Abstract
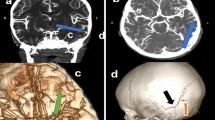
Traumatic intracavernous aneurysms are a distinctly uncommon lesion in children. They usually present with compressive symptoms of the III, IV, V, or VI cranial nerves rather than epistaxis. Epistaxis is rare and usually minor and brief in duration. A child with severe head injury and basal skull fracture, who did not have any preceding symptoms or signs of ophthalmoplegia or exophthalmus, developed massive epistaxis as a leading symptom of the ruptured intracavernous aneurysm. Since there are no reported pediatric cases with fatal epistaxis as a presenting sign, we would like to share our experience.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta C, Williams PE Jr, Clark K (1972) Traumatic aneurysm of the cerebral vessels. J Neurosurg 36:531–536
Araki C, Handa H, Handa J, Yoshida K (1962) Traumatic aneurysm of the intracranial extradural portion of the internal carotid artery: report of a case. J Neurosurg 23:64–67
Asari S, Nakamura S, Yamada O, Beck H, Sugatani H, Higashi T (1977) Traumatic aneurysm of peripheral cerebral arteries: report of two cases. J Neurosurg 46:795–803
Barr HWK, Blackwood W, Meadows SP (1971) Intracavernous carotid aneurysms: a clinical pathological report. Brain 94:607–622
Benoit BG, Wortzman G (1973) Traumatic cerebral aneurysms: clinical features and natural history. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 36:127–138
Berenstein A, Ransohoff J, Kupersmith M (1982) Transvascular treatment of giant aneurysms of the cavernous carotid and vertebral arteries. Functional investigation and embolization. Surg Neurol 21:3–12
Brihaye J, Mage J, Verhiest G (1954) Aneurysms traumatique de la carotide interne dans sa portion supaclinicoidienne. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg 54:411–438
Burton C, Velasco F, Dorman J (1968) Traumatic aneurysm of a peripheral cerebral artery: review and case report. J Neurosurg 28:468–474
Busty DR, Siemmons DH, Miller TE Jr (1968) Fatal epistaxis via carotid aneurysm and eustachian tube. Arch Otolaryngol 87:295–298
Chadduck WM (1969) Traumatic cerebral aneurysm due to speargun injury: case report. J Neurosurg 31:77–79
Chambers EF, Rosenblum AE, Norman D, Newton TH (1981) Traumatic aneurysms of cavernous internal carotid artery with secondary epistaxis. AJNR 2:405–409
Clifton GL, Haden HT, Taylor JR, Sobel M (1988) Cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity after carotid artery occlusion. J Neurosurg 69:24–28
Day AL, Rhoton AL Jr (1982) Aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulae of the intracavernous carotid artery and its branches. In: Youmans JR (ed) Neurological surgery, vol 3, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1764–1785
Debrun G, Fox A, Drake C (1981) Giant unclipped aneurysms: treatment with detachable balloons. AJNR 2:167–173
Dolenc V (1983) Direct microsurgical repair of intracavernous vascular lesions. J Neurosurg 58:824–831
Drake CG (1979) Giant intracranial aneurysms: experience with surgical treatment in 174 patients. Clin Neurosurg 26: 12–95
Eichler LA, Story JL, Bennett DE, Gulo MV (1969) Traumatic aneurysms of a cerebral artery: case report. J Neurosurg 31: 72–76
Fox AJ, Vinuela F, Pelz DM, Peerless SJ, Ferguson GC, Drake CG, Debrun G (1987) Use of detachable balloons for proximal artery occlusion in the treatment of unclippable cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 66:40–46
Gelber BR, Sundt TM Jr (1980) Treatment of intracavernous and giant carotid aneurysms by combined internal carotid ligation and extra- to intracranial bypass. J Neurosurg 52:1–10
Hahn YS, McLone DG (1987) Traumatic bilateral ophthalmic artery aneurysms: a case report. Neurosurgery 21:86–89
Hammon WM (1971) Analysis of 2187 consecutive penetrating wounds of the brain from Viet Nam. J Neurosurg 34:127–131
Handa J, Handa H (1976) Severe epistaxis caused by traumatic aneurysm of cavernous carotid artery. Surg Neurol 5:241–243
Handa J, Shimizu Y, Matsuda M, Handa H (1970) Traumatic aneurysm of the middle cerebral artery. AJR 109:119–127
Handa J, Shimizu Y, Sato K, Iwayama K (1970) Traumatic aneurysm and arteriovenous fistula of the middle meningeal artery. Clin Radiol 21:39–41
Hodes J, Fletcher WA, Goodman DF, Hoyt WF (1988) Rupture of cavernous carotid artery aneurysm causing subdural hematoma and death. J Neurosurg 69:617–619
Hornibrook J, Rhode JC (1981) Fatal epistaxis from an aneurysm of the intracranial internal carotid artery. Aust N Z J Surg 51:39–41
Jefferson G (1938) On the saccular aneurysms of the internal carotid artery in the cavernous sinus. Br J Surg 26:267–302
Laurent JP, Cheek WR, Mims T, McCluggage CW (1981) Traumatic intracranial aneurysm in an infant: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 9:303–306
Liu MY, Shih CJ, Wang YC, Tsai SH (1985) Traumatic intracavernous carotid aneurysm with massive epistaxis. Neurosurgery 17:569–573
Locksley HB (1966) Report on the cooperative study of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage, sect V, part 1: Natural history of subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracranial aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. Based on 6368 cases in the cooperative study. J Neurosurg 25:219–239
Markwalkder TM, Meienberg O (1983) Acute painful cavernous sinus syndrome in unruptured intracavernous aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Possible pathogenic mechanisms. J Clin Neuro Ophthalmol 3:31–35
Martinez SN, Bertrand C, Thierry A (1966) Les faux aneurysmes posttraumatiques. Can J Surg 9:397–402
Maurer JJ, Mills M, German WJ (1961) Triad of unilateral blindness, orbital fractures and massive epistaxis after head injury. J Neurosurg 18:837–840
Meadows SP (1959) Intracavernous aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Their clinical features and natural history. Arch Ophthalmol 62:566–574
Overton MC III, Calvin TH Jr (1966) Iatrogenic cerebral cortical aneurysm: case report. J Neurosurg 24:672–675
Parkinson D, West M (1980) Traumatic intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 52:11–20
Seftel DM, Kolson H, Gordon BS (1959) Ruptured intracranial carotid artery aneurysm with fatal epistaxis. Arch Otolaryngol 70:52–60
Serbinenko FA (1974) Balloon catheterization and occlusion of major cerebral vessels. J Neurosurg 41:125–145
Shallat RF, Taekman MS, Nagle RC (1981) Delayed complications of craniocerebral trauma: case report. Neurosurgery 8:569–573
Simpson RK Jr, Harper RL, Bryan RN (1988) Emergency balloon occlusion for massive epistaxis due to traumatic carotid-cavernous aneurysm: case report. J Neurosurg 68:142–144
Taylor PE (1961) Delayed postoperative hemorrhage from intracranial aneurysm after craniotomy for tumor. Neurology (NY) 11:225–231
Wang AN, Winfield JA, Gucer G (1986) Traumatic internal carotid artery aneurysm with rupture in the sphenoid sinus. Surg Neurol 25:77–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hahn, Y.S., Welling, B., Reichman, O.H. et al. Traumatic intracavernous aneurysm in children: massive epistaxis without ophthalmic signs. Child's Nerv Syst 6, 360–364 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298285
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298285