Summary
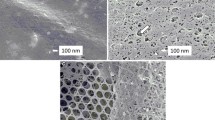
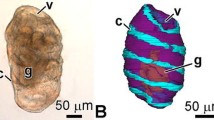
The embryonic development of the brush-border of anterior midgut cells of Calliphora was studied by electron microscopy. Dense surface-forming vesicles, as described by Bonneville (1970), are found prior to microvillus formation. These dense vesicles provide membranous and coating material for the moulding of the microvilli. The number of dense vesicles increases rapidly to a maximum just before brush-border formation, after which it decreases very rapidly, accompanied by an increase in the number of microvilli. Formation of microvilli proceeds in essentially the same way as in Xenopus. First, some of the vesicles fuse with the apical cell membrane, resulting in an increase of the cell surface, part of which is coated with filamentous material deriving from the dense vesicles. This in turn leads to bulging, and short irregular microvilli appear. These are erected and elongated.
Prefabricated tubular elements are believed to play a part in this erection and elongation, probably due to the unwinding of spirally coiled strands.
Microvillus formation proper lasts 2 to 3 hours in Calliphora. Almost the entire amount of membranous and coating material is prefabricated prior to the formation of microvilli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertolini, B., Monaco, G., Rossi, A.: Ultrastructure of a regular arrangement of microtubules and neurofilaments. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 33, 173–186 (1970).
Bonneville, M. A., Weinstock, M. J.: Brush-border development in the intestinal absorptive cells of Xenopus during metamorphosis. J. Cell Biol. 44, 151–171 (1970).
Brown, A. L.: Microvilli of the human jejunal epithelial cell. J. Cell Biol. 12, 623–627 (1962).
Hirsch, J. G., Fedorko, M. E.: Ultrastructure of human leukocytes after simultaneous fixation with glutaraldehyde and osmium tetroxide and “postfixation” in uranyl acetate. J. Cell Biol. 38, 615–628 (1968).
Hugon, J. S., Borgers, M.: Ultrastructural differentiation and enzymatic localization of phosphatases in the developing duodenal epithelium of the mouse. I. The foetal mouse. Histochemie 19, 13–30 (1969).
Ito, S.: The enteric surface coat on cat intestinal microvilli. J. Cell Biol. 27, 475–491 (1965).
McNabb, J. D., Sandborn, E.: Filaments in the microvillous border of intestinal cells. J. Cell Biol. 22, 701–704 (1964).
Metuzals, J.: Configuration of a filamentous network in the axoplasm of the squid (Loligo pealii L.) giant nerve fiber. J. Cell Biol. 43, 480–505 (1969).
Mukherjee, T. M.: A comparative study of the ultrastructure of microvilli in the epithelium of small and large intestine of mice. J. Cell Biol. 34, 447–461 (1967).
— Staehelin, L. A.: The fine structural organization of the brush-border of intestinal epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 8, 573–599 (1971).
Overton, J.: Fine structure of the free cell surface in developing mouse intestinal mucosa. J. exp. Zool. 159, 195–202 (1965).
-- Eichholz, A., Crane, R. K.: Fine structure of the microvilli of hamster small intestine. J. Cell Biol. 23, 110a (1964).
— Shoup, J.: Fine structure of cell surface specializations in the maturing duodenal mucosa of the chick. J. Cell Biol. 21, 75–85 (1964).
Planqué-Huidekoper, B., Priester, W. de, van der Starre-van der Molen, L. G.: Ultrastructural development of the midgut during embryogenesis of Calliphora erythrocephala Meigen. (In preparation) (1972).
Shaw Dunn, J.: The fine structure of the absorptive epithelial cells of the developing small intestine of the rat. J. Anat. (Lond.) 101, 57–68 (1967).
Starre-van der Molen, L. G. van der: The embryogenesis of Calliphora erythrocephala M. I. Morphology. Neth. J. Zool. (In press).
-- The embryogenesis of Calliphora erythrocephala M. II. The glycogen pattern. Neth. J. Zool. (In press.)
Toner, P. G.: Cytology of intestinal epithelial cells. Int. Rev. Cytol. 24, 233–343 (1968).
Trier, J. S.: Studies on small intestinal crypt epithelium. I. The fine structure of crypt epithelium of the proximal small intestine of fasting humans. J. Cell Biol. 18, 599–620 (1963).
Venable, J. H., Coggeshall, R.: A simplified lead citrate stain for use in electronmicroscopy. J. Cell Biol. 25, 407–408 (1965).
Vollrath, L.: Über die Mikrovillibildung im fetalen Rattendünndarm. Z. Zellforsch. 114, 546–556 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Starre-van der Molen, L.G., de Priester, W. Brush-border formation in the midgut of an insect, Calliphora erythrocephala meigen. Z.Zellforsch 125, 295–305 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306628
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306628