Summary
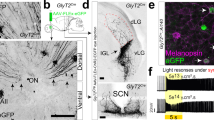
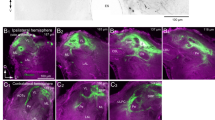
In Xenopus laevis the development of hypothalamic monoaminergic cells was studied in relation to adaptation to background colour. The first melanophores appear at stage 33/34 (normal table of Nieuwkoop and Faber, 1956), gradually increasing in number. The melanine granules are dispersed throughout the cell, irrespective of the background colour. The dispersion apparently is caused by MSH released by the developing pars intermedia cells. Between stage 39 and stage 41, larvae placed on a white background changed colour from black to white due to aggregation of the melanine granules within the melanophores. With Falck's method for demonstrating monoamines, a small number of fluorescent cells was observed in the hypothalamus simultaneously with the first background-dependent colour change. These cells were arranged in a paired nucleus, bordering the third ventricle. Initially, the nucleus extends from 50 microns behind the optic chiasma to the lateral dilatations of the third ventricle; 8–10 hours later, similar cells were also found at the lateral dilatations and in the dorso-lateral part of the infundibular lobe. The cells have apical processes protruding in the ventricular lumen. Fluorescent axons, originating from the cells, were occasionally observed. Considering the above-mentioned results in combination with the electron microscopical data of Nyholm (1972), it is concluded that the MSH producing cells are under monoaminergic nervous control from the beginning of background colour adaptation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartels, W.: Die Ontogenese der aminhaltigen Neuronensysteme im Gehirn von Rana temporaria. Z. Zellforsch. 116, 94–118 (1971)
Braak, H.: Biogene Amine im Gehirn vom Frosch (Rana esculenta). Z. Zellforsch. 106, 269–308 (1970)
Cohen, A. G.: Observations on the pars intermedia of Xenopus laevis. Nature (Lond.) 215, 55–56 (1967)
Corrodi, H., Jonsson, G.: The formaldehyde fluorescence method for the histochemical demonstration of biogenic monoamines. A review on the methodology. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 65–78 (1967)
Dawson, A. B.: Evidence for the termination of neurosecretory fibres within the pars intermedia of the frog (Rana pipiens). Anat. Rec. 115, 63–69 (1953)
Dierickx, K.: The function of the hypophysis without preoptic neurosecretory control. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 114–130 (1967)
Dierst, K. E., Ralph, C. L.: Effect of hypothalamic stimulation on melanophores in the frog. Gen. comp. Endocr. 2, 347–353 (1962)
Dierst-Davis, K., Ralph, C. L., Pechersky, J. L.: Effects of pharmacological agents on the hypothalamus of Rana pipiens in relation to the control of skin melanophores. Gen. comp. Endocr. 6, 409–419 (1966)
Doerr-Schott, J.: Développement de l'hypophyse de Rana temporaria L. Etude au microscope électronique. Z. Zellforsch. 90, 616–645 (1968)
Doerr-Schott, J., Follenius, E.: Localisation des fibres aminergiques dans l'hypophyse de Rana esculenta. Etude autoradiographique au microscope électronique. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 269, 737–740 (1969)
Doerr-Schott, J., Follenius, E.: Innervation de l'hypophyse intermédiaire de Rana esculenta, et identification des fibres aminergiques par autoradiographie au microscope électronique. Z. Zellforsch. 106, 99–108 (1970)
Enemar, A., Falck, B.: On the presence of adrenergic nerves in the pars intermedia of the frog, Rana temporaria. Gen. comp. Endocr. 5, 577–583 (1965)
Enemar, A., Falck, B., Iturriza, F. C.: Adrenergic nerves in the pars intermedia of the pituitary in the toad, Bufo arenarum. Z. Zellforsch. 77, 325–330 (1967)
Etkin, W.: The first appearance of functional activity in the pars intermedia in the frog, Xenopus. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 47, 425–428 (1941)
Etkin, W.: Hypothalamic inhibition of pars intermedia activity in the frog. Gen. comp. Endocr., Suppl. 1, 148–159 (1962a)
Etkin, W.: Neurosecretory control of the pars intermedia. Gen. comp. Endocr. 2, 161–169 (1962b)
Falck, B., Owman, C.: A detailed description of the fluorescence method for the cellular demonstration of biogenic monoamines. Acta Univ. Lund., Sect. II, 7, 1–23 (1965)
Goos, H. J. Th.: Hypothalamic control of the pars intermedia in Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Z. Zellforsch. 97, 118–124 (1969)
Goos, H. J. Th.: Halewijn, R. van: Biogenic amines in the hypothalamus of Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Naturwissenschaften 55, 393–394 (1968)
Guardabassi, A.: The hypophysis of Xenopus laevis Daudin larvae after removal of the anterior hypothalamus. Gen. comp. Endocr. 1, 348–363 (1961)
