Abstract
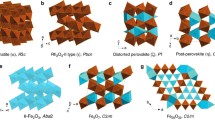
The structure of Mn and Fe oxides and oxyhydroxides has been probed by EXAFS. It is shown that EXAFS spectroscopy is sensitive to the nature of interpolyhedral linkages relying on metal-two nearest metal distances. Spectra recorded at 290 K and 30 K indicate that intercationic distances can be determined by EXAFS with a good accuracy (0.02 Å) assuming a purely Gaussian distribution function, even at room temperature. Although the accuracy on atomic numbers determination is fair for these disordered systems, EXAFS can differentiate structures with contrasted edge- over corner-sharing ratio like pyrolusite, ramsdellite, todorokite and lithiophorite or lepidocrocite and goethite. A direct application of this result has shown that the proportion of pyrolusite domains within the lattice of nsutite from Ghana is equal to 35±15 percent. The systematic study of Mn dioxides also put forward the sensitivity of EXAFS to the presence of corner-sharing octahedra, with a detection limit found to be less than 8 percent. In spite of their similar XRD patterns, the EXAFS study of todorokite and asbolane confirms that they possess a distinct structure; that is, a tunnel structure for the former and a layered structure for the second.
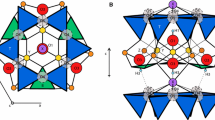
Such a topological approach has been used to probe the structure of ferruginous vernadite; a highly disordered iron-bearing Mn oxide. Fe and Mn K-edges EXAFS spectra are very dissimilar, traducing a different short range order. The Mn phase is constituted by MnO2 layers. Its large local structural order contrasts with the short range disorder of the iron phase. This hydrous Fe oxyhydroxide is constituted by face-, edge- and corner-sharing octahedra. This iron phase possesses the same local order as feroxy-hyte, but is long range disordered. The presence of face-sharing Fe(O,OH)6 octahedra prevents its direct solid-state transformation into well crystallized oxyhydroxides, and explains the necessary dissolution-reprecipitation mechanism generally invoked for the hydrous ferric gel → goethite transformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrhenius G, Cheung K, Crane S, Fisk M, Frazer J, Korkisch J, Mellin T, Nakao S, Tsai A, Wolf G (1979) Counterions in marine manganates. Colloq Int CNRS 289:333–356
Blake RL, Hessevick RE, Zoltai T, Finger L (1966) Refinement of the hematite structure. Am Mineral 51:123–129
Bonnin D, Calas G, Suquet H, Pezerat H (1985) Sites occupancy of Fe3+ in Garfield nontronite: a spectroscopic study. Phys Chem Minerals 12:55–64
Bunker G (1983) Application of the ratio method of EXAFS analysis to disordered systems. Nucl Instrum Methods 207:437–444
Bunker G, Stern EA (1984) Experimental study of multiple scattering in x-ray absorption near-edge structure. Phys Rev Letters 52,22:1990–1993
Burns RG, Burns VM (1977) Mineralogy of manganese nodules. In: “Marine Manganese Deposits”, Glasby GP (Ed) Elsevier:85–148
Burns, RG, Burns VM (1979) Manganese oxides. In: Burns RG (Ed) Marine Minerals, p 1–46. Reviews of Mineralogy, Vol. 6. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Byström AM (1949) The crystal structure of ramsdellite, an orthorhombic modification of MnO2. Acta Chem Scand 3:163–173
Byström A, Byström AM (1950) The crystal structure of hollandite, the related manganese oxide minerals, and αMnO2. Acta Crystallogr 3:146–154
Carlson L, Schwertmann U (1980) Natural occurrence of feroxyhyte (δ′-FeOOH). Clays Clay Miner 28,4:272–280
Chukhrov FV, Zvyagin BB, Yermilova LP, Gorshkov AI (1976) Mineralogical criteria in the origin of marine iron-manganese nodules. Mineral Deposita 11:24–32
