Abstract
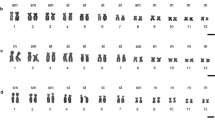
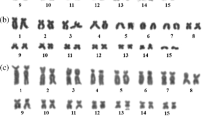
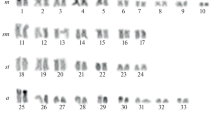
Specimens of the endemic New Zealand frog Leiopelma hochstetteri from Tapu on North Island were found to have six, nine or ten supernumerary chromosomes in their karyotypes. In comparison with previously published data, these results further indicate probable geographic variation in supernumerary chromosome number between populations. Increased numbers of supernumeraries in these frogs is correlated with apparent decrease of centromeric heterochromatin in the five large metacentric chromosomes of the karyotype, as detected by C-banding. Meiosis was abnormal in a male with a high number of supernumeraries. In lampbrush preparations from a single female with one supernumerary univalent, the supernumerary often had a denser, beaded appearance in comparison with the regular bivalents. Evidence is consistent with the notion that these supernumerary chromosomes may have arisen from centromeric fragments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baverstock PR, Watts CHS, Hogarth JT (1976) Heterochromatin variation in the Australian rodent Uromys caudimaculatus. Chromosoma 57:397–403
Bell BD (1982) The amphibian fauna of New Zealand. In: Newman DG (ed) New Zealand herpetology. New Zealand Wildlife Service, Wellington, pp 27–89
Bell BD (1986) The conservation status of New Zealand wildlife. Occ Publ N-Z Wildlife Serv 12:1–103
Bogart JP (1981) Chromosome studies in Sminthillus from Cuba and Eleutherodactylus from Cuba and Puerto Rico (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Life Sci Contrib R Ontario Museum 129:1–22
Dev VG, Miller DA, Tantravani RR, Schreck RR, Roderick TH, Erlanger BF, Miller OJ (1976) Chromosome markers in Mus musculus: differences in C-banding between the subspecies M. m. musculus and M. m. molossinus. Chromosoma 53:335–344
Duellman WE, Trueb L (1986) The biology of amphibians. McGraw-Hill Book Co. New York, p 670
Green DM (1985) Differentiation in amount of centromeric heterochromatin between subspecies of the red-legged frog, Rana aurora. Copeia 1985:1071–1074
Green DM, Bogart JP, Anthony EH, Genner DL (1980) An interactive, microcomputer based karyotype analysis system for phylogenetic cytotaxonomy. Comput Biol Med 10:219–227
Green DM, Kezer J, Nussbaum RA (1984a) Triploidy in Hochstetter's frog Leiopelma hochstetteri from New Zealand. NZ J Zool 11:457–461
Green DM, Myers PZ, Reyna DL (1984b) CHROMPAC III: an improved package for micro-computer assisted analysis of karyotypes. J Hered 75:143
Harvey AW, Hewitt GM (1979) B-chromosomes slow development in a grasshopper. Heredity 42:397–401
Jones RN, Rees H (1982) B-Chromosomes. Academic Press, New York, p 266
Kezer J, Sessions SK (1979) Chromosome variation in the plethodontid salamander Aneides ferreus. Chromosoma 71:65–80
Kezer J, Léon PE, Sessions SK (1980) Structural differentiation of the meiotic and mitotic chromosomes of the salamander Ambystoma macrodactylum. Chromosoma 81:177–197
King M (1980) C-banding studies on Australian hylid frogs: Secondary constriction structure and the concept of euchromatin transformation. Chromosoma 80:191–217
Levan A, Fredga D, Sandberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220
Morescalchi A (1967) The karyotype of two specimens of Leiopelma hochstetteri Fitz. (Amphibia Salientia). Caryologia 21:37–46
Morescalchi A (1973) Amphibia. In: Chiarelli A, Capanna E (eds) Cytotaxonomy and vertebrate evolution. Academic Press, New York, pp 233–283
Patton JL (1977) B-chromosome systems in the pocket mouse, Perognathus baileyi: Meiosis and C-band studies. Chromosoma 60:1–14
Parker JS, Ainsworth CC, Taylor S (1981) The B-chromosome system of Hypochoeris maculata II. B-effects on meiotic Achromosome behaviour. Chromosoma 67:123–143
Schmid M (1978) Chromosome banding in amphibia I. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organizer regions in Bufo and Hyla. Chromosoma 66:361–388
Schmid M (1983) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VII. Analysis of the structure and variability of NORs in Anura. Chromosoma 87:327–344
Sessions SK (1984) Cytogenetics and evolution in salamanders. Ph.D. dissertation. University of California, Berkeley
Stephenson EM, Robinson ES, Stephenson NG (1972) Karyotype variation within the genus Leiopelma (Amphibia: Anura). Can J Genet Cytol 14:691–702
Stephenson EM, Robinson ES, Stephenson NG (1974) Inter-specific relationships of Leiopelma (Amphibia: Anura). Further karyological evidence: Experientia 30:1248–1250
Yosida TH, Sagai T (1975) Variation of C-bands in the chromosomes of several subspecies of Rattus rattus. Chromosoma 50:283–300
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Green, D.M., Kezer, J. & Nussbaum, R.A. Supernumerary chromosome variation and heterochromatin distribution in the endemic New Zealand frog Leiopelma hochstetteri . Chromosoma 95, 339–344 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293180
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293180