Abstract
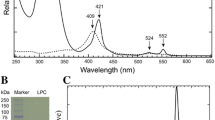
The complete amino acid sequence of cytochrome c-552 derived from the chemoautotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea was determined. The cytochrome consisted of 81 amino acid residues, and its molecular weight was calculated to be 9098 including heme c. Although the sequence of cytochrome c-552 was highly homologous to those of cytochromes c-551, which were known as the electron-donating components to dissimilatory nitrite reductase in pseudomonads, cytochrome c-552 differed from cytochrome c-551 in two points: (1) the sequence of cytochrome c-552 was shorter by two amino acid residues than that of cytochrome c-551 at the N-terminus and (2) one amino acid insertion was present in cytochrome c-552.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Ambler RP (1963) The amino acid sequence of Pseudomonas cytochrome c-551. Biochem J 89:349–378
Ambler RP (1980) In: Robinson AB, Kaplan NO, eds. From cyclotrons to cytochromes. London/New York: Academic Press, pp. 263–279
Ambler RP, Wynn M (1973) Amino acid sequences of cytochromes c-551 from three species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J 131:485–498
Arciero DM, Peng Q, Peterson J, Hooper AB (1994) Identification of axial ligands of cytochrome c-552 from Nitrosomonas europaea. FEBS Lett 342:217–220
Crestfield AM, Moore S, Stein WH (1963) The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem 238:622–627
Dickerson RE (1980) Cytochrome c and the evolution of energy metabolism. Sci Am 242:98–110
Fontana A, Veronese FM, Boccu E (1973) Reaction of sulfenyl halides with cytochrome c. A novel method for heme cleavage. FEBS Lett 32:135–138
Hooper AB, Nason A (1965) Characterization of hydroxylamine-cytochrome c reductase from the chemoautotrophs Nitrosomonas europaea and Nitrosocystis oceanus. J Biol Chem 240:4044–4057
Hooper AB, Maxwell PC, Terry KR (1978) Hydroxylamine oxidoreductase from Nitrosomonas: absorption spectra and content of heme and metal. Biochemistry 17:2984–2989
Korszun ZR, Salemme FR (1977) Structure of cytochrome c-555 of Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum: primitive low-potential cytochrome c. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5244–5247
Matsuura Y, Takano T, Dickerson RE (1982) Structure of cytochrome c-551 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa refined at 1.6 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 156:389–409
McTavish H, Fuchs JA, Hooper AB (1993) Sequence of the gene coding for ammonia monooxygenase in Nitrosomonas europaea. J Bacteriol 175:2436–2444
Mikami T, Tanaka N, Sato T, Moriyama H, Numata M, Fujiwara T, Fukumori Y, Yamanaka T, Sato M, Kakiuchi K, Katsube Y, Kishimoto S (1991) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray studies of hydroxylamine oxidoreductase from Nitrosomonas europaea. J Biochem 110:681–682
Miller DJ, Nicholas DJD (1986) N-Terminal amino acid sequence of cytochrome c-552 from Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochemistry Int. 12:167–172
Sayavedra-Soto LA, Hommes NG, Arp DJ (1994) Characterization of the gene encoding hydroxylamine oxidoreductase in Nitrosomonas europaea. J Bacteriol 176:504–510
Speckman SH, Stein WH, Moore S (1958) Automatic recording apparatus for use in the chromatography of amino acids. Anal Chem 30:1190–1206
Tsang DCY, Suzuki I (1982) Cytochrome c-554 as a possible electron donor in the hydroxylation of ammonia and carbon monoxide in Nitrosomonas europaea. Can J Biochem 60:1018–1024
Van Beeumen J, Ambler RP, Meyer TE, Kamen MD, Olson JM, Shaw EK (1976) The amino acid sequences of the cytochromes c-555 from two green sulfur bacteria of the genus Chlorobium. Biochem J 159:757–774
Wood PM (1987) In: Prosser JI, ed. Nitrification. Oxford: IRL Press, pp 39–62
Yamanaka T (1975) A comparative study on the redox reactions of cytochromes c with certain enzymes. J Biochem 77:493–499
Yamanaka T, Fukumori Y (1981) Functional and structural comparisons between prokaryotic and eukaryotic aa 3-type cytochrome c oxidases from an evolutionary point of view. Plant Cell Physiol 22:1223–1230
Yamanaka T, Fukumori Y (1989) In: Hattori T. et al., eds. Recent advances in microbial ecology. Tokyo: Japan Scientific Societies Press, pp 209–213
Yamanaka T, Shinra M (1974) Cytochrome c-552 and cytochrome c-554 derived from Nitrosomonas europaea: purification, properties, and their function in hydroxylamine oxidation. J Biochem 75:1265–1273
Yamazaki T, Fukumori Y, Yamanaka T (1985a) Cytochrome a 1of Nitrosomonas europaea resembles aa 3-type cytochrome c oxidase in many respects. Biochim Biophys Acta 810:174–183
Yamazaki T, Fukumori Y, Yamanaka T (1985b) Catalytic properties of cytochrome c oxidase purified from Nitrosomonas europaea. J Biochem 103:499–503
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, T., Yamanaka, T. & Fukumori, Y. The amino acid sequence of Nitrosomonas europaea cytochrome c-552. Current Microbiology 31, 1–4 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294624
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294624