Summary
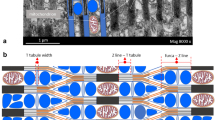
The fine structure of the red and white myotomal muscles of a marine teleost, the coalfish Gadus virens, has been examined and ultrastructural measurements and analyses carried out. The sarcomere lengths of the red and white fibres were found to be 1.60 μ minimum, 1.82 μ maximum and 1.70 μ minimum, 1.85 μ maximum, respectively. No significant difference was found between the red and white fibres in their percentage of sarcoplasmic reticulum and T system. Both were found to have regularly occurring triads at the Z disk level, to have distinctive M lines and to be multiply innervated. Ultrastructurally the two fibres can be distinguished by the thicker Z line and more abundant mitochondria of the red fibre, and by the ribbon-shaped peripheral myofibrils of the white fibres. The structure of the fibres in these two types of muscle is discussed in relation to their possible role in swimming.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurden die Feinstruktur roter und weißer Muskelfasern des Seewasserteleostiers Seelachs (Gadus virens) untersucht und ultrastrukturelle Messungen und Analysen durchgeführt. Die Sarcomerlängen der roten Fasern liegen zwischen 1,60 und 1,82 μ, die der weißen zwischen 1,70 und 1,85 μ. Hinsichtlich des prozentualen Vorkommens von sarcoplasmatischem Reticulum und T-System bestehen zwischen roten und weißen Fasern keine wesentlichen Unterschiede. Beide Fasertypen zeichnen sich durch regelmäßiges Vorkommen von Triaden am Z-Streifen, deutliche M-Streifen und multiple Innervation aus. Ultrastrukturell unterscheiden sich die beiden Fasertypen dadurch, daß die roten Fasern dickere Z-Streifen und mehr Mitochondrien, die weißen peripher bandförmige Myofibrillen besitzen. Die Struktur der Fasern dieser beiden Muskeltypen wird im Hinblick auf deren mögliche Rolle beim Schwimmen diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auber, J.: La myofibrillogenèse du muscle strie. I Insectes. J. Microscopie 8, 197–232 (1969).
Awan, M. Z., Goldspink, G.: Energetics of the development and maintenance of isometric tension by mammalian fast and slow muscle. J. Mechanochem. Cell Motility 1, 97–108 (1972).
Bainbridge, R.: The speed of swimming of fish as related to the size and to the frequency and amplitude of tailbeat. J. exp. Biol. 35, 109–133 (1958).
Barets, A.: Contribution a l'étude des systèmes moteurs “lent” et “rapide” du muscle latéral des téléostéens. Arch. Anat. micr. Morph. exp. 50, 91–187 (1961).
Bishop, C. M., Odense, P. H.: The ultrastructure of the white striated myotomal muscle of the cod, Gadus morrhua. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada 24, 2549–2553 (1967).
Bone, Q.: On the function of the two types of myotomal muscle in elasmobranch fish. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U. K. 46, 321–349 (1966).
Braeken, O. R.: Function of red muscle in fish. Nature (Lond.) 178, 747–748 (1959).
Franzini-Armstrong, C., Porter, K. R.: Sarcolemmal invaginations constituting the T-system in fish muscle fibres. J. Cell Biol. 22, 675–696 (1964).
Gauthier, G. F.: The ultrastructure of three fibre types in mammalian skeletal muscle: In: The physiology and biochemistry of muscle as food. vol. II, p. 103–130, eds. Briskey, E. J. Cassens, R. G., Marsh, B. B. Wisconsin: The University of Wisconsin 1970.
George, J. C.: A histophysiological study of the red and white muscles of the mackerel. Amer. Midl. Nat. 68, 487–494 (1962).
Goldspink, G.: Sarcomere length during post-natal growth of mammalian muscle fibres. J. Cell Sci. 3, 539–548 (1968).