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Sivtsov AV, Berezovskaya VV (1978) Structural varieties of todorokite. Izv Akad Nauk Kaz SSSR, Ser Geol 12:86–95
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Sivtsov AV, Berezovskaya VV (1979a) New data on natural todorokites. Nature 278:631–632
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Beresovskaya VV, Sivtsov AV (1979b) Contributions to the mineralogy of authigenic manganese phases from marine manganese deposits. Miner Deposita 14:249–261
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Vitovskaya IV, Drits VA, Sivtsov AI, Dikov YuP (1980a) Crystallochemical nature of Ni asbolan. Izv Akad Nauk Kaz SSSR, Ser Geol 9:108–120
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Vitovskaya IV, Drits VA, Sivtsov AI, Rudnitskaya YeS (1980b) Crystallochemical nature of Co-Ni asbolan. An SSSR Izv, Ser Geol 6:73–81 (Trans Internat Geol Rev 24:598–604 (1982))
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Sivtsov AV (1981) A new structural variety of todorokite. Izs Akad Nauk Kaz SSSR, Ser Geol 5:88–91
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Drits VA, Sivtsov AI, Dikov YuP (1982) New structural variety of asbolite. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR, Ser Geol 6:69–77
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov VA, Drits VA, Shterenberg Ye, Sivtsov AV, Sakharov BA (1983) Mixed-layer asbolite-buserite minerals and asbolites in oceanic iron-manganese nodules. AN SSR Izvest 5:91–99 (Trans Internat Geol Rev 25,7,1983)
Chukhrov FV, Sakharov AI, Gorshkov AI, Drits VA, Dikov YuP (1985a) Crystal structure of birnessite from the Pacific ocean. Izvest AN SSSR, Ser Geol 8:66–73 (Trans Internat Geol Rev 27,9:1082–1088 (1985))
Chukhrov FV, Gorshkov AI, Drits VA, Dikov YuP (1985b) Structural varieties of todorokite. Izvest AN SSSR, Ser Geol 11:61–71 (Trans Internat Geol Rev 27,12:1481–1491 (1985))
Combes JM, Manceau A, Calas G (1986) Study of the local structure in poorly-ordered precursors of iron oxi-hydroxides. J Phys (Paris) C8 47,2:697–701
Combes JM, Manceau A, Calas G, Bottero JY (1988) The pathway of formation of hematite: a topological approach by x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Geochemica Cosmochem Acta (submitted)
Crozier ED, Seary AJ (1980) Asymmetric effects in the extended X-ray absorption fine structure analysis of solid and liquid zinc. Can J Phys 58:1388–1399
de Crescenzi M, Antonangeli F, Bellini C, Rosei R (1983) Temperature induced asymmetric effects in the surface extended energy loss fine structure of Ni(100). Solid State Commun 46,12:875–880
de Wolff PM (1959) Interpretation of some γMnO2 diffraction pattern. Acta Crystallogr 12:341–345
Drits VA, Petrova VV, Gorshkov AI, Svalnov VN, Sokolova AL, Sivtsov AV, Karpova GV (1985) Mn minerals from iron nodules found in sediments in central part of Pacific ocean and their postsedimentation transformation. Lithologia i poleznye iskopaemye (in russian)
Eisenberger P, Brown G (1979) The study of disordered systems by EXAFS: limitations. Solid State Commun 29:481–484
Eisenberger P, Lengeler B (1980) Extended x-ray absorption fine-structure determination of coordination numbers: limitations. Phys Review B 22,8:3551–3562
Giovanoli R, Maurer R, Feitnecht W (1967) Zur Struktur des γMnO2. Helv Chem Acta 50:1072–1080
Giovanoli R (1980) Vernadite is random-stacked birnessite. Miner Deposita 15:251–253
Goulon J, Cortes R, Retournard A, Georges A, Battioni JP, Frety R, Moraweck B (1984) Soft x-ray absorption measurements at the K-edges of sulphur and chlorine. In “EXAFS and NEAR Edge Structure III” Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York. Proc Inter Conf Stanford 449–451
