Abstract
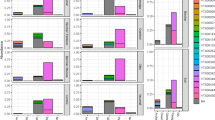
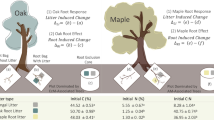
Red alder (Alnus rubra Bong.) is well recognized as an effective host plant for the symbiotic fixation of N. While this fixation process leads to the rapid accumulation of N within the ecosystem, it also enhances nutrient accumulation in biomass and soil organic matter and increases nitrification and cation leaching. We hypothesized that changes in soil properties resulting from these processes would decrease site productivity for second rotation red alder. Adjacent stands of 55 yr old alder and Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.] Franco) were studied at the Thompson Research Center on the Cedar River Watershed in western Washington, USA.The presence of red alder caused the following soil changes: decreased soil solution pH, increased CEC, increased exchangeable acidity accompanied by a decreased soil pH and base saturation. This decreased soil and soil solution pH resulted in increased A1 concentration in the soil solution and on exchange sites as well as decreased P availability. To determine the effect of these changes on the productivity of the 2nd rotation alder forest, a species conversion experiment was initiated 5 yr ago. Results from this conversion study clearly indicated that the first rotation red alder forest has caused a relative decrease in the productivity of the second rotation red alder plantation. Compared to the growth of red alder on the former Douglas fir site, the second rotation red alder on the former red alder site exhibited 339 less height growth and 759, less aboveground biomass accumulation after 5 yr. Future research will focus on identifying those factors causing this lower productivity including P availability, soil acidity and Al toxicity, cation availability, and competition with other vegetation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsen, G., Tveite, B. and Stuanes, A.O.: 1987, Wet acid deposition effects of soil properties in relation to forest growth. Experimental results. Paper presented at the IUFRO Conference: Woody Plant Growth in a changing Physical and Chemical Environment. Vancouver, Canada, July 27–31, 1987.
Binkley, D.: 1986, Forest Nutrition Management, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Binkley, D. and Husted, L.: 1983, Can. J. For. Res. 13, 122.
Binkley, D., Lousier, J.D. and Cromack, Jr., K: 1984, For. Sci. 1, 26.
Bohn, H., McNeal, B. and O'Connor, G.: 1985, Soil Chemistry, 2nd Edition. John Wiley, New York.
Bormann, B.T. and DeBell, D.S.: 1981, Soil Sci. Am. J. 45, 428.
Cole, D.W. and Gessel, S.P.: 1968, Cedar River Research — A program for studying the pathways, rates and processes of elemental cycling in a forest ecosystem. Contrib. No. 4, Inst. For. Products. College of Forest Resources, Univ. Washington, Seattle.
Dixon, R.O.D. and Wheeler, C.T.: 1983, Biochemcial, physiological and environmental aspects of symbiotic nitrogen fixation, p. 108–171, in J.C. Gordon and C.T. Wheeler (eds), Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Forest Ecosystems: Foundations and Applications. Martinus Nijhoff/Dr. W. Junk Publ., The Hague, The Netherlands.
Franklin, J.F., Dyrness, C.T., Moore, D.G. and Tarrant, R.F.: 1968, Chemical soil properties under coastal Oregon stands of alder and conifers, p. 157–172, in J.M. Trappe et al., (eds), Biology of Alder. USDA PNW For. Range Exp. Sta., Portland, Oregon.
Gordon, J.C. and Wheeler, C.T.: 1983, Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Forest Ecosystems: Foundations and Applications. Martinus Nijhoff/Dr. W. Junk Publ., The Hague, The Netherlands.
Huss-Dannell, K.: 1986, Can. J. For. Res. 16, 847.
Johnson, D.W., Cole, D.W., Van Miegroet, H. and Horng, F.W.: 1986, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 776.
McCormick, L.H. and Steiner, K.C.: 1978, For. Sci. 4, 565.
Mikola, P., Uomala, P. and Malkonen, E.: 1983, Application of biological nitrogen fixation in European silviculture, p. 279–294, in J.C. Gordon and C.T. Wheeler (eds), Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Forest Ecosystems: Foundations and Applications. Martinus Nijhoff/Dr. W. Junk Publ. The Hague, The Netherlands.
Miller, R.E. and Murray, M.D.: 1978, The effects of red alder on growth of Douglas fir, p. 283–306, in G. Briggs et al. (eds), Utilization and Management of Alder. USDA For. Serv. Gen. Tech. Rep. PNW-70.
Paul, E.A. and Kucey, R.M.N.: 1981, Science 213, 473.
Radwan, M.A.: 1987, Effects of fertilization on growth and foliar nutrients of red alder seedlings. Research paper PNW-RP-375. Portland, OR., USDA For. Serv., PNW Research Station. 14 p.
Reuss, J.O. and Johnson, D.W.: 1986, Acid deposition and acidification of soils and waters. Ecological Series, Vol. 59, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Seiler, J.R. and McCormick, L.H.: 1982, Can. J. For. Res. 12, 576.
Sposito, G.: 1989, The Chemistry of Soils. Oxford University Press, New York.
Tarrant, R.F. and Miller, R.E.: 1963, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 27, 231.
Thornton, F.C., Schaedle, M. and Raynal, D.J.: 1986, J. Exp. Bot. 37 775.
Van Cleve, K. and Vierek, L.A.: 1972, Arct. Alp. Res. 4, 239.
Van Miegroet, H. and Cole, D.W.: 1984, J. Environ. Qual. 13, 586.
Van Miegroet H. and Cole, D.W.: 1985, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 49, 1274.
Van Miegroet, H. and Cole, D.W.: 1988, Influence of nitrogen-fixing alder on acidification and cation leaching in a forest soil, in D.W. Cole and S.P. Gessel (eds), Forest Site Evaluation and Long-term Productivity. University of Washington Press, Seattle.
Van Miegroet, H., Cole, D.W., Binkley, D. and Sollins, P.: 1989, The effect of nitrogen accumulation and nitrification on soil chemical properties in alder forests. Paper presented at the 82nd Annual Meeting of the Air and Waste Management Association, Anaheim, CA, June 25–30, 1989. Preprint 89-134.1.
Van Miegroet, H., Cole, D.W. and Homann, P.S.: 1990, The effect of alder forest cover and alder forest conversion on site fertility and productivity, in S.P. Gessel (ed), Sustained Productivity of Forest Land. Proceedings of the 7th North American Forest Soil Conference, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cole, D.W., Compton, J., Van Miegroet, H. et al. Changes in soil properties and site productivity caused by red alder. Water Air Soil Pollut 54, 231–246 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298668
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298668