Abstract
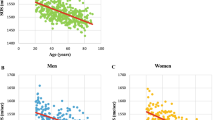
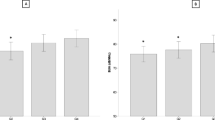
Urinary pyridinoline (pyr) and deoxypyridinoline (dpyr) are new markers for bone resorption, and serum osteocalcin reportedly indicates osteoblastic activity. Recently, a new ultrasound bone densitometer instrument has been developed that measures ultrasonic properties of the os calcis, namely, the speed of sound (SOS), broadband ultrasound attenuation (BUA), and stiffness index. The effects of menopause on biochemical markers and ultrasound densitometry were investigated in 40 healthy females, 36–39 years, with regular menstruation, and in 117 healthy perimenopausal females, 47–57 years, who were divided into a premenopausal group and a postmenopausal group. Significantly elevated values of pyr, dpyr, and serum osteocalcin were found for the postmenopausal group as a whole compared with the premenopausal group. We examined postmenopausal groups 48–57 years of age stratified into 2-year intervals (within 2 years of the menopause, 2–4 years postmenopause and 4–6 years postmenopause). Elevated values of urinary pyr, dpyr, and serum osteocalcin were evident even in the first 2 years postmenopause compared with the premenopausal group, and these higher values were exhibited until 6 years after menopause. We found a significant decrease in SOS, BUA, and stiffness index of the postmenopausal group as a whole, compared with those of the premenopausal group. SOS, BUA, and stiffness index of the group within 2 years of menopause significantly decreased compared with those of the premenopausal group. The Z-scores of the increase in biochemical markers and the decrease in stiffness index in the postmenopausal group were approximately 0.7–1.3 compared with the premenopausal group. The results suggest that these biochemical markers and ultrasound densitometry are potentially sensitive parameters of postmenopausal bone change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riggs BL, Melton LJ III (1986) Involutional osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 314:1676–1686
Whyte MP, Bergfeld MA, Murphy WA, Avioli LV, Teitelbaum SL (1982) Postmenopausal osteoporosis: a heterogeneous disorder as assessed by histomorphometric analysis of iliac crest bone from untreated patients. Am J Med 72:193
Parfitt AM (1982) The contribution of bone histology to understanding the pathogenesis and improving the management of osteoporosis. Clin Invest 5:163–167
Nilas L, Christiansen C (1987) Bone mass and its relationship to age and menopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65:697–702
Pouilles JM, Tremollieres F, Ribot C (1993) The effect of menopause on longitudinal bone loss from the spine. Calcif Tissue Int 52:340–343
Prockop DJ (1964) Isotopic studies on collagen degradation and the urine excretion of hydroxyproline. Clin Invest Med 43:453–460
Eyre DR (1987) Collagen cross-linking amino acids. Methods Enzymol 144:115–139
Delmas PD, Schlemmer A, Gineyts E, Riis BJ, Christiansen C (1991) Urinary excretion of pyridinoline crosslinks correlates with bone turnover measured in iliac crest biopsy in patients with vertebral osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 6:639–644
Black D, Dunkan A, Robins SP (1988) Quantitative analysis of the pyridinum crosslinks of collagen in urine using ion-paired reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 169:197–203
Uebelhart D, Gineyts E, Chapuy MC (1990) Urinary excretion of pyridinum crosslinks: a new marker of bone resorption in metabolic disease. Bone Miner 8:87–96
Harvey RD, Mchardy KC, Reid IW, Paterson F, Bewsher PD, Dankan A, Robins SP (1991) Measurement of bone collagen degradation in hyperthyroidism and during tyroxine replacement therapy using pyridinium crosslinks as specific urinary markers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:1189–1194