Hogben, L. T., Slome, D.: The pigmentary effector system VI. The dual character of endocrine coördination in amphibian color change. Proc. roy. Soc. B 108, 10–53 (1931)
Hopkins, C. R.: Localization of adrenergic fibers in the amphibian pars intermedia by electron microscope autoradiography and their selective removal by 6-hydroxydopamine. Gen. comp. Endocr. 16, 112–120 (1971)
Imai, K.: Color change and pituitary function in Xenopus laevis. In: Biology of normal and abnormal melanocytes (eds. T. Kawamura, T. B. Fitzpatrick and M. Seiji), p. 17–30. Baltimore-London-Tokyo: University Park Press 1971
Ito, T.: Changes in skin color and fine structure of the intermediate pituitary gland of the frog, Rana nigromaculata, after extirpation of the median eminence. Neuroendocrinology 8, 180–197 (1971)
Iturriza, F. C.: Electron microscopic study of the pars intermedia of the pituitary of the toad, Bufo arenarum. Gen. comp. Endocr. 4, 492–502 (1964)
Iturriza, F. C.: Monoamines and control of the pars intermedia of the toad pituitary. Gen. comp. Endocr. 6, 19–25 (1966)
Iturriza, F. C.: The secretion of intermedin in autotransplants of pars intermedia growing in the anterior chamber of intact and sympathectomized eyes of the toad. Neuroendocrinology 2, 11–18 (1967)
Iturriza, F. C.: Further evidences for the blocking effect of catecholamines on the secretion of melanocyte-stimulating hormone in toads. Gen. comp. Endocr. 12, 417–426 (1969)
Jonsson, G.: Quantitation of fluorescence of biogenic monoamines. Progr. Histochem. Cytochem. vol. 2, p. 1–36. Stuttgart-Portland-Oregon (U.S.A.): Gustav Fischer 1971
Jørgensen, C. B., Larsen, L. O.: Nature of the nervous control of pars intermedia function in amphibians: rate of functional recovery after denervation. Gen. comp. Endocr. 3, 468–472 (1963)
Jørgensen, C. B., Larsen, L. O., Rosenkilde, P., Wingstrand, K. G.: Effect of extirpation of median eminence on function of pars distalis of the hypophysis in the toad Bufo bufo (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1, 38–43 (1960)
Mazzi, V.: Sulla presenza e sul possibile significato di fibre neurosecretorie ipotalamo-ipofisarie nel lobe intermedio dell'ipofisi del Tritone cristato. Monit. zool. ital. 62, 1–8 (1954)
Nakai, Y., Gorbman, A.: Evidence for a double innervated secretory unit in the anuran pars intermedia II. Electron microscopie studies. Gen. comp. Endocr. 13, 108–116 (1969)
Nieuwkoop, P. D., Faber, J.: Normal table of Xenopus laevis Daudin. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Co. 1956
Nyholm, N.E.I.: On the melanophore regulation of early Xenopus tadpoles. Gen. comp. Endocr. 13, 523 (1969)
Nyholm, N.E.I.: Hypophysial activity and melanophore regulation in early Xenopus tadpoles. Gen. comp. Endocr. 18, 613 (1972)
Oordt, P.G.W.J. van, Goos, H.J.Th., Peute, J., Terlou, M.: Hypothalamo-hypophysial relations in amphibian larvae. Gen. comp. Endocr., Suppl. 3, 41–50 (1972)
Pehlemann, F. W.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Determination und Differenzierung der Hypophyse bei Anuren (Pelobates fuscus, Rana esculenta). Whilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org. 153, 551–602 (1962)
Pehlemann, F. W.: Early development and function of adenohypophysis in anuran tadpoles in correlation to brain. Gen. comp. Endocr. 5, 704–705 (1965)
Pehlemann, F. W.: Ultrastructure and innervation of the pars intermedia of the pituitary of Xenopus laevis. Gen. comp. Endocr. 9, 481 (1967)
Saland, L. C.: Ultrastructure of the frog pars intermedia in the relation to hypothalamic control of hormone release. Neuroendocrinology 3, 72–88 (1968)
Terlou, M., Ploemacher, R. E.: The distribution of monoamines in the tel-, di- and mesencephalon of Xenopus laevis tadpoles, with special reference to the hypothalamo-hypophysial system. Z. Zellforsch. 137, 521–540 (1973)
Terlou, M., Straaten, H.W.M. van, Oordt, P.G.W.J. van: The development of hypothalamic monoaminergic neurons in Xenopus laevis tadpoles in relation to background-dependent colour change. J. Endocr. 57, XXIV (1973)
Terlou, M., Stroband, H.W.J.: The distribution of monoamine oxidase and acetylcholinsterase in the brain of Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Z. Zellforsch. 140, 261–275 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to thank Prof. Dr. P.G.W.J. van Oordt for his stimulating interest and helpful suggestions. The photographs were made by Mr. H. van Kooten and his co-workers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terlou, M., van Straaten, H.W.M. The development of a hypothalamic monoaminergic system for the regulation of the pars intermedia activity in Xenopus laevis . Z.Zellforsch 143, 229–238 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307480
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307480