Abstract
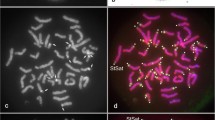
The longitudinal differentiation of metaphase chromosomes of the Indian muntjac was studied by digestion with restriction enzymes, in situ hybridization with cloned DNA probes and distamycin A plus DAPI (4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) fluorescence staining. The centromeric regions of chromosomes 3 and 3 + X of a male Indian muntjac cell line were distinct from each other and different from those of other chromosomes. Digestion with a combination of EcoRI* and Sau3A revealed a pattern corresponding to that of C-banding. Digestion with AluI, EcoRII or RsaI yielded a band specific to the centromeric region only in chromosomes 3 and 3 + X. Furthermore, HinfI digestion yielded only a band at the centromeric region of chromosome 3, whereas DA-DAPI staining revealed a single band limited to the extreme end of the C-band heterochromatin of the short arm of 3 + X. These results suggest that centromeres of Indian muntjac chromosomes contain at least four different types of repetitive DNA. Such diversity in heterochromatin was also confirmed by in situ hybridization using specific DNA probes isolated and cloned from highly repetitive DNA families. Heterozygosity between chromosome homologs was revealed by restriction enzyme banding. Evidence is presented for the presence of nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) on the long arm of chromosome 1 as well as on the secondary constrictions of 3 and 3 + X.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DA :
-
distamycin A
- DAPI :
-
4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- NOR(s) :
-
nucleolus organizer region(s)
- PBS :
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PI :
-
propidium iodide
References
Adams JC (1981) Heavy metal intensification of DAB-based HRP reaction product. J Histochem Cytochem 29:775
Blin N, Stafford DW (1976) A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 3:2303–2308
Bogenberger J, Schnell H, Fittler F (1982) Characterization of X-chromosome specific satellite DNA of Muntiacus muntjak vaginalis. Chromosoma 87:9–20
Brat SV, Verma RS, Dosik H (1979) Structural organization of chromosomes of the indian muntjac (Muntiacus muntjak). Cytogenet Cell Genet 24:201–208
Brinkley BR, Valdivia MM, Tousson A, Brenner SL (1984) Compound kinetochores of the Indian muntjac. Chromosoma 91:1–11
Carrano AV, Wolff S (1975) Distribution of sister chromatid exchanges in the euchromatin and heterochromatin of the Indian muntjac. Chromosoma 53:361–369
Comings DE (1971) Heterochromatin of the Indian muntjac. Exp Cell Res 67:441–460
Comings DE, Okada TA (1971) Fine structure of kinetochore in Indian muntjac. Exp Cell Res 67:97–110
Goodpasture C, Bloom SE (1975) Visualization of nucleolar organizer regions in mammalian chromosomes using silver staining. Chromosoma 53:37–50
Green RJ, Bahr GF (1975) Comparison of G-, Q-, and EM-banding patterns exhibited by the chromosome complement of the Indian muntjac, Muntiacus muntjak, with reference to nuclear DNA content and chromatin ultrastructure. Chromosoma 50:53–67
Hsu TC, Arrighi FE (1971) Distribution of constitutive heterochromatin in mammalian chromosomes. Chromosoma 34:243–245
Kato H, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida TH (1974) Constitutive heterochromatin of Indian muntjac chromosomes revealed by DNase treatment and a C-banding technique. Can J Genet Cytol 16:273–280
Kimura S, Yamazaki K, Kato Y (1980) Kinetics of DNA replication in the Indian muntjac chromosomes as studied by quantitative autoradiography. Chromosoma 77:309–323
Lima-de-Faria A, Isaksson M, Olsson E (1980) Action of restriction endonucleases on the DNA and chromosomes of Muntiacus muntjak. Hereditas 92:267–273
Liming S, Yingying Y, Xingsheng (1980) Comparative cytogenetic studies on the red muntjac, Chinese muntjac, and their F1 hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet 26:22–27
Mainguy PNR, Heddle JA, Brunette DM (1975) A reliable method of quantifying G-band position in chromosomes. Chromosoma 50:301–312
Manuelidis L, Langer-Safer PR, Ward DC (1982) High resolution mapping of satellite DNA using biotin-labeled DNA probes. J Cell Biol 95:619–625
Mezzanotte R, Bianchi R, Vanni R, Ferrucci L (1983) Chromatin organization and restriction endonuclease activity on human metaphase chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 36:562–566
Miller DA, Choi YC, Miller OJ (1983) Chromosome localization of highly repetitive Human DNA's and amplified ribosomal DNA with restriction enzymes. Science 219:395–397
Pardue ML, Hsu TC (1975) Locations of 18S and 28S ribosomal genes on the chromosomes of the Indian muntjac. J Cell Biol 64:251–254
Polisky B, Greene P, Garfin DE, McCarthy BJ, Goodman HM, Boyer HW (1975) Specificity of substrate recognition by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:3310–3314
Schmid M (1982) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VII. Analysis of the structure and variability of NORs in Anura. Chromosoma 87:327–344
Schweizer D (1976) Reverse fluorescent chromosome banding with chromomycin and DAPI. Chromosoma 58:307–324
Schweizer D (1980) Simultaneous fluorescent staining of R bands and specific heterochromatic regions (DA-DAPI bands) in human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 27:190–193
Schweizer D (1981) Counterstain-enhanced chromosome banding. Hum Genet 57:1–14
Schweizer D, Mendelak M, White MJD, Contreras N (1983) Cytogenetics of the parthenogenetic grasshopper Warramaba vigro and its bisexual relatives X. Patterns of fluorescent banding. Chromosoma 88:227–236
Sharma T, Dhaliwal MK (1974) Relationship between patterns of late S DNA synthesis and C-and G-banding in muntjac chromosomes. Exp Cell Res 87:394–397
Ueda T, Irie S, Nishikawa T, Yamazaki K, Kato Y (1983) Specific banding of chromosomes with fluorescent dyes and restriction endonucleases. Dev Growth Differ 25:424
Wurster DH, Benirschke K (1970) Indian muntjac, Muntiacus muntjak: a deer with a low diploid chromosome number. Science 168:1364–1366
Yu LC, Lowensteiner D, Wong EFK, Sawada I, Mazrimas J, Schmid C (1986) Localization and characterization of recombinant DNA clones derived from the highly repetitive DNA sequences in the Indian muntjac cells: Their presence in the Chinese muntjac. Chromosoma 93:521–528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, T., Irie, S. & Kato, Y. Longitudinal differentiation of metaphase chromosomes of Indian muntjac as studied by restriction enzyme digestion, in situ hybridization with cloned DNA probes and distamycin A plus DAPI fluorescence staining. Chromosoma 95, 251–257 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294781
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294781