Summary
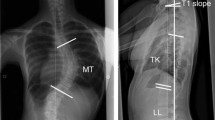
The rotation and structural changes of the apex vertebra in the horizontal plane as well as of the thoracic cage deformity were quantified by measurements on computed tomography (CT) scans from patients with right convex thoracic idiopathic scoliosis (IS). The CT scans were obtained from 12 patients with moderate scoliosis (mean Cobb angle 25.8°, r 13°–30°) and from 33 with severe scoliosis (mean Cobb angle 46.2°, r 35°–71°). In addition, CT scans of thoracic vertebrae from 15 patients without scoliosis were used as reference material. Ten of the scoliotic cases had had Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation (CDI) and posterior fusion and had entered a longitudinal study on the effect of operative correction on the re-modelling of the apical vertebra. An increasingly asymmetrical vertebral body, transverse process angle, pedicle width and canal width were found in the groups with scoliosis as compared with the reference material. Vertebral rotation and rib hump index were significantly larger in patients with early and advanced scoliosis than in normal subjects. The modelling angle of the vertebral body, the transverse process angle index and the vertebral rotation in relation to the middle axis of the thoracic cage were significantly greater in patients with severe than with moderate scoliosis. The results of this longitudinal study suggest that the structural changes of the apical vertebra regress 2 years or more after CD instrumentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaro S, Dahlborn, Svensson L (1981) Estimation of vertebral rotation and the spinal and rib cage deformity in scoliosis by computer tomography. Spine 6:460–467
Arkin AM (1949) The mechanism of structural changes in scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 31:519–527
Cobb JR (1948) Outline for the study of scoliosis. In: Edwards JW (ed) Instructional course lectures, 5. American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons Ann Arbor, pp 261–275
Cundy PJ, Paterson DC, Hillier TM, Sutherland AD, Stephen JP, Foster B (1990) Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation and vertebral rotation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 72:670–764
Deacon P, Flood BM, Dickson RA (1984) Idiopathic scoliosis in three dimensions. A radiographic and morphometric analysis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 66:509–512
Deane G, Duthie RB (1973) A new projectional look at articulated scoliotic spines. Acta Orthop Scand 44:351–365
Dickson RA, Lawton JO, Archer IA, Butt WP (1984) The pathogenesis of idopathic scoliosis: biplanar spinal asymmetry. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 66:8–15
Enneking WF, Harrington P (1969) Pathological changes in scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 51:165–184
Fabris D, Costantini S (1988) Vertebral rotation during the initial stages of scoliosis: the costovertebral interaction mechanism. Ital J Orthop Traumatol 14:59–66
Farkas A (1954) The pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 36:717–754
Frost HM (1992) Perspectives: bone's mechanical usage window. Bone Miner 19:257–271
Harrington PR (1976) Is scoliosis reversible? In vivo observations of reversible morphological changes in the production of scoliosis in mice. Clin Orthop 116:103–111
Harrington PR (1977) The etiology of idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Orthop 126:17–25
James JIP (1951) Two curve patterns in idiopathic structural scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 33:399–406
James JIP (1970) The etiology of scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 52:410–429
Karaharju EO (1967) Deformation of vertebrae in experimental scoliosis. The cause of bone adaptation and modeling in scoliosis with reference to the normal growth of the vertebra. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 105
Knutsson F (1963) Contribution to the discussion of the biological cause of idiopathic scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand 33: 98–104
Knutsson F (1966) Vertebral genesis in idiopathic scoliosis in children. Acta Radiol 4:395–402
Lloyd-Roberts GC, Pincott JR, McMeniman P, Bayley IJL, Kendall B (1978) Progression in idiopathic scoliosis. A preliminary report of a possible mechanism. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 60:451–460
Michelsson JE (1965) The development of spinal deformity in experimental scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 81
Miles M (1944) Lateral vertebral dimensions and lateral spinal curvature. Hum Biol 16:153–171
Moe JH, Winter RB, Bradford DS, Lonstein JE (1978) Scoliosis and other spinal deformities. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Perdriolle R, Vidal J (1985) Thoracic idiopathic scoliosis curve evolution and progression. Spine 10:785–791
Perdriolle R, Becchetti S, Vidal J, Lopez P (1993) Mechanical process and growth cartilages. Essential factors in the progression of scoliosis. Spine 18:343–349
Ponseti IV, Pedrini V, Wynne-Davies R, Duval-Beaupere G (1976) Pathogenesis of scoliosis. Clin Orthop 120:268–280
Risser JC (1964) Scoliosis: past and present. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 46:167–199
Roaf R (1958) Rotation movements of the spine with special reference to scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 40:312–332
Roaf R (1960) Vertebral growth and its mechanical control. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 42:40–59
Roaf R (1966) The basic anatomy of scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 48:786–792
Smith RM, Pool RD, Butt WP, Dickson RA (1991) The transverse plane deformity of structural scoliosis. Spine 16:1126–1129
Somerville EW (1952) Rotational lordosis: the development of the single curve. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 34:421–427
Taylor JR (1983) Scoliosis and growth. Patterns of asymmetry in normal vertebral growth. Acta Orthop Scand 54:596–602
Thulbourme T, Gillespie R (1976) The rib hump in idiopatiic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 58:64–71
Willers U, Hedlund R, Aaro S (1993) Mid-term effects of Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation on the configuration of the spine and the thoracic cage in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 2:99–103
Xiong B, Sevastik J, Hedlund R, Sevastik B (1994) Radiographic changes at coronal plane in early scoliosis. Spine 19:159–164
Xiong B, Sevastik J, Hedlund R, Sevastik B (1994) Sagittal configuration of the spine and growth of the posterior elements in early scoliosis. J Orthop Res (in press)
Xiong B, Sevastik B, Sevastik J, Hedlund R, Suliman I, Kristjansson S (1994) Horizontal plane morphometry of normal and scoliotic vertebra. A methodological study. Eur Spine J 4:6–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, B., Sevastik, B., Willers, U. et al. Structural vertebral changes in the horizontal plane in idiopathic scoliosis and the long-term corrective effect of spine instrumentation. Eur Spine J 4, 11–14 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298411
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298411