Summary
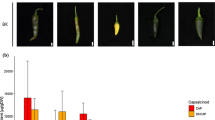
30000 transgenic petunia plants carrying a single copy of the maize A1 gene, encoding a dihydroflavonol reductase, which confers a salmon red flower colour phenotype on the petunia plant, were grown in a field test. During the growing season plants with flowers deviating from this salmon red colour, such as those showing white or variegated phenotypes and plants with flowers exhibiting only weak pigmentation were observed with varying frequencies. While four white flowering plants were shown at the molecular level to be mutants in which part of the A1 gene had been deleted, other white flowering plants, as well as 13 representative plants tested out of a total of 57 variegated individuals were not mutants but rather showed hypermethylation of the 35S promoter directing A1 gene expression. This was in contrast to the homogeneous fully red flowering plants in which no methylation of the 35S promoter was observed. While blossoms on plants flowering early in the season were predominantly red, later flowers on the same plants showed weaker coloration. Once again the reduction of the A1-specific phenotype correlated with the methylation of the 35S promoter. This variation in coloration seems to be dependent not only on exogenous but also on endogenous factors such as the age of the parental plant from which the seed was derived or the time at which crosses were made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broillard R (1983) The in vivo expression of anthocyanin colour in plants. Phytochemistry 22:1311–1323
During HP (1989) Tagging genes with maize transposable elements. An overview. Maydica 34:73–88
Federoff NV (1983) Comparison of host strains for cloning maize DNA into bacteriophage Lambda. Plant Mol Biol 1:27–29
Federoff NV, Banks JA (1988) Is the Suppressor-Mutator element controlled by a basic developmental mechanism? Genetics 120:559–570
Frischauf AM, Lehrach H, Poutska A, Murray N (1983) Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol 170:827–842
Linn F, Heidmann I, Saedler H, Meyer P (1990) Epigenetic changes in the expression of the maize A1 gene in petunia: Role of numbers of integrated gene copies and state of methylation. Mol Gen Genet 222:329–336
Maddaloni M, Bossinger G, Di Fonzo N, Motto M, Salamini F, Bianchi A (1990) Unstable alleles of the glossy-1 locus of maize show a light-dependent variation in the pattern of somatic reversion. Maydica 35:409–420
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning; A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Martienssen R, Barkan A, Taylor WC, Freeling M (1990) Somatically heritable switches in the DNA modification of Mu transposable elements monitored with a suppressible mutant in maize. Genes Dev 4:331
Meyer P, Walgenbach E, Bussmann K, Hombrecher G, Saedler H (1985) Synchronized tobacco protoplasts are efficiently transformed by DNA. Mol Gen Genet 201:513–518
Meyer P, Heidman I, Forkmann G, Saedler H (1987) A new petunia flower colour generated by transformation of a mutant with a maize gene. Nature 330:667–678
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Schwarz-Sommer Z, Shephard N, Tacke E, Gierl A, Rohde W, Leclercq L, Mattes M, Berndgen RT, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1987) Influence of transposable elements on the structure and function of the A1 gene of Zea mays. EMBO J 6:287–294
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Schell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, P., Linn, F., Heidmann, I. et al. Endogenous and environmental factors influence 35S promoter methylation of a maize A1 gene construct in transgenic petunia and its colour phenotype. Molec. Gen. Genet. 231, 345–352 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292701
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292701