Summary
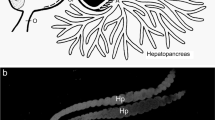
Two species of Antarctic acanthonotozomatid amphipods (Echiniphimedia hodgsoni and Maxilliphimedia longipes) have been investigated in regard to their food preference. Examinations of food remains in foreguts and midguts indicate that Echiniphimedia hodgsoni feeds on sponges and Maxilliphimedia longipes ingests Cnidaria. These foregut analyses are supported by a study of the functional morphology of the mouthparts. The structure of the mandibles in particular can be interpreted as an adaptation to the presumed food source. The right mandible of Echiniphimedia hodgsoni bears a lacinia mobilis which works as an additional cutting edge. By means of this cutting mechanism Echiniphimedia hodgsoni should be able to bite out tough sponge material. The mandibular endites of Maxilliphimedia longipes are medially excavated, the incisors are regulary toothed and the molars vestigial. Such kinds of mandibles are adapted to cut large fragments of soft food, i.e. the mucous tissue of Cnidaria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres HG (1985) Die Gammaridea (Crustacea: Amphipoda) der Deutschen Antarktis-Expeditionen 1975/76 und 1977/78. 4. Acanthonotozomatidae, Paramphithoidae und Stegocephalidae. Mitt Hamb Zool Mus Inst 82:119–153
Ansell AD (1969) Association of the amphipod Acidostoma neglectum Dahl with the anthozoan Peachia hastata Gosse. J Nat Hist 3:345–347
Arnaud PM (1970) Frequency and ecological significance of necrophagy among the benthic species of Antarctic coastal waters. In: Holdgate MV (ed) Antarctic ecology, vol 1. Academic Press, London New York, pp 256–267
Arnaud PM (1977) Adaptations within the Antarctic marine ecosystem. In: Llano GA (ed) Adaptations within Antarctic ecosystems. Proc 3rd SCAR Symp Antarct Biol; Houston, pp 135–158
Arndt W (1933) Die biologischen Beziehungen zwischen Schwämmen und Krebsen. Mitt Zool Mus Berl 19:221–325
Barnard JL (1969) The families and genera of marine gammaridean Amphipoda. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington DC, pp 1–535
Barnard KH (1932) Amphipoda. Discovery Rep 5:1–326
Bone DG (1972) Aspects of the biology of the Antarctic amphipod Bovallia gigantea Pfeffer at Signy Island, South Orkney Islands. Br Antarct Surv Bull 27:105–122
Bregazzi PK (1972) Life cycles and seasonal movements of Cheirimedon femoratus (Pfeffer) and Tryphosella kergueleni (Miers). Br Antarct Surv Bull 30:1–34
Bregazzi PK (1973) Locomotor activity rhythms in Tryphosella kergueleni (Miers) and Cheirimedon femoratus (Pfeffer). Br Antarct Surv Bull 33/34:17–32
Burton M (1932) Sponges. Discovery Rep 6:237–293
Dahl E (1979) Deep-sea carrion feeding amphipods: evolutionary patterns in niche adaptation. Oikos 33:167–175
Dayton PK, Robilliard GA, Paine RT, Dayton LB (1974) Biological accomodation in the benthic community at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Ecol Monogr 44:105–128
Just J (1978) Taxonomy, biology and evolution of the circumarctic genus Acanthonotozoma (Amphipoda) with notes on Panoploeopsis. Acta Arct 20:1–140
Knox GA, Lowry JK (1977) A comparison between the benthos of the Southern Ocean and the North Polar Ocean with special reference to the Amphipoda and the Polychaeta. In: Dunbar MJ (ed) Polar Oceans. Montreal, pp 423–462
Lowry JK, Bullock S (1976) Catalogue of the marine gammaridean Amphipoda of the Southern Ocean. Bull R Soc NZ 16:1–187
Moore PG, Rainbow PS (1984) Ferritin crystals in the gut caeca of Stegocephaloides christianiensis Boeck and other Stegocephalidae (Amphipoda: Gammaridea): A functional interpretation. Philos Trans R Soc London, Ser B 306:219–245
Oshel PE, Steele DH (1985) Amphipod Paramphithoe hystrix: a micropredator on the sponge Haliclona ventilabrum. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 23:307–309
Rakusa-Suszczewski S (1972) The biology of Paramoera walkeri (Stebbing) (Amphipoda) and the Antarctic sub-fast ice community. Pol Arch Hydrobiol 19:11–36
Richardson MG, Whitaker TM (1979) An Antarctic fast-ice food chain, observations on interactions of the amphipod Pontogeneia antarctica Chevreux with ice-associated microalgae. Br Antarct Surv Bull 47:107–115
Salvini-Plawen L von (1972) Cnidaria as food-sources for marine invertebrates. Cah Biol Mar 13:385–400
Stockton WL (1982) Scavenging amphipods. Deep-Sea Res 29:819–836
Vader W (1983) Associations between amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda) and sea anemones (Anthozoa, Actiniaria). Mem Aust Mus 18:141–153
Werner B (1984) Stamm Cnidaria, Nesseltiere. In: Gruner HE (ed) Lehrbuch der Speziellen Zoologie, Band 1. Wirbellose Tiere, 2. Teil. Fischer Stuttgart New York, pp 1–305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coleman, C.O. On the nutrition of two Antarctic acanthonotozomatidae (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Polar Biol 9, 287–294 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00287425
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00287425