Summary
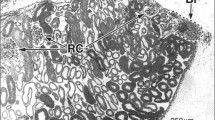
The renal appendages of the octopods Octopus vulgaris Lam., Eledone moschata Lam. and of the decapods of the order Sepioidea Sepia officinalis L., and of sea water suggest osmotic filtration combined with active ion transport and methods of light and electron microscopy and of cytochemistry. The cells of the excretory epithelium are polarised; in all species, they show a basal labyrinth with a thick positive PAS and alcian blue reaction. The cells contain numerous mitochondria, which show the crista type of internal structure, and in the basal as well as in the apical part there are lysosomal dense bodies with high phosphatase activity. The fine structure, the osmolality and the ionic composition of the blood, the urine and of sea water suggest osmotic filtration combined with active ion transport and apocrine excretory secretion and reabsorption. In Sepia only, crypts of the epithelium were found to contain spherical mixed crystals which contain Ca, K, Na, Mg, Cl, S, P according to the electron probe and cytochemical analysis; the matrix shows concentric layers, it gives a positive PAS and alcian blue reaction. The chemical composition, the genesis and the possible function of these crystals are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargmann, W., von Hehn, G.: Über das Nephron der Elasmobranchier. Z.Zellforsch. 114,1–21 (1971)
Becker, G. L., Chen, C. H., Greenawalt, I. W., Lehninger, A. C.: Calcium-phosphat granules in the hepatopancreas of the blue crab Callinectus sapidus. J. Cell Biol. 61, 316–326 (1974)
Berridge, M., Oschman, J. L.: Transporting epithelia. New York-London: Academic Press 1972
von Boletzky, S.: Untersuchungen über die Ontogenese des Kreislaufsystems von Octopus vulgaris Lam. Rev. Suisse Zool. 75, 765–812 (1968)
von Boletzky, S.: Effets de la sous-nutrition prolongée sur le développement de la coquille de Sepia officinalis L. (Mollusca, Cephalopoda). Bull. Soc. Zool. France 99, 667–673 (1974)
Boucaud-Camou, E.: Étude infrastructurale du pancréas de Sepia officinalis L. Bull. Sec. Zool. France, 97, 197–203 (1972)
Carasso, N., Favard, P.: Mise en évidence du calcium dans les myonèmes pédonuclaires de ciliés péritriches. J. Microsc. 5, 759–770 (1966)
Delaunay, H.: L'exeretion azotée des invertébrés. Biol. Rev. 6, 265–301 (1931)
Eichelberg, D., Wessing, A.: Elektronenoptische Untersuehungen an den Nierentubuli (Malpighische Gefäße von Drosophila melanogaster. II. Transzelluläre membrangebundene Stofftransportmechanismen. Z. Zellforsch. 121, 127–152 (1971)
Emmanuel, C. F.: The composition of Octopus renal fluid. II. Organic constituents. Z. vergl. Physiol. 39, 477–482 (1956)
Emmanuel, C. F.: The composition of Octopus renal fluid. III. The isolation and chemical properties of Dicyemin. Z. vergl. Physiol. 39, 483–491 (1957a)
Emmanuel, C. F.: The composition of Octopus renal fluid. IV. Isolation and identification of the methanol soluble substances. Z. vergl. Physiol. 40, 1–7 (1957b)
Emmanuel, C. F., Martin, A. W.: The composition of Octopus renal fluid. I. The inorganic constituents. Z. vergl. Physiol. 39, 226–234 (1956)
Ericsson, J. L. E., Olsen, S.: On the fine structure of the aglomerular renal tubule in Lophius piscatorius. Z. Zellforsch. 104, 240–258 (1970)
Fioroni, P., Meister, G.: Embryologie von Loligo vulgaris Lam. In: Gr. Zool. Praktikum. Stuttgart: Fischer 1974
Grobben, C.: Morphologische Studien über den Harn- und Geschlechtsapparat sowie die Leibeshöhle der Cephalopoden. Arb. aus dem zool. Inst. der Univ. Wien und der Zool. Station Triest 5, 179–252 (1883)
Harrison, F. M., Martin, A. W.: Excretion in the cephalopod Octopus dofleini. J. exp. Biol. 42, 71–98 (1965)
Hevert, F., Wolburg, H., Wessing, A.: Die Konkremente des larvalen Primäharns von Drosophila hydei. II. Anorganische Bestandteile. Cytobiologie 8, 312–319 (1974)
Istin, M., Girard, J. P.: Carbonic anhydrase and mobilisation of calcium reserves in the mantle of lamellibranchs. Calcif. Tiss. Res. 5, 247–260 (1970)
