Summary
The effects of chlorpromazine hydrochloride (CPZ HCl) and prochlorperazin-metansulfonate (PCPZ) on the fast axonal transport of labelled proteins were examined in vitro in a peripheral frog nerve.
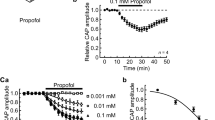
A 0.1 mM concentration of CPZ HCl and PCPZ reduced the amount of transported proteins by more than 50 per cent. An almost complete block was obtained with a 0.5 mM concentration of these two drugs. The lower concentration hardly affected the protein synthesis. The transport inhibiting effect of 0.1 mM of the drugs was reversible but not that of the higher concentration.
The number of microtubuli was strongly decreased and the number of filaments increased at the transport inhibiting concentrations. The ultrastructural changes induced by 0.1 mM of the phenothiazine tranquilizer were largely reversible. The local anesthetics lidocaine (18.3 mM) and tetracaine (3.3 mM) both caused similar changes, i.e. a reduction in the number of microtubuli. No ultrastructural effects were observed after treatment with 1 mM ouabain. These three drugs are known to block the axonal flow in the present system at the above mentioned concentrations.
The biochemical and ultrastructural results are discussed in relation to those induced by other drugs affecting axonal transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, K.-E., Edström, A.: Effects of nerve blocking agents on fast axonal transport of proteins in frog sciatic nerves in vitro. Brain Res. 50, 125–134 (1973).
Anderson, K.-E., Edström, A., Mattsson, H.: Effects of cytochalasin B on uptake of glucosamine, leucine and sulphate into nerve cells; incorporation into glycoproteins and rapid axonal transport. Brain Res. 48, 343–353 (1972)
Dahlström, A.: Axoplasmic transport (with particular respect to adrenergic neurons). Phil. Trans. B 261, 325–358 (1971).
den Hertog, A., Ritchie, J. M.: The effect of some quaternary ammonium compounds and local anesthetics on the electrogenic component of the sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibers. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 6, 138–142 (1969)
Edström, A., Hanson, M.: Temperature effects on fast axonal transport of proteins in vitro in frog sciatic nerves. Brain Res. (in press).
Edström, A., Hanson, M.: Retrograde axonal transport of proteins in vitro in frog sciatic nerves. Brain Res. (in press)
Edström, A., Hansson, H.-A., Norström, A.: The effect of chlorpromazin and tetracaine on the rapid axonal transport of neurosecretory material in the hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal system of the rat. A biochemical and ultrastructural study. To be published 1973
Edström, A., Mattsson, H.: Fast axonal transport in vitro in the sciatic system of the frog. J. Neurochem. 19, 205–221 (1972)
Ehrenpreis, S.: Drug-macromolecular interactions: Implications for pharmacological activity. Progr. Drug Res. 14, 59–138 (1970)
Fink, B. R., Kennedy, R. D., Hendrickson, A. E., Middaugh, M. E.: Lidocaine inhibition of rapid axonal transport. Anesthesiology 36, 422–432 (1972)
Gey, K. F., Pletscher, A.: Influence of chlorpromazine and chlorprothixene on the cerebral metabolism of 5-hydroxytryptamine, norepinephrine and dopamine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 133, 18–24 (1961)
Gordon, M.: Phenothiazines. In: Psychopharmacological agents. Medicinal chemistry, vol. 4-II (Gordon, M., ed.). New York: Academic Press 1967
Hinkley, R. E., Samson, F. E.: Anesthetic-induced transformation of axonal microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 53, 258–263 (1972)
Karnovsky, N. J.: A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron-microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 27, 137A (1965).
Kirkpatrick, W. E., Lomax, P.: Comparison of the effects of procaine, chlorpromazine and their quaternary derivatives on nerve action potentials. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1, 149–155 (1970)
Kuchler, G., Gorski, R., Elze, P.: Zur Prokainwirkung am isolierten Skelettmuskel. Acta biol. med. germ. 23, 271–283 (1969)
Lasek, R. L.: Protein transport in neurons. In: International review of neurobiology, p. 289–324 (Pfeiffer, C. C. and Smythies, J. R., eds.). New York-London: Academic Press 1970
Ochs, S.: Fast transport of materials in mammalian nerve fibers. Science 176, 252–260 (1972)
Poste, G., Reeve, P.: Inhibition of cell fusion by local anesthetics and tranquilizers. Exp. Cell Res. 72, 556–559 (1972)
Quastel, J.: Effects of anesthetics, depressants and tranquilizers on cerebral metabolism. In: Metabolic inhibitors. A comprehensive treatise, vol. II., p. 517–538 (Hochster, R. M. and Quastel, J. H., eds.). New York-London: Academic Press 1963
Samson, F. E.: Mechanism of axoplasmic transport. J. Neurobiol. 2, 347–360 (1971)
Seeman, P., Kwant, W. O., Goldberg, M., Chau-Wong, M.: The effects of ethanol and chlorpromazine on the passive membrane permeability ot Na+. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 241, 349–355 (1971)
Shelanski, M. L., Feit, H.: Filaments and tubules in the nervous system. In: The structure and function of nervous tissue, vol. 5 (G. H. Bourne, ed.). New York-London: Academic Press 1972
Stormorken, H.: The release reaction of secretion. Scand. J. Haemat., Suppl. 9, 1–24 (1969)
Su, C., Lee, C. Y.: The mode of neuromuscular blocking action of chlorpromazine. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 15, 88–94 (1960)
Wuerker, R. B., Kirkpatrick, J. B.: Neuronal microtubules, neurofilaments and microfilaments. Int. Rev. Cytol. 33, 45–75 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The present work was supported by grants from “Statens Naturvetenskapliga Forskningsråd (No. 2535-8)”, “C.-B. Nathorsts Vetenskapliga och Allmännyttiga Stiftelser”, the Swedish Medical Research Council (B73-12X-2543-05B), “H. Hierta's Stiftelse” and “W. och M. Lundgrens Stiftelse”. Thanks are due to Mrs B. Egnér, Mrs E. Fjällstedt, Mrs. E. Norström and Mrs U. Svedin for expert technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edström, A., Hansson, HA. & Norström, A. Inhibition of axonal transport in vitro in frog sciatic nerves by chlorpromazine and lidocaine. Z.Zellforsch 143, 53–69 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307451
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307451