Robins SP, Black D, Paterson CR, Reid DM, Duncan A, Seibei MJ (1991) Evaluation of urinary hydroxypyridinium crosslink measurements as resorption markers in metabolic bone diseases. Eur J Clin Invest 21:310–315
Ohishi T, Takahashi M, Kushida K, Horiuchi K, Ishigaki S, Inoue T (1992) Quantitative analysis of urinary pyridinoline and deoxypyridinoline excretion in patients with hyperthyroidism. Endocrinol Res 18(4):281–290
Seibel MJ, Gartenberg F, Silverberg SJ, Ratcliffe A, Robins SP, Bilezikian JP (1992) Urinary hydroxypyridinium crosslinks of collagen in primary hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 74:481–486
Ohishi T, Kushida K, Takahashi M, Kawana K, Yagi K, Kawakami K, Horiuchi K, Inoue T (1994) Urinary bone resorption markers in patients with metabolic bone disorders. Bone 15(1):15–20
Ohishi T, Takahashi M, Kawana K, Aoshima H, Horiuchi K, Kushida K, Inoue T (1992) Age-related changes of urinary pyridinoline and deoxypyridinoline in Japanese subjects. Clin Invest Med 16/5:319–325
Nishimoto SK, Price PA (1980) Secretion of the vitamine K-dependent protein of bone by rat osteosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem 255:6579–6583
Brown JP, Delmas PD, Malaval L, Edouard C, Chapuy MC, Meunier PJ (1984) Serum bone gla protein, a specific marker for bone formation in postmenopausal osteoprosis. Lancet 19: 1091–1093
Nilas L, Christiansen C (1989) The pathophysiology of peri- and postmenopausal bone loss. Br J Obster Gynaecol 96:580–587
Pino J, Martin-Gomez E, Martin-Rodriguez M, Lopez-Sosa C, Cordero M, Lanchares JL, Garcia-Talavera JR (1991) Influence of sex, age and menopause in serum osteocalcin (BGP) levels. Klinische Wochenschrift 69:1135–1138
Hosoda K, Eguchi H, Nakamoto T, Kubota T, Honda H, Jindai S, Hasegawa R, Kiyoki M, Yamaji T, Shiraki M (1992) A sand-with immunoassay for human intact osteocalcin. Clin Chem 38/11:2233–2238
Langton CM, Palmer SB, Porter RW (1984) The measurement of broadband ultrasound attenuation in cancellous bone. Eng Med 13:89–91
Heaney RP, Avioli LV, Chesnut CH, Lappe J, Recker RP, Brandenburger GH (1989) Osteoporosis bone fragility. Detection by ultrasound transmission velocity. JAMA 29:2986–2990
Lees B, Stevenson JC (1993) Preliminary evaluation of a new ultrasound bone densitometer. Calcif Tissue Int 53:149–152
Yamazaki K, Kushida K, Ohmura A, Sano M, Inoue T (1994) Ultrasound bone densitometry of the os calcis in Japanese females. Osteoporosis Int 4:220–225
Takahashi M, Ohishi T, Aoshima H, Kushida K, Inoue T, Horiuchi K (1993) Pre-fraction with cation exchanger for determination of intermolecular crosslinks, pyridinoline and pentosidine, in hydrolysate. J Liq Chromatogr 16(6):1355–1370
Ubelhart D, Schlemmer A, Johansen JS, Gineyts E, Christiansen C, Delmas PD (1991) Effect of menopause and hormone replacement therapy on the urinary excretion of pyridinium crosslinks. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:367–373
Seibel MJ, Cosman F, Shen V, Gordon S, Dempster DW, Ractcliffe A, Lindsy R (1993) Urinary hydroxypyridinium crosslinks of collagen as markers of bone resorption and estrogen efficacy in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 7:881–889
Hassager C, Colwell A, Assiri AMA, Estell R, Russel RGG, Christiansen C (1992) Effect of menopause and hormone replacement therapy on urinary excretion of pyridinum crosslinks: a longitudinal and cross-sectional study. Clin Endocrinol 37:45–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawana, K., Kushida, K., Takahashi, M. et al. The effect of menopause on biochemical markers and ultrasound densitometry in healthy females. Calcif Tissue Int 55, 420–425 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298555
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298555