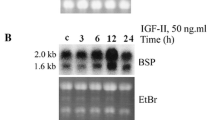
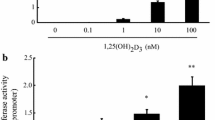
Abstract
The nuclear signaling events activated when epidermal growth factor (EGF) interacts with osteoblasts to produce effects on growth and differentiation are not clearly understood, and may include induction of immediate early genes such as Egr-1, a zinc finger transcription factor. In the present study, Northern analyses were performed to define the effects of EGF on the expression of Egr-1 mRNA in MC3T3-E1 mouse osteoblastic cells. Following treatment of quiescent, subconfluent MC3T3-E1 cells with 0.1–100 ng/ml EGF for various periods, maximal induction of Egr-1 mRNA occurred when cells were treated for 30–60 minutes with 1–10 ng/ml EGF. Inhibition of protein kinase C activity by pretreatment with 1 μM chelerythrine chloride or by prolonged stimulation with 50 ng/ml tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate (TPA) partially diminished the induction of Egr-1 by EGF. . Using an immunohistochemical approach, 10 ng/ml EGF was this induction was localized to the nucleus. These observations indicate that EGF induces Egr-1 mRNA and protein via protein kinase C and other signaling pathways, and that Egr-1 may be part of the regulatory network mediating the actions of EGF on growth and differentiation of osteoblasts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng KW, Partridge NC, Niall M, Martin TJ (1983) Epidermal growth factor receptors in clonal lines of a rat osteogenic sarcoma and in osteoblast-rich rat bone cells. Calcif Tissue Int 35:298–303
Shupnik MA, Tashjian AH (1980) Characterization and regulation of receptors for epidermal growth factor in mouse calvaria. Endocrinology 107:1738–1746
Kumegawa M, Hiramatsu M, Hatakeyama K, Yajima T, Kodama H, Osaki T, Kurisu K (1983) Effects of epidermal growth factor on osteoblastic cells in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int 35:542–548
Ng KW, Partridge NC, Niall M, Martin TJ (1983) Stimulation of DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor in osteoblast-like cells. Calcif Tissue Int 35:624–628
Nicolas V, Nefussi JR, Collin P, Forest N (1990) Effects of acidic fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor on subconfluent fetal rat calvaria cell cultures: DNA synthesis and alkaline phosphatase activity. Bone Miner 8:145–156
Marie PJ, Hott M, Perheentupa J (1990) Effects of epidermal growth factor on bone formation and resorption in vivo. Am J Physiol 258 (Endocrinol Metab 21):E275-E281
Antosz ME, Bellows CG, Aubin JE (1987) Biphasic effects of epidermal growth factor on bone nodule formation by isolated rat calvaria cells in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 2:385–393
Canalis E (1983) Effects of hormones and growth factors on alkaline phosphatase activity and collagen synthesis in cultured rat calvariae. Metabolism 32:14–20
Chen TL, Mallory JB, Chang SL (1989) Modulation of transforming growth factor-beta actions in rat osteoblast-like cells: the effects of bFGF and EGF. Growth Factors 1:335–345
Gutierrez GE, Mundy GR, Derynck R, Hewlett EL, Katz MS (1987) Inhibition of parathyroid hormone-responsive adenylate cyclase in clonal osteoblast-like cells by transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 262: 15845–15850
Chen TL, Chang LY, DiGregorio DA, Perlman AJ, Huang YF (1993) Growth factor modulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in rat osteoblast-like cells. Endocrinology 3: 1382–1389
van Leeuwen JP, Pols HA, Schilte JP, Visser TJ, Birkenhager JC (1991) Modulation by epidermal growth factor of the basal 1,25(OH)2D3 receptor level and the heterologous up-regulation of the 1,25(OH)2D3 receptor in clonal osteoblast-like cells. Calcif Tissue Int 49:35–42
Cheng SL, Shen V, Peck WA (1991) Regulation of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor production by growth factors and cytokines in rat calvarial cells. Calcif Tissue Int 49:321–327
Cook S, McCormick F (1994) Ras blooms on sterile ground. Nature 369:361–362
Hernandez-Sotomayor SM, Carpenter G (1992) Epidermal growth factor receptor: elements of intracellular communication. J Membr Biol 128:81–89
