Summary
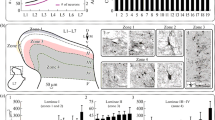
Neural elements in the lumbar enlargement of the developing Rana catesbeiana spinal cord were labelled by placing chips of dessicated horseradish peroxidase (HRP) into various lesions of the spinal cord. Of the elements labelled in the lumbar enlargement, a population of cells circumjacent to the gray matter was seen to be distinct from all others on the basis of their morphology, position and their putative embryonic origin. One cell type not previously described was a large circumferential cell (LCC) with primary processes completely circumscribing the gray matter. The ventral process crosses the midline and ascends or descends in the ventral funiculus. The dorsal primary process was observed to extend to the midline and turn ipsilaterally in a rostro-caudal direction in the dorsal funiculus. LCC's were present at early stages of larval development (stage III, Taylor and Kollros 1946) but could not be labelled in juvenile frogs. LCC's were only observed in the lumbar enlargement and could only be labelled through HRP applications at that level. They receive abundant synaptic input from the ipsilateral lateral funiculus. Possible roles for the LCC in the early function and development of the ranid lumbar spinal cord are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC (1977) Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neurosci 2:141–145
Athias M (1897) Structure histologique de la moelle epiniere du tetard de la grenouille (rana temporairia). Bibl Anat 5:58–89
Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC, King JS (1978) Ultrastructural identification of dorsal root primary afferent terminals after anterograde injury filling with horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res 153:127–134
Campbell HL, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC (1982) Large circumferential cells of the developing Rana catesbeiana spinal cord are labelled after HRP application to lateral funiculus. Soc Neurosci Abstr 8:820
Celio MR, Gray EG, Yasargil GM (1979) Ultrastructure of the Mauthner axon collateral and its synapses in the goldfish spinal cord. J Neurocytology 8:19–29
Chu-Wang IW, Oppenheim RW, Farel PB (1981) Ultrastructure of migrating spinal motoneurons in Anuran larvae. Brain Res 213:302–318
Farel PB (1980) Reflex development in anuran larvae: electrophysiological and anatomical correlates. Soc Neurosci Abstr 6:847
Forehand CJ, Farel PB (1982a) Spinal cord development in anuran larvae: I. primary and secondary neurons. J Comp Neurol 209:386–394
Forehand CJ, Farel PB (1982b) Spinal cord development in anuran larvae: II. ascending and descending pathways. J Comp Neurol 209:395–408
Fox H (1984) In: Amphibian Morphogenesis. Humana Press, New Jersey, pp 81–89
Herrick CJ, Coghill GE (1915) The development of reflex mechanisms in ambystoma. J Comp Neurol 25 (1):65–85
Holley JA (1982) Early development of the circumferential axonal pathway in mouse and chick spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 205:371–382
Hughes A (1963) On the labelling of larval neurones by melanin of ovarian origin in certain anura. J Anat 97:217–224
Jhaveri S, Frank E (1980) Morphological development of sensory axons and motoneurons in the branchial spinal cord of bullfrog tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana). Soc Neurosci Abstr 6:846
Kollros JJ (1981) Transitions in the nervous system during amphibian metamorphosis. In: Gilbert LI, Frieden E (eds) Metamorphosis a problem in developmental biology (2nd edn). Plenum Press, New York, pp 445–458
Kuwada JY (1985) Pathfinding by identifiable growth cones in the embryonic fish spinal cord. Soc Neurosci Abstr 102.4
Kuwada JY (1986) Cell recognition by neuronal growth cones in a simple vertebrate embryo. Science 233:740–746
Lamborghini JE (1980) Rohon-Beard cells and other large neurons in Xenopus embryos originate during gastrulation. J Comp Neurol 189:323–333
Liuzzi FJ, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC (1983) Dorsal root afferents contact migrating motoneurons in the developing frog spinal cord. Brain Res 262:299–392
Liuzzi FJ, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC (1985) The development of the relationship between dorsal root afferents and motoneurons in the larval bullfrog spinal cord. Brain Res Bull 14:377–392
Mawe GM, Bresnahan JC, Beattie MS (1983) Ultrastructure of HRP-labelled neurons: a comparison of two sensitive techniques. Brain Res Bull 10:551–558
Roberts A, Clarke JDW (1982) The neuroanatomy of an amphibian embryo spinal cord. Phil Trans R Soc (Lond B) 286:195–212
Sala y Pons C (1892) Estructura de la medulla espinal de los batracios. Trab Lab Invest Histol, pp 3–22
Silver M (1942) The motoneurons of the spinal cord of the frog. J Comp Neurol 77:1–39
Taylor AC, Kollros JJ (1946) Stages in the normal development of Rana pipiens larvae. Anat Rec 94:7–23
Van Gehuchten A (1897) La moelle epiniere des larves des batraciens (Salamandra maculosa). Arch de Biol 15:599–619
Wood MR, Cohen MJ (1981) Synaptic regeneration and glial reactions in the transected spinal cord of the lamprey. J Neurocytol 10:57–79
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campbell, H.L., Beattie, M.S. & Bresnahan, J.C. Circumferential cells of the developing Rana catesbeiana lumbar spinal cord. Anat Embryol 176, 155–163 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310048
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310048