. Water influx into the chambers is guaranteed by prosopylar openings in the pinacocyte cover at the outer chamber surface. The chambers are connected to the excurrent canal system in the eurypylous way by wide apopyles, each of which is surrounded by a small ring of flagellated cone cells. About 15% of the choanocyte chambers in H. elegans contain central cells, which are thought to derive from migrating pinacocytes of the canal systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boury-Esnault N (1972) Une structure inhalante remarquable des spongiaires: Le crible étude morphologique et cytologique. Arch Zool Exp Gén 113:7–23
Boury-Esnault N, De Vos L, Donadey C, Vacelet J (1984) Comparative study of the choanosome of Porifera: I. The Homoscleromorpha. J Morphol 180:3–17
Brien P (1932) Contribution à l'étude de la régéneration naturelle chez les Spongillidae. Spongilla lacustris (L.); Ephydatia fluviatilis (L.). Arch Zool Exp Gén 74:461–506
Brien P (1943) La formation des orifices inhalants chez les Spongillidae (Spongilla lacustris L. — Ephydatia fluviatlis L.). Bull Mus Roy Hist Nat Belg 14:1–16
Brien P (1973) Les Démosponges. In: Grassé P.-P (ed) Traité de Zoologie, Vol. III. Spongiaires. Masson et Cie, Paris, pp 133–461
Brien P, Meewis H (1938) Contribution à l'étude de l'embryogénèse des Spongillidae. Arch Biol 49:177–250
Connes R, Diaz J-P, Paris J (1971) Choanocytes et cellule centrale chez la Démosponge Suberites massa Nardo, CR Séances Acad Sci 273:1590–1593
Duboscq O, Tuzet O (1939) Les diverses formes des choanocytes des éponges calcaires hétérocoeles et leur signification. Arch Zool Exp Gén 80:353–388
Garrone R (1978) Phylogenesis of connective tissue. In: Robert L (ed) Frontiers of matrix Biology, Vol. 5. Karger, Basel
Harrison FW (1972) Phase contrast photomicrography of cellular behaviour in spongillid porocytes (Porifera: Spongillidae). Hydrobiol 40:513–517
Hyman LH (1940) The Invertebrates, Vol. I: Protozoa through Ctenophora. Mc Graw-Hill Book Company, New York, London
Johnston IS, Hildemann WH (1982) Cellular organization in the marine demosponge Callyspongia diffusa. Mar Biol 67:1–7
Langenbruch P-F (1983) Body structure of marine sponges. I. Arrangement of the flagellated chambers in the canal system of Reniera sp. Mar Biol 75:319–325
Langenbruch P-F (1985) Die Aufnahme partikulärer Nahrung bei Reniera sp. Helgoländer Meeresunters 39:263–272
Langenbruch P-F, Simpson TL, Scalera-Liaci L (1985) Body structure of marine sponges. III. The structure of choanocyte chambers in Petrosia ficiformis (Porifera, Demospongiae) Zoomorphology 105:383–387
Lévi C (1967) Les fibres segmentées intracellulaires d'Haliclona elegans Bow. (Démosponge Haploscléride). Arch Zool Exp Gén 108:611–615
Michin EA (1900) Sponges. In: Lankester ER (ed) A treatise on Zoology. Vol. II: The Porifera and Coelenterata. Adam and Charles Black, London, pp 1–178
Pavans de Ceccatty M (1955) Le système nerveux des éponges calcaires et siliceuses. Ann Sci Nat Zool 17:203–288
Reiswig HM (1975) The aquiferous systems of three marine Demospongiae. J Morphol 145:493–502
Reiswig HM, Brown MJ (1977) The central cells of sponges. Zoomorphology 88:81–94
Simpson TL (1968) The structure and function of sponge cells: New criteria for the taxonomy of poecilosclerid sponges (Demospongiae). Bull Peabody Mus Natur Hist (Yale Univ.) 25:1–141
Simpson TL (1984) The cell Biology of sponges. Springer, New York, Berlin, Heidelberg, Tokyo
Sollas WJ (1888) Report on the Tetractinellida collected by H.M.S. “Challenger”, during the years 1873–1876. H.M.S. Challenger Scient Results Zool 25:1–458
Weissenfels N (1980) Bau und Funktion des Süßwasserschwamms Ephydatia fluviatilis L. (Porifera). VII. Die Porocyten. Zoomorphology 95:27–40
Weissenfels N (1982) Rasterelektronenmikroskopische Histologie von spongiösem Material. Microsc Acta 85:345–350
Wierzejski A (1935) Süßwasserspongien. Mem Acad Polon (B) 9:1–242
Willenz Ph, Van de Vyver G (1982) Endocytosis of latex beads by the exopinacoderm in the fresh water sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis: An in vitro and in situ study in SEM and TEM. J Ultrastruct Res 79:294–306
Wintermann-Kilian G, Kilian EF, Ankel WE (1969) Musterbildung und Entwicklungsphysiologie der Epithelien beim Süßwasserschwamm Ephydatia fluviatilis. Zool Jahrb Abt Anat Ontog Tiere 86:459–492
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langenbruch, PF., Scalera-Liaci, L. Body structure of marine sponges. Zoomorphology 106, 205–211 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312041
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312041