Laudy JA, de Wolff PM (1963) X-ray investigation of the δ-β transformation of MnO2. Appl Sci Res B10:157–168
Lee PA, Citrin PH, Eisenberger P, Kincaid BM (1981) Extended x-ray absorption fine structure-its strengths and limitations as a structural tool. Rev Mod Phys 53,4:769–805
Llorca S (1986) Les concentrations cobaltifères supergènes en Nouvelle Calédonie: géologie, minéralogie. Thèse de l'Université de Toulouse. 90p
Llorca S (1987) Nouvelles données sur la composition et la structure des lithiophorites, d'après des échantillons de Nouvelle-Calédonie. Compte-Rendu Acad Sciences Paris 304,II,1:15–18
Manceau A, Calas G (1986) Nickel-bearing clay minerals. 2. Intra-crystalline distribution of nickel: a x-ray absorption study. Clay Miner 21,2:341–360
Manceau A, Llorca S, Calas G (1987) Crystal chemistry of cobalt and nickel in lithiophorite and asbolane from New Caledonia. Geochem Cosmochem Acta 51:105–113
Miura H (1986) The crystal structure of hollandite. Miner J 13,3:119–129
Murad E (1979) Mössbauer and x-ray data on βFeOOH (akaganeite). Clay Miner 14:273
Olès A, Szytula A, Wanic A (1970) Neutron diffraction study of γ-FeOOH. Phys Status Solidi 41:173–177
Ostwald J (1984) Ferriginous vernadite in an Indian Ocean ferromanganese nodule. Geol Mag 121,5:483–488
Patrat G, de Bergevin F, Pernet M, Joubert JC (1983) Structure locale de δ-FeOOH. Acta Crystallogr B39:165–170
Pauling L, Kamb B (1982) The crystal structure of lithiophorite. Am Mineral 67:817–821
Perseil EA, Giovanoli R (1982) Étude comparative de la todorokite d'Ambollas (Pyrénées Orientales), des manganates à 10 Å rencontrés dans les nodules polymétalliques des océans et des produits de synthèse. Compte-Rendu Acad Sciences Paris Sér II,294:199–202
Post JE, Von Dreele RB, Buseck PR (1982) Symmetry and cation dispacements in hollandites: structure refinements of hollandite, cryptomelane and priderire. Acta Crystallogr B38:1056–1065
Rask JH, Miner BA, Buseck PR (1987) Determination of manganese oxidation states in solids by electron energy loss spectroscopy. Ultramicroscopy (to press)
Szytula A, Burewicz A, Dimitrijevic Z, Krasnicki S, Rzany H, Todorovic J, Wanic A, Wolski W (1968) Neutron diffraction studies of α-FeOOH. Phys Status Solidi 26:429–434
Szytula A, Balanda M, Dimitrijevic Z (1970) Neutron diffraction studies of β-FeOOH. Phys Status Solidi 3:1033–1037
Teo BK, Lee PA (1980) Ab initio calculation of amplitude and phase function for Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. J Am Chem Society 101:2815–2830
Turner S, Buseck PR (1979) Manganese oxide tunnel structures and their intergrowths. Science 203:456–458
Turner S, Buseck PR (1981) Todorokites: a family of naturally occuring manganese oxide. Science 212:1024–1027
Turner S, Siegel MD, Buseck PR (1982) Structural features of todorokite intergrowths in manganese nodules. Science 296:841–842
Turner S, Buseck PR (1983) Defects in nsutite (γMnO2) and dry-cell battery efficiency. Nature 304, 5922:143–146
Vicat J, Fanchon E, Strobel P, Duc Tran Qui (1986) The structure of K1.33Mn8O16 and cation ordering in hollandite-type structures. Acta Crystallogr B42:162–167
Wadsley AD (1952) The structure of lithiophorite, (Al, Li) MnO2(OH)2. Acta Crystallogr 5:676–680
Wadsley AD (1953) The crystal structure of psilomelane, (Ba, H2O)2Mn5O10. Acta Crystallogr 6:433–438
Wadsley AD (1955) The crystal structure of chalcophanite ZnMn3O7.3H2O Acta Crystallogr 8:165–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manceau, A., Combes, J.M. Structure of Mn and Fe oxides and oxyhydroxides: A topological approach by EXAFS. Phys Chem Minerals 15, 283–295 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307518
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307518