Goldspink, G.: Changes in striated muscle fibres during contraction and growth with particular reference to myofibril splitting. J. Cell Sci. 9, 123–138 (1971).
Goldspink, G., Larson, R. E., Davies, R. E.: Thermodynamic efficiency and physiological characteristics of chick anterior latissimus dorsi muscle. Z. vergl. Physiol. 66, 379–388 (1970a).
Goldspink, G., Larson, R. E., Davies, R. E.: The immediate energy supply and the cost of maintenance of isometric tension for different muscles in the hamster. Z. vergl. Physiol. 66, 389–397 (1970b).
Hess, A.: The structure of extrafusal fibres in the frog and their innervation studied by the cholinesterase technique. Amer. J. Anat. 107, 129–152 (1960).
Hess, A.: Vertebrate slow fibres. Physiol. Rev. 50, 40–62 (1970).
Howells, K., Goldspink, G.: In preparation (1972).
Huxley, H. E.: The fine structure of striated muscle and its functional significance. Harvey Lect. 60, 85–118 (1966).
Johnston, I. A., Frearson, N., Goldspink, G.: Myofibrillar ATPase activities of red and white myotomal muscles of marine fish. Experientia (Basel) 28, 713 (1972a).
Johnston, I. A., Goldspink, G.: The effect of sustained swimming on the concentrations of glycogen and lactate occurring in the myotomal muscles and liver of the coalfish (Gadus virens). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U. K. (In press) (1972b).
Johnston, I. A., Goldspink, G.: A study of the swimming performance of the crucial carp (Carassius carassius) in relation to the effects of exercise and recovery on the biochemical changes in the myotomal muscles and liver. J. Fish. Biol. (In press) (1972c).
Kilarski, W.: The fine structure of striated muscles in teleosts. Z. Zellforsch. 79, 562–580 (1967).
Kilarski, W., Bigaj, J.: Organisation and fine structure of extraocular muscles in Carassius and Rana. Z. Zellforsch. 94, 194–204 (1969).
Koelle, G. B., Friedenwald, J. S.: A histochemical method for localizing cholinesterase activity. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 70, 617–622 (1949).
Nishihara, H.: Studies on the fine structure of red and white fin muscles of the fish (Carassius auratus). Arch. histol. jap. 28, 425–447 (1967).
Peachey, L. D.: Transverse tubules in excitation-contraction coupling. Fed. Proc. 24, 1124–1134 (1965).
Peachey, L. D., Huxley, A. F.: Structural identification of twitch and slow striated muscle fibres of the frog. J. Cell Biol. 13, 177–180 (1962).
Rauthman, A.: Methods in cell research. London: G. Bell & Sons Ltd. 1970. (Translated from revised text. Original edition published in Germany. Stuttgart: W. Keller & Co. 1966.)
Rayner, M. D., Keenan, M. J.: Role of red and white muscles in the swimming of the skipjack tuna. Nature (Lond.) 214, 392–393 (1967).
Smit, H., Amelink-Koutstaal, J. M., Vyverberg, J., Vaupel-Klein, J. C. von: Oxygen consumption and efficiency of swimming in goldfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 39, 1–29 (1971).
Smith, C. S., Guttman, L.: Measurements of internal boundaries in three-dimensional structures by random sectioning. J. Metals. 197, Trans. AIME, 81–87 (1953).
Walker, M. G.: Effects of starvation and exercise on the skeletal muscles fibres of the cod (Gadus morrhua L.) and the coalfish (Gadus virens L.) respectively. J. Cons. int. Explor. Mer. 33, 421–426 (1971).
Weibel, E. R.: Stereological principles for morphometry in electron microscope cytology. Int. Rev. Cytol. 26, 235–300 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a research grant from the National Environmental Research Council.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patterson, S., Goldspink, G. The fine structure of red and white myotomal muscle fibres of the coalfish (Gadus virens). Z.Zellforsch 133, 463–474 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307129
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307129