Summary
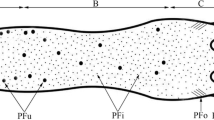
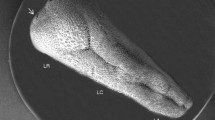
With a view to augment the understanding of the tongue mucosubstances and their significance in the physiology of taste, tongues of two amphibians were investigated histochemically to determine the distribution and nature of the mucosubstances by employing recent techniques, and the results were considered comparatively with the tongue mucins of other vertebrates and the animal mucosubstances in general. A heterogenous distribution of neutral mucins, sulfomucins and sialomucins in fungiform and filiform papillae, ventral epithelium, lingual glands and connectives tissue could be significantly noted on the basis of which various cell types having specialised mucosubstances were identified in the papillae and the ventral epithelium.
The tongue mucosubstances, especially sulfomucins and sialomucins, exhibited inharent heterogenity. Sulfomucins at some sites were hyaluronidas-labile and at other hyaluronidaseresistant, their azurophilia especially at low pH was also different, some being azurophilic and others nonazurophilic. Sialomucins also exhibited such heterogenity, at some sites they were labile to acid hydrolysis and mild methylation but in others they were resistant to the latter, though sialomucins at both sites were sialidase-labile. The mucosubstances localised in the serous glands were highly typical, since they exhibited extraordinary histochemical reactions, they possessed intensely PAS positive reactivity resistant to diastase, hyaluronidase and sialidase, negative to alcian blue both at pH 1 and 2.5, and exhibited no metachromasia at both low and high pH levels, but showed alcianophilia only at high pH levels. Such high pH alcianophilia was sialidase and hyaluronidase resistant but labile to mild methylation. These mucosubstances bear some similarity to those of mammalian parotid.
Such heterogenity was reflected at species-specific level, since some interesting speciesspecific differences were observed in mucosubstances of histologically identical cells and tissues of tongues of the two species of amphibians which might assist in the elucidation of phylogenetic importance of mucins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aureli, G., Ferri, G., Castellani, A. A.: Content of sialic acid in serous glands of equines. Nature (Lond.) 190, 914 (1961).
Bignardi, C., Aureli, G., Balduini, C., Castellani, A. A.: Sulfosialopoly-saccharide-peptide from dog submaxillary gland. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 17, 310–312 (1964).
Burstone, M. S.: A cytological study of salivary glands of the mouse tongue. J. dent. Res. 32, 126–132 (1953).
Carvalho, A., Dulce, V. D., Jose, C. N.: Some morphological aspects and a histochemical study of polysaccharide in the posterior lingual salivary glands of mammalia. I. Rodentia (Rattus novegicus albinus, Mus musculus, Cavia porcellus and Crisetus auratus). Arq. cent. Estud. Fac. Odontal. Univ. Feder. Minas Gera. is Bels. Horizonte 4, 95–112 (1967).
Dempsey, E. W., Bunting, H., Singer, W., Wislocki, G. B.: The dye-binding capacity and other chemo-histological properties of mammalian mucopolysacchardides. Anat. Rec. 98, 417–429 (1947).
Fahrmann, W.: Light and electron microscopic investigation on the taste buds of the neotene axolotle (Siredon mexicanum) (Shaw). Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 77, 117–122 (1967).
—, Schuchardt, E.: Light and electron microscopic investigation on the taste buds in the tongue of the axolotle. Experientia (Basel) 23, 657–659 (1967).
Fisher, E. R., Lillie, R. D.: The effect of methylation on basophilia. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2, 81–87 (1954).
Francis Eric, T. B.: The sources and nature of salivary secretions in amphibia. Proc. Zool. Soc. (London). 136, 456–476 (1961).
French, J. E., Benditt, E. P.: The histochemistry of connective tissue. II. The effects of proteins on the selective staining of mucopolysaccharide by basic dyes. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1, 321–325 (1953).
Fuji, S., Tamura, T.: Histochemical studies on the mucin of the chicken salivary glands. Hiroshima Univ. Fac. Fish. Anim. Husb. J. 6, 345–355 (1966).
Gerard, A., de Graff, J., Lev, R., Glass, G. B.: Secretion of chondroitin sulfate-like substances by the chief cells of the dog gastric mucosa. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 773–774 (1967).
Gottschalk, A.: In: The chemistry and biology of sialic acids and related compounds. London: Cambridge University Press 1960.
Hammerman, D. L.: The frog tongue. II. Histogenesis of fungiform papillae in Rana catesbiana. Acta zool. (Stockh.) 50, 25–33 (1969).
Kelly, J. W.: Suppression of metachromasia by basic proteins. Arch. Biochem. 55, 130–137 (1955).
Lehtonen, A., Karkkainen, J., Haahti, E.: Carbohydrate components in the epithelial mucins of the common Atlantic hagfish, Myxine glutinosa. Acta chem. scand. 20, 1456–1462 (1966).
