Abstract
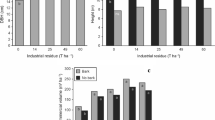
The 6000 ha of Armand Pine in the Wushan mountainous area East of Sichuang Province in southwestern China, have almost declined completely. The preliminary investigation in the area shows that the needle chlorosis (yellowing) of Armand Pine is a common symptom of forest decline in the mountainous region, and a significant increase of the symptom has been seen in the past decade.The SO2 and rain pH data were collected from three monitoring sites in the area.Soil and needle analysis were carried out.The preliminary results indicate that yellowing was evident at all sites of lower soil pH and that soil nutrient status of Mg deficiencies were most notable on acid soils with base saturations at 3.2 to 7.5%. Magnesium, K, Zn (particularly Mg) contents of current needles were all deficient.Exchangeable Mg in the soil of the heavily damaged forest stand was lower than that of the well-growing forest. But the degree of yellowing does not rise along with the increase of A1 concentration. The preliminary investigation in the southwest indicates that the forest damage is associated with nutritional disturbances and the existence of Mg deficiency is reported as the most predominant agent in causing symptoms of yellowing foliage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonneau, M.: 1988, Essais de fertilisation dans les Vosges. Journées de Travail DEFORPA 6, 63.
Liu Houtian: 1986, Research report on the relationship between the Masson Píne Forest decline and death in Nanshan of Chongqing and acid rain. Thesis of 1986 Annual Meeting of the Chinese Society of Plant Physiology.
Liu Jinchen: 1988, Ernahrungskundliche Auswertung von diagnostischen Dungungsversuchen in Fichtenbestanden (Picea abies Karst) Sudwestdeutschlands, Freiburger Bodenkundl. Heft 21. p 158.
Ma Guangjing, Zhang Yaomin and Cao Hongfa: 1987, An investigation report on the injuries of acid rain to China's agriculture and some preventive and curative measures. Proceedings of Meeting on the injuries of acid rain to China's agriculture and some preventive and curative measures (in press).
Ma Guangjing: 1987, La pollution atmosphérique et le déperissement des forêts en Chine. IUFRO Meeting in Interlaken. Air Pollution and Forest Decline, EAFV. l.51.
Murach, D.: 1987, Judgement of the applicability of liming to restabilize forest stands — with special consideration of root ecological aspects, D. Reidel Publishing Co. p 445.
Ulrich, B.: 1983, A concept of forest ecosystem stability and of acid deposition as driving force for destabilization, Effects of accumulation of air pollutants in forest ecosystems, D. Reidel Publishing Co. p 1, 29, 127.
Zöttl, H.W. and Hüttl, R.F.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut., 31, 449.
Zhang Wanru: 1986, Soil of Armand Pine stands. Forest Soil of China, Science Press, p 411.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guangjing, M. Nutritional disturbances and declining armand pine in Southwestern China. Water Air Soil Pollut 54, 91–96 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298655
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298655