Carpenter G, Wahl MI (1990) The epidermal growth factor family Handbk Exptl Pharmacol 951:69–171
Herschman HR (1991) Primary response genes induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. Annu Rev Biochem 60: 281–319
Christy BA, Lau LF, Nathans D (1988) A gene activated in mouse 3T3 cells by serum growth factors encodes a protein with “zinc finger” sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:7857–7861
Sukhatme VP (1992) The Egr transcription factor family: from signal transduction to kidney differentiation. Kidney Int 41:550–553
McMahon AP, Champion JE, McMahon JA, Sukhatme VP (1990) Developmental expression of the putative transcription factor Egr-1 suggests that Egr-1 and c-fos are coregulated in some tissues. Development 108:281–287
Suva LJ, Ernst M, Rodan GA (1991) Retinoic acid increases zif268 early gene expression in rat preosteoblastic cells. Mol Cell Biol 11:2503–2510
Harada S, Wesolowski G, Suva LG, Rodan SB, Rodan GA (1991) The role of zif268 and insulin-like growth factor-Lin prostaglandin stimulation of growth in osteoblastic cells. J Bone Miner Res 6(suppl 1):A220
Nose K, Shibanuma M, Kikuchi K, Kageyama H, Sakiyama S, Kuroki T (1991) Transcriptional activation of early response genes by hydrogen peroxide in a mouse osteoblastic cell line. Eur J Biochem 201:99–106
Nose K, Shibanuma M (1994) Induction of early response genes by hypergravity in cultured mouse osteoblastic cells (MC3T3-E1). Exp Cell Res 211:168–170
Fang MA, Kujubu DA, Hahn TJ (1992) The effects of prostaglandin E2, parathyroid hormone, and epidermal growth factor on mitogenesis, signaling, and primary response genes in UMR 106-01 osteoblast-like cells. Endocrinology 131:2113–2119
Stein GS, Lian JB (1993) Molecular mechanisms mediating proliferation/differentiation interrelationships during progressive development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocrine Reviews 14:424–442
Quarles LD, Yohay DA, Lever LW, Caton R, Wenstrup RJ (1992) Distinct proliferative and differentiated stages of murine MC3T3-E1 cells in culture: an in vitro model of osteoblast development. J Bone Miner Res 7:683–692
Okazaki R, Ikeda K, Sakamoto A, Nakano T, Morimoto K, Kikuchi T, Urakawa K, Ogata E, Matsumoto T (1992) Transcriptional activation of c-fos and c-jun protooncogenes by serum growth factors in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells. J Bone Miner Res 7:1149–1155
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Lim RW, Varnum BC, Herschman HR (1987) Cloning of tetradecanoyl phorbol ester-induced “primary response” sequences and their expression in density-arrested Swiss 3T3 cells and a TPA non-proliferative variant. Oncogene 1:263–270
Fort PH, Marty L, Piechaczk M, El Sabrouty S, Dani CH, Jeanteur PH, Blanchard JM (1985) Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res 13:1431–1442
Lemaire P, Vesque C, Schmitt J, Stunnenberg H, Frank R, Charnay P (1990) The serum-inducible mouse gene Krox-24 encodes a sequence-specific transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol 10:3456–3467
Herbert JM, Augereau JM, Gleye J, Maffrand JP (1990) Chelerythrine chloride is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 172:993–999
Coleman DL, Bartiss AH, Sukhatme VP, Liu J, Rupprecht H (1992) Lipopolysaccharide induces Egr-1 mRNA and protein in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol 149:3045–3051
Liu J, Lacy J, Sukhatme VP, Coleman DL (1991) Granulocytemacrophage-colony-stimulating factor induces transcriptional activation of Egr-1 in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem 266:5929–5933
Bernstein SH, Kharbanda SM, Sherman ML, Sukhatme VP, Kufe DW (1991) Posttranscriptional regulation of the zinc finger-encoding Egr-1 gene by granulocyte-macrophage-colony-stimulating factor in human U-937 monocytic leukemia cells: involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Cell Growth Differ 2:273–278
