Abstract
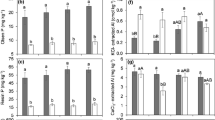
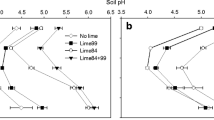
Results from a factorial acid treatment and liming experiment in a stand of Scots pine planted in 1968 to 1970 are presented. Field plots, 75 m2 in size, were supplied with 50 mm of artificial rain 38 times from 1974 to 1981. “Rain” of varying acidities was produced using groundwater mixed with H2SC4. Lime was applied at four levels in 1974 in a factorial acid treatment-liming-design. Tree growth and foliar nutrient concentrations were measured annually from 1974 to 1988. The soil was sampled periodically from 1975 to 1988 at mainly 3 yr intervals. Tree growth was initially stimulated by increased acid loadings. Negative effects occurred after 5 yr. Positive effects of liming developed after 9 yr. No major signs of recovery from the most acid treatments have yet been found. Treatment effects appeared to be linear, indicating no threshold values for growth reactions. Treatment effects on foliar concentrations were found for a majority of elements analyzed. Increased acid loadings decreased the Mg, Ca and Mn concentrations, while K concentrations increased — especially during later years. Liming improved the nutrient status at increased acid loadings for Mg, Ca and Mn and decreased K concentrations. Soil sampling in 1984 showed major losses of Mg, Ca and Mn by increased acid loadings, while the K content was less affected. A link seems to exist between tree growth and the Mg situation in soil and foliage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsen, G., Bjor, K., Horntvedt, R. and Tveite, B.: 1976a, “Effects of acid precipitation on coniferous forest”, in F.H. Braekke (ed), Impact of Acid Precipitation on Forest and Freshwater Ecosystems in Norway, SNSF-project, FR 6/76, 37–63.
Abrahamsen, G., Bjor, K. and Teigen, 0.: 1976b, “Field experiments with simulated acid rain in forest ecosystems”, SNSF-project FR 4/76, 15 pp, Oslo-Ås.
Abrahamsen, G.: 1983, “Sulphur pollution: Ca, Mg and Al in soil and soil water and possible effects on forest trees”, in B. Ulrich and J. Pankrath (eds), Effects of accumulation of air pollutants in forest ecosystems, D. Reidel, 207–218.
Abrahamsen, G., Stuanes, A.O. and Tveite, B.: 1983, Water Qual. Bull. 8, 89.
Abrahamsen, G.: 1984, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B305, 369.
Abrahamsen, G., Tveite, B. and Stuanes, A.O.: 1987, “Wet acid deposition effects on soil properties in relation to forest growth. Experimental results”, in D. Lavender (ed), Proceedings IUFRO Conference on Woody Plant Growth in a Changing Physical and Chemical Environment, Vancouver, July 1987 (in press).
Bosch, C., Pfannkuch, E., Baum, U. and Rehfuess, K.E., 1983: Foresw. Cbl. 102, 167.
Foerst, K., Sauter, U. and Neuerburg, W.: 1987, Forstl. Forschungsberichte München, 79, 90.
Heinsdorf, D., Krauss, H.H. and Hippeli, P.: 1988, Beitr. Forstwirtschaft 22, 160.
Ogner, G., Haugen, A., Opem, M., Sjøtveit, G. and Sørlie, B.: 1984, “The chemical analysis program at the Norwegian Forest Research Institute, 1984”, Norsk institutt for skogforskning, 1432 Ås-NLH, 27.
Stefan, K.: 1989, “Schwefel- und Nährstoffgehalt in Pflanzenproben des österreichischen Bioindikatornetzes”, in J.B. Bucher and I. Bucher-Wallin (eds), Air pollution and Forest Decline, Birmensdorf, Switzerland, 99–104.
Stuanes, A. and Sveistrup, T.E.: 1979, “Field experiments with simulated acid rain in forest ecosystems. 2. Description and classification of the soil used in field, lysimeter and laboratory experiments”, SNSF-project, FR 15/79, 35 pp, Oslo-Ås.
Stuanes, A.O.: 1980, “Effects of acid precipitation on soil and forest. 5. Release and loss of nutrients from a Norwegian forest soil due to artificial rain of varying acidity”, in D. Drabløs and A. Tollan (eds), Proceedings Int. conf. ecol. impact acid precip., SNSF-project, Oslo-Ås, 198–199.
Tveite, B.: 1980a, “Effects of acid precipitation on soil and forest. 8. Foliar nutrient concentrations in field experiments”, in D. Drabløs and A. Tollan (eds), Proceedings Int. conf. ecol. impact acid precip., SNSF-project, Oslo-ÅS, 204–205.
Tveite, B.: 1980b, “Effects of acid precipitation on soil and forest. 9. Tree growth in field experiments”, in D. Drabløs and A. Tollan (eds), Proceedings Int. conf. ecol. impact acid precip., SNSF-project, Oslo-Ås, 206–207.
Tveite, B. and Abrahamsen, G.: 1980, “Effects of artificial acid rain on the growth and nutrient status of trees”, in T.C. Hutchinson and M. Havas (eds), Effects of Acid Precipitation on Terrestrial Ecosystems, Plenum Press, New York, London, 305–318.
Zöttl, H.W. and Mies, E.: 1983, Allg. Forst-u.J.-Ztg 154, 110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tveite, B., Abrahamsen, G. & Stuanes, A.O. Liming and wet acid deposition effects on tree growth and nutrition:Experimental results. Water Air Soil Pollut 54, 409–422 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298682
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298682