Komnick, H.: Histochemische Calcium-Lokalisation in der Skelettmuskulatur des Frosches. Histochemie 18, 24–29 (1969)
Marthy, H. J.: Die Organogenese des Coelomsystems von Octopus vulgaris. Rev. Suisse Zool. 75, 723–763 (1968)
Meister, G.: Organogenese von Loligo vulgaris Lam. Zool. J. b. Anat. 89, 247–300 (1972)
Naef, A.: Die Organogenese des Cölomsystems und der zentralen Blutgefäße von Loligo. Jena. Z. Med. Naturw. 45, 1–46 (1909)
Naef, A.: Teutologische Notizen XI: Zur Morphologic des Cölomsystems. Zool. Anz. 40, 324–336 (1912)
Naef, A.: Die Cephalopoden. In: Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel, Berlin (1923)
Olsen, S., Ericsson, J. L. E.: Ultrastructure of the tubule of the aglomerular teleost Nerophis ophidion. Z. Zellforsch. 87, 17–30 (1968)
Potts, W. T. W.: Ammonia excretion in Octopus dofleini. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 14, 339–355 (1965)
Potts, W. T. W.: Excretion in the molluscs. Biol. Rev. 42, 1–42 (1967)
Potts, W. T. W., Todd, M.: Kidney function in Octopus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 16, 479–489 (1965)
Riegel, J. A.: In vitro studies of fluid and ion movements due to the swelling of formed bodies. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 35, 843–856 (1970a)
Riegel, J. A.: A new model of transepithelial fluid movement with detailed application to fluid movement in the crayfish antennal gland. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 36, 403–410 (1970b)
Robertson, J. D.: Further studies on ionic regulation in marine invertebrates. J. exp. Biol. 30, 277–296 (1953)
Roinel, N., Morel, F., Istin, M.: Étude des granules calcifiés du manteau des lamellibranches à l'aide de la microsonde éctronique. Calcif. Tiss. Res. 11, 163–170 (1973)
Schipp, R., von Boletzky, S.: Morphology and function of the excretory organs in dibranchiate cephalopods. 3. International Symposium of the “Akademie der Wissenschaften und Literatur”. Mainz 1974 — Excretion. In: Fortschr. Zool. 23, 89–110 (1975)
Schipp, R., Höhn, P., Schafer, A.: Elektronenmikroskopische und histochemische Untersuchungen zur Funktion des Kiemenherzanhanges (Pericardialdrüse) von Sepia of ficinalis. Z. Zellforsch. 117, 252–274 (1971)
Schipp, R., Schäfer, A.: Vergleichende elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an den zentralen Herzorganen der Cephalopoden (Sepia officinalis). Feinstruktur und Funktion der Kiemenherzen. Z. Zellforsch. 101, 367–379 (1969)
Tice, L. W., Barnett, R. J.: Alcianblue staining for electron microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 688–689 (1962)
Vigelius, W. J.: Über das Exkretionssystem der Cephalopoden. Niederländ. Arch. Zool. 5, 115–184 (1880)
Wessing, A.: Die Funktion der MalpighischenGefäße. In: Funktionelleund morphologische Organisation der Zelle. Sekretion und Exkretion. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1965
Wessing, A., Eichelberg, D.: Morphology of the transport and accumulation of substances in the Malpighian tubules of Drosophila. 3. International Symposium of the “Akademie der Wissenschaften and Literatur”. Mainz 1974—Excretion. In: Fortschr. Zool. (in press)
Wolburg, H., Hevert, F., Wessing, A., Porstendoerfer, J.: Die Konkremente des larvalen Primärharns von Drosophila hydei. I. Struktur. Cytobiologie 8, 25–38 (1973)
Yokota, S.: Electron microscopic demonstration of carbonic anhydrase activity in mouse liver cells. Histochemie 19, 255–261 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Animals were collected and prepared at the Station biologique d'Arcachon and the Laboratoire Arago, Banyuls-sur-Mer (France). This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schipp, R., von Boletzky, S. & Doell, G. Ultrastructural and cytochemical investigations on the renal appendages and their concrements in dibranchiate cephalopods (Mollusea, Cephalopoda). Z. Morph. Tiere 81, 279–304 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298489
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298489