Summary
The anatomy of the cecum of the vole, Microtus agrestis, was investigated using macroscopic dissections, “wet” and dried total specimens, and correlated light, scanning and electron microscopy.
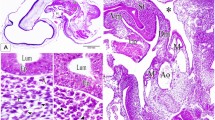
The cecum of the vole reveals a series of structural differentiations including a mural lip in the ampulla ceci and a spiral fold in the corpus ceci. The mucosa covering the cecal wall possesses short, wide-opened crypts and differs from the classical descriptions of the large intestinal mucosa. Fine structural observations suggest the cecal epithelium to be capable of active absorption.
The morphological findings are correlated with the herbivorous habit of the vole and compared with observations in the rabbit and other rodents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behmann, H.: Vergleichend- und funktionell-anatomische Untersuchungen am Caecum und Colon myomorpher Nagetiere. Z. Wiss. Zool. 186, 173–294 (1973)
Björnhag, G.: Separation and delay of contents in the rabbit colon. Swedish J. Agr. Res. 2, 125–136 (1972)
Bond, J.H., Levitt, M.D.: Fate of soluble carbohydrate in the colon of rats and man. J. Clin. Invest. 57, 1158–1164 (1976)
Davenport, H.W.: Physiology of the digestive tract. Chicago: Year Book Medical 1971
Davis, C.P., Mulcahy, D., Takeuchi, A., Savage, D.C.: Location and description of spiral-shaped microorganisms in the normal rat caecum. Infect. Immun. 6, 184–192 (1972)
Eberhard, I.H., McNamara, J., Pearse, R.J., Southwell, I.A.: Ingestion and excretion of Eucalyptus punctata D.C. and it essential oil in the koala, Phascolarctos cinereus (Goldfuss). Aust. J. Zool. 23, 169–179 (1975)
Gorgas, M.: Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen am Magen-Darm-Kanal der Sciuromorpha, Hystricomorpha und Caviomorpha (Rodentia). Z. Wiss. Zool. 175, 237–404 (1967)
Henrikson, R.C.: Ultrastructural aspects of mouse cecal epithelium. Z. Zellforsch. 140, 445–449 (1973)
Janis, C.: The evolutionary strategy of the equidae and the origins of rumen and cecal digestion. Evolution 30, 757–774 (1976)
Kostanecki, K.: Le caecum des vertébrés. Bull. intern. acad. polonaise, Classe sc. mathém. et naturelle. Série B. Cracovie, No. Supplémentaire 1926
Langer, P.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen von taenierten Abschnitten des Verdauungstraktes bei Säugetieren. Verh. Anat. Ges. 1979a in press
Langer, P.: Functional anatomy of taenia, haustra, and semilunar folds in the digestive tract of mammals. Anat. Embryol. submitted for publication 1979b
Leach, W.D., Lee, A., Stubbs, R.P.: Localisation of bacteria in the gastrointestinal trac: a possible explanation of intestinal spirochaetosis. Infect. Immun. 7, 961–972 (1973)
Leng, E.: Absorption of inorganic ions and volatile fatty acids in the rabbit caecum. Br. J. Nutr. 40, 509–519 (1978)
Loeschke, K.: Intestinale Adaptation der Elektrolyt- und Wasserresorption. Fortschr. Med. 93, 1613–1615 (1975)
McKenzie, R.A.: The caecum of the koala, Phascolarctos cinereus: Light, scanning and transmission electron microscopic observations on its epithelium and flora. Aust. J. Zool. 26, 249–256 (1978)
Mitchell, C.: On the intestinal tract of mammals. Trans. Zool. Soc. Lond. (XVII 1903–1906), 437–536 (1905)
Möller, W.: Paraffinum liquidum in einer Intermediumkombination für die Paraffineinbettung. Mikroskopie (Wien) 32, 100–104 (1976)
Mottaz, P., Worbe, J.-F.: Transfert des acides gras volatils dans la paroi du caecum isolé de rat. Comptes rend. Séances Soc. Biol. 171, 375–380 (1977)
Murray, R.M., Marsh, H., Heinsohn, G.E., Spain, A.V.: The role of the midgut caecum and large intestine in the digestion of sea grasses by the dudong (Mammalia: Sirenia). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 56 A, 7–10 (1977)
Muthmann, E.: Beiträge zur vergleichenden Anatomie des Blinddarmes und der lymphoiden Organe des Darmkanals bei Säugetieren und Vögeln. Anat. Hefte I, Abt. 144, 48, 4–114 (1913)
Owen, R.L., Nemanic, P.: Antigen processing structures of the mammalian intestinal tract: an SEM study of lymphoepithelial organs. Scanning Electron Microscopy Vol. II SEM Inc. AMF O'Hare, III. 60666 USA, 1978
Parker, D.: The measurement of production rates of volatile fatty acids in the caecum of the conscious rabbit. Br. J. Nutr. 36, 61–70 (1976)
Pfeiffer, C.J., Rowden, G., Weibel, J.: Gastrointestinal Ultrastructure. Georg Theime Publ. Stuttgart & Igaku Shoin Ltd. Tokyo, 1975
Rayssiguier, Y., Remesy, C.: Magnesium absorption in the caecum of rats related to volatile fatty acids production. Ann. Rech. Vét. 8, 105–110 (1977)
Rérat, A.: Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates and nitrogenous matters in the hindgut of the omnivorous nonruminant animal. J. Anim. Sci. 46, 1808–1837 (1978)
Ruckebusch, Y., Hörnicke, H.: Motility of the rabbit's colon and cecotrophy. Physiol. Behav. 18, 871–878 (1977)
Savage, D.C., Dubos, R., Schaedler, R.W.: The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochtonous bacterial flora. J. Exp. Med. 127, 97–110 (1968)
Schofield, G.C., Atkins, A.M.: Secretory immunoglobulin in columnar epithelial cells of the large intestine. J. Anat. (Lond.) 107, 491–504 (1970)
Snipes, R.L.: Limited fat absorption in the large intestine of mice. A morphological study. Acta Anat. 99, 435–439 (1977)
Snipes, R.L.: Anatomy of the rabbit cecum. Anat. Embryol. 155, 57–80 (1978)
Tomasi, T.B.: Secretory immunoglobulins, New Engl. J. Med. 287, 500–506 (1972)
Toner, P.G., Carr, K.E., Wyburn, G.M.: The Digestive System — an Ultrastructural Atlas and Review. Butterworths, London, 1971
Vorontsov, N.N.: The ways of food specialization and evolution of the alimentary system in Muroidea. Symp. Ther. Proc. Internat. Symp. Meth. Mammal. Invest. Brno (1960) Prag 360–377
Vorontsov, N.N.: Die Ungleichmäßigkeit der Tempi der Umgestaltung der Organe und das Prinzip der Kompensation der Funktionen. Zool. J. 9, 1289–1305 (1963)
Wille, K.-H.: Über die Schleimhautoberfläche des Blinddarmes einiger Haussäuger. Eine rasterelektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung. Zbl. Vet. Med. C4, 265–273 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snipes, R.L. Anatomy of the cecum of the vole, Microtus agrestis . Anat Embryol 157, 181–203 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305159
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305159