Summary
The splitting of 6-Br-2-naphthyl-, α-naphthyl-, and 4-Cl-5-Br-3-indolyl-glycosides which proved useful for the assessment of cytological localization of intestinal enzymes in previous studies was investigated using isolated human and rat intestinal disaccharidases as a source of enzyme activities.
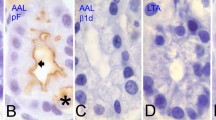
Previous findings based on histochemical studies were confirmed and extended. 6-Br-2naphthylα-D-glucoside is cleaved by glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase. The participatio of trehalase in splitting of this substrate is very low and can be neglected. The mentioned α-glucosidases are responsible for the brush border staining of enterocytes with this substrate when unfixed cold microtome sections are used. Even when a differential heat inactivation of sucrase-isomaltase and of glucoamylase occurs during paraffin embedding (so that the staining in paraffin sections is due mostly to glucoamylase) the use of natural substrates is desirable for a more precise assessment of sucrase-isomaltase activity (but without the possibility of a correct localization).
4-Cl-5-Br-3-indolyl-β-D-fucoside is the substrate of choice for the demonstration of lactase. Even when this substrate is split also by “hetero-β-galactosidase” and by acid (lysosomal) β-galactosidase these activities do not disturb the histochemical demonstration of lactase. If however some doubts arise, the inhibition with p-Cl-mercuribenzoate (2 · 10−4 M) is to be emloyed (lactase activity is not inhibited). Due to a low Km and a high Vmax of indolyl-fucoside and due to its extreme stability in solution (which enables to use the substrate solution repeatidly) this substrate is suitable in routine practice even though it is expensive.
α-naphthyl- and 4-Cl-5-Br-3-indolyl-β-D-glucosides are split by lactase and β-glucosidase. Due to the fact that the mutual delineation of these activities is not easy and that Km an Vmax for lactase are not so favourable as in the case of fucoside these substrates are not recommended for the assessment of lactase.
6-Br-2-naphthyl-β-D-glucoside is the substrate of choice for the histochemical studies concerned with “hetero-β-galactosidase” and 4-Cl-5-Br-3-indolyl-β-D-galactoside for acid β-galactosidase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asp, N.-G.: Small-intestinal β-galactosidases. Diss. Lund, 1971.
Asp, N.-G., Dahlqvist, A.: Rat small intestinal β-galactosidases. Kinetic studies with three separated fractions. Biochem J. 110, 143–150 (1968).
Asp, N.-G., Dahlqvist, A., Koldovský, O.: Human small-intestinal β-galactosidases. Separation and characterization of one lactase and one hetero β-galactosidase. Biochem. J. 114, 351–359 (1969).
Dahlqvist, A.: Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Enzym. biol. clin. 11, 52–66 (1970).
Gray, G. M., Santiago, N. A.: Intestinal β-galactosidases. I. Separation and characterization of three enzymes in normal human intestine. J. clin. Invest. 48, 716–728 (1969).
Gray, G. M., Santiago, N. A., Colver, E. H., Genel, M.: Intestinal β-galactosidases. II. Biochemical alteration in human lactase deficiency. J. clin. Invest. 48, 729–735 (1969).
Jos, J., Frézal, J., Rey, J., Lamy, M.: Histochemical localization of intestinal disaccharidases. Application to peroral biopsy specimens. Nature (Lond.) 213, 516–518 (1967a).
Jos, J., Frézal, J., Rey, J., Lamy, M., Wegmann, R.: La localisation histochimique des disaccharidases intestinales avec un procédé nouveau. Ann. Histochim. 12, 53–61 (1967b).
Kolínská, J., Kraml, J.: Separation and characterization of sucrase-isomaltase and of glucoamylase of rat intestine. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 284, 235–247 (1972).
Kraml, J., Kolínská, J., Ellederová, D., Hiršová, D.: β-glucosidase (phlorizin hydrolase) activity of the lactase fraction isolated from the small intestinal mucosa of infant rats, and the relationship between β-glucosidases and β-galactosidases. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 258, 520–530 (1972).
Lineweaver, H., Burk, D.: The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Amer. chem. Soc. 56, 658–666 (1934).
Lojda, Z.: Some remarks concerning the histochemical detection of disaccharidases and glucosidases. Histochemie 5, 339–360 (1965).
Lojda, Z.: Histochemie der Disaccharidasen und anderer Enzyme im Bürstensaum des Darmes. In: Biochemische und klinische Aspekte der Zuckerabsorption (Rommel, K., Clodi, P.H., eds.), P. 15–34. Stuttgart-New York: F. K. Schattauer 1970a.
Lojda, Z.: Indigogenic methods for glycosidases. I. An improved method for β-D-glucosidase and its application to localization studies of intestinal and renal enzymes. Histochemie 22, 347–361 (1970b).
Lojda, Z.: Indigogenic methods for glycosidases. II. An improved method for β-D-galactosidase and its application to localization studies of the enzymes in the intestine and in other tissues. Histochemie 23, 266–288 (1970c).
Lojda, Z.: Diskussion zur Materialfixation. Acta histochem. (Jena), Suppl. 9, 239 (1971).
Lojda, Z.: An improved histochemical method for the demonstration of disaccharidases with natural substrates. Histochemie 30, 277–280 (1972a).
Lojda, Z.: Aktuelle Probleme der Cytochemie der lysosomalen Hydrolasen. Acta morph. Acad. Sci. hung. (1972b) (in press).
Lojda, Z., Frič, P., Jodl, J.: Histochemie des Dünndarmes bei der Malabsorption. Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Path. 53. Tagg. 93–110 (1969).
Lojda, Z., Frič, P., Jodl, J., Chmelík, V.: Cytochemistry of the human jejunal mucosa in the norm and in malabsorption syndrome. Curr. Top. Path. 52, 1–63 (1970).
Lojda, Z., Kraml, J.: Indigogenic methods for glycosidases. III. An improved method with 4-Cl-5-Br-3-indolyl-β-D-fucoside and its application in studies of enzymes in the intestine, kidney and other tissues. Histochemie 25, 195–207 (1971).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Meijer, A. E. F. H.: Semipermeable membranes for improving the histochemical demonstration of enzyme activities in tissues sections. I. Acid phosphatase. Histochemie 30, 31–39 (1972).
Swaminathan, N., Radhakrishnan, A. N.: Characterization of two hetero-β-galactosidases from monkey small intestine. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 135, 288–295 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lojda, Z., Slabý, J., Kraml, J. et al. Synthetic substrates in the histochemical demonstration of intestinal disaccharidases. Histochemie 34, 361–369 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306308
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306308