Summary
The effects of zinc added to a diluvial sandy clay loam soil on its microflora and the metabolic products of amended glucose in the soil were investigated, and its influences on both biological and chemical turnover are discussed.
Changes in the soil microflora were followed by counting the microbes and measuring their contributions to soil respiration. The transformations of 14C-glucose products were traced in five divided fractions.
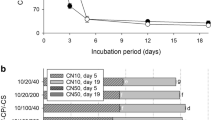
Amended glucose was readily assimilated into microbial tissues and transformed to metabolites in the control soil. Within the initial 24 h of the incubation, most of the glucose was decomposed and about 40% of the substrate evolved as carbon dioxide. This primary metabolism was attributed to the bacterial population, and the subsequent secondary metabolism was associated with fungal growth rather than
bacteria. On the other hand, zinc (1000 μg/g) added as chloride prolonged the primary metabolism of glucose and a large part of the incubation period for 96 h was occupied by this metabolism, which was mostly dependent on the fungal population. Viable bacterial number noticeably within the first 24 h of the incubation. During the course of the subsequent incubation, however, this number increased and the selection for zinc tolerance was suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JPE, Domsch KH (1973) Quantification of bacterial to fungal contributions to soil respiration. Archiv Mikrobiol 93:113–127
Anderson JPE, Domsch KH (1975) Measurement of bacterial and fungal contributions to respiration of selected agricultural and forest soils. Can J Microbiol 21:314–322
Behera B, Wagner GH (1974) Microbial growth rate in glucose-amended soil. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 38:591–594
Chahal KS, Wagner GH (1965) Decomposition of organic matter in Sanborn field soils amended with C14 glucose. Soil Sci 100:96–103
Cornfield AH (1977) Effects of addition of 12 metals on carbon dioxide release during incubation of an acid sandy soil. Geoderma 19:199–203
Domsch KH (1984) Effects of pesticides and heavy metals on biological processes in soil. Plant and Soil 76:367–378
Duxbury T, Bicknell B (1983) Metal-tolerant bacterial populations from natural and metal-polluted soils. Soil Biol Biochem 15:243–250
Iimura K (1981) Background contents of heavy metals in Japanese soils. In: Kitagishi K, Yamane I (eds) Heavy metal pollution in soils of Japan. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, pp 19–26
Jordan MJ, Lechevalier MP (1975) Effects of zinc-smelter emissions on forest soil microflora. Can J Microbiol 21: 1855–1865
Komai Y (1981) Heavy metal pollution in urban soils. In: Kitagishi K, Yamane I (eds) Heavy metal pollution in soils of Japan. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, pp 193–217
Ladd JN, Paul EA (1973) Changes in enzymic activity and distribution of acid-soluble, amino acid-nitrogen in soil during nitrogen immobilization and mineralization. Soil Biol Biochem 5:825–840
Nannipieri P, Pedrazzini F, Arcara PG, Piovanelli C (1979) Changes in amino acids, enzyme activities, and biomasses during soil microbial growth. Soil Sci 127:26–34
Oades JM, Wagner GH (1971) Biosynthesis of sugars in soils incubated with 14C glucose and 14C dextran. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 35:914–917
Tyler G (1973) Heavy metal pollution and decomposition of spruce needle litter. Oikos 24:402–416
Zunino H, Borie F, Aguilera S, Martin JP, Haider K (1982) Decomposition of 14C-labelled glucose, plant and microbial products and phenols in volcanic ash-derived soils of Chile. Soil Biol Biochem 14:37–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohya, H., Komai, Y. & Yamaguchi, M. Zinc effects on soil microflora and glucose metabolites in soil amended with 14C-glucose. Biol Fert Soils 1, 117–122 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301778
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301778