Rupprecht HD, Dann P, Sukhatme VP, Sterzel RB, Coleman DL (1992) Effect of vasoactive agents on induction of Egr-1 in rat mesangial cells: correlation with mitogenicity. Am J Physiol 263 (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 32):F623-F636
Cao X, Guy GR, Sukhatme VP, Tan YH (1992) Regulation of the Egr-1 gene by tumor necrosis factor and interferons in primary human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 267:1345–1349
Kharbanda S, Rubin E, Datta R, Hass R, Sukhatme V, Kufe D (1993) Transcriptional regulation of the early growth response 1 gene in human myeloid leukemia cells by okadaic acid. Cell Growth Differ 4:17–23
Gupta MP, Gupta M, Zak R, Sukhatme VP (1991) Egr-1, a serum-inducible zinc finger protein, regulates transcription of the rat cardiac α-myosin heavy chain gene. J Biol Chem 266:12813–12816
Cao X, Mahendran R, Guy GR, Tan YH (1992) Protein phosphatase inhibitors induce the sustained expression of the Egr-1 gene and the hyperphosphorylation of its gene product. J Biol Chem 267:12991–12997
Yu C-L, Prochownik EV, Imperiale MJ, Jove R (1993) Attenuation of serum inducibility of immediate early genes by oncoproteins in tyrosine kinase signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biol 13:2011–2019
Lau F, Nathans D (1987) Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/C 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1182–1186
Nishizawa N, Okano Y, Chatani Y, Amano F, Tanaka E, Nomoto H, Nozawa Y, Kohno M (1990) Mitogenic signaling pathways of growth factors can be distinguished by the involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanosine triphosphate-binding protein and of protein kinase C. Cell Regul 1:747–761
Morrison P, Takashima K, Rosner MR (1993) Role of threonine residues in regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 268:15536–15543
Ohno S, Mizuno K, Adachi Y, Hata A, Akita Y, Akimoto K, Osada S, Hirai S, Suzuki K (1994) Activation of novel protein kinases C delta and C epsilon upon mitogenic stimulation of quiescent rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 269:17495–17501
Seyfert VL, McMahon S, Glenn W, Cao X, Sukhatme VP, Monroe JG (1990) Egr-1 expression in surface Ig-mediated B cell activation: kinetics and association with protein kinase C activation. J Immunol 145:3647–3653
Hallahan DE, Sukhatme VP, Sherman ML, Virudachalam S, Kufe D, Weichselbaum RR (1991) Protein kinase C mediates x-ray inducibility of nuclear signal transducers EGR1 and JUN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2156–2160
Alexandropoulos K, Qureshi SA, Bruder JT, Rapp U, Foster DA (1992) The induction of Egr-1 expression by v-Fps is via a protein kinase C-independent intracellular signal that is sequentially dependent upon HaRas and Raf-1. Cell Growth Differ 3:731–737
Gashler AL, Swaminathan S, Sukhatme VP (1993) A novel repression module, an extensive activation domain, and a bipartite nuclear localization signal defined in the immediate-early transcription factor Egr-1. Mol Cell Biol 13:4556–4571
Dey BR, Sukhatme VP, Roberts AB, Sporn MB, Rauscher FJ III, Kim S-J (1994) Repression of the transforming growth factor-β1 gene by the Wilms' tumor suppressor WT1 gene product. Mol Endocrinol 8:595–602
Cao X, Koski RA, Gashler A, McKiernan M, Morris CF, Gaffney R, Hay RV, Sukhatme VP (1990) Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol 10:1931–1939
Kim S-J, Park K, Rudkin BB, Dey BR, Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1994) Nerve growth factor induces transcription of transforming growth factor-β1 through a specific promoter element in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 269:3739–3744
Hyun SW, Park K, Lee YS, Lee YI, Kim SJ (1994) Inhibition of protein phosphatases activates P4 promoter of the human insulin-like growth factor II gene through the specific promoter element. J Biol Chem 269:364–368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, M.A., Noguchi, G.M. & McDougall, S. Epidermal growth factor induces Egr-1 messenger RNA and protein in mouse osteoblastic cells. Calcif Tissue Int 57, 450–455 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301949
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301949