Leppi, T. J.: Morphochemical analysis of mucous cells in the skin and slime glands of hagfish. Histochemie 15, 68–78 (1968).
—, Kinnison, P. A.: Histochemical evaluation of acidic carbohydrates in pig colonic mucosa. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 774 (1967).
—, Spicer, S. S.: The histochemistry of mucins in certain primate salivary glands. Amer. J. Anat. 118, 833–860 (1966).
—: The histochemistry of carbohydrate-rich substances in certain ungulate salivary glands. Anat. Rec. 159, 179–191 (1967).
—, Henson, J. G., Fioravanti, J.: Correlated histochemical staining and S35 labelling of salivary gland mucosubstances. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 745–751 (1967).
Lev, R., Spicer, S. S.: Specific staining of sulphate groups with alcian blue at low pH. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 12, 309 (1964).
McManus, J. F. A.: Histological demonstration of mucin after periodic acid. Nature (Lond.) 15, 202 (1946).
Mowry, R. W.: Alcian blue technics for the histochemical study of acidic carbohydrates. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 4, 407 (1956).
—: The special value of methods that color with both acidic and vicinal hydroxyl groups in the histochemical study of mucins. With revised directions for the colloidal iron stain, the use of alcian blue 8 GX and their combinations with the periodic acid Schiff reaction. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 106, 402–423 (1963).
—, Winkler, C. H.: The coloration of acidic carbohydrates of bacteria and fungi in tissue sections with special reference to capsules of Cryptococcus neoformans, Pneumococcus and Staphylococcus. Amer. J. Path. 32, 628–629 (1956).
Neuberger, A., Marshall, R. D., Gottschalk, A.: Some aspects of the chemistry of the component sugars of glycoproteins. In: Glycoproteins, vol. 5, p. 158–189, ed. by Gottschalk, A. New York: Elsevier Publishing Company 1966.
Quintarelli, G.: Masking action of basic proteins on sialic acid carboxyls in epithelial mucins. Experientia (Basel) 19, 1–3 (1963).
—, Dellovo, M. C.: Studies on the exocrine secretions. Histochemical investigation on the major salivary glands of exotic animals. Histochemie 19, 199–223 (1969).
Schrager, J.: Mucopolysaccharide of the gastric secretion. Nature (Lond.) 201, 1220–1222 (1964).
Scott, J. E., Dorling, J.: Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) by alcian blue in salt solutions. Histochemie 5, 221–223 (1965).
—, Quintarelli, G.: Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans by alcian blue in salt solutions. Biochem. J. 90, 4p-5p (1964).
Shin, T. S., Soo, Y. P.: A histological and histochemical study of the glands of Von Ebner in the human tongue: additional report on the staining properties of the mucous cells. Yonsei med. J. 2, 6–9 (1961).
Spicer, S. S.: A correlative study of the histochemical properties of rodent acid mucopolysaccharides. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 8, 18–35 (1960).
—, Hensen, J. G.: Methods for localizing mucosubstances in epithelial and connective tissues. Meth. Achiev. exp. Path. 2, 78–112 (1967).
- Horn, R. G., Leppi, T. J.: Histochemistry of connective tissue mucopolysaccharides. In: The connective tissue. Int. Acad. Path. Monograph No. 7, p. 251–303 (1967).
—, Jarrels, M. H.: Histochemical reaction of an aromatic diamine with acid groups and periodate engendered aldehydes in mucopolysaccharides. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 9, 368–379 (1961).
Spicer, S. S., Lillie, R. D.: Saponification as a means of selective reversing the methylation blockade of tissue basophilia.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 7, 123–125 (1959).
—, Meyer, D. B.: Histochemical differentiation of acid mucopolysaccharides by means of combined aldehyde fuchsin-alcian blue staining. Amer. J. clin. Path. 33, 453–460 (1960).
—, Stoward, P. J.: Suggestions for a histochemical terminology of carbohydrate-rich tissue components. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 13, 599–603 (1965).
Varute, A. T., Jirge, S. K.: Histochemical analysis of mucosubstances in oral mucosa of mouth breeding Cichlid fish and seasonal variations in them. Histochemie 25, 91–102 (1971).
—, Patil, V. A.: Histochemical analysis of molluscan stomach and intestinal alkaline phosphatase: A sialoglycoprotein. Histochemie 25, 77–90 (1971).
Wislocki, G. B., Bunting, H., Dempsey, E. W.: Metachromasia in mammalian tissues and its relationship to mucopolysaccharides. Amer. J. Anat. 81, 1–37 (1947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation forms a part of Ph. D. Thesis to be submitted by Mr. M. N. Nalavade to Shivaji University, Kolhapur, under the guidance of Dr. A. T. Varute.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nalavade, M.N., Varute, A.T. Histochemical studies on the mucins of the vertebrate tongues. Histochemie 27, 351–365 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305337
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305337