Summary
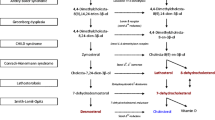
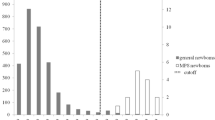
Hexosaminidase (Hex) A, B, and C/S were electrophoretically separated from cultured amniotic fluid cells, fetal brain, and white blood cells. Photographs of cellulose acetate zymograms were evaluated by reflectometric scanning. The usefulness and limitations of this rapid method were shown. Hex A was completely absent in the amniotic fluid cells of one out of three pregnancies at risk for Tay-Sachs disease, but Hex C/S was present in this case. The prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease was made, and confirmed with the fetal material after abortion. Hex C/S was distinguishable from a residual or “heterozygous” Hex A activity. In the two other risk pregnancies, reflectometric Hex A activities were found to be 50 and 34% of control; the heterozygous stage was presumed for the fetuses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besley GTN, Broadhead DM (1976) Studies on human N-acetyl-β-D-hexosaminidase C separated from neonatal brain. Biochem J 155:205–208
Beutler E, Kuhl W, Comings D (1975) Hexosaminidase isozyme in type 0 GM2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff-Jatzkewitz disease). Am J Hum Genet 27:628–638
Beutler E, Kuhl W (1975) Subunit structure of human hexosaminidase verified: interconvertibility of hexosaminidase isozymes. Nature 258:262–264
Beutler E (1979) The biochemical genetics of the hexosaminidase system in man. Am J Hum Genet 31:95–105
Dreyfus JC, Poenaru L (1979) Prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Lancet 16:1296
Ellis RB, Ikonne JU, Patrick AD, Stephens R, Willcox P (1973) Prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Lancet 17:1144–1145
Harzer K, Wässle W, Sandhoff K, Jatzkewitz H (1968) Densitometrische Mikrobestimmung von Lipiden nach Dünnschicht-Chromatographie des Gesamtlipidextraxkts Z Anal Chem 243:527–536
Harzer K (1970) Analytische isoelektrische Fraktionierung der N-Acetyl-β-D-Hexosaminidasen. Z Anal Chem 252:170–174
Harzer K, Gußmann KI (1981) Zur Diagnostik der metachromatischen Leukodystrophie durch Arylsulfatase-A-Bestimmung im Blut. Arch Psychiatr nervenkr 229:291–304
Hooghwinkel GJM, Veltkamp WA, Overdijk B, Lisman JJW (1972) Electrophoretic separation of β-N-acetylhexosaminidases of human and bovine brain and liver and of Tay-Sachs brain tissue. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 353:839–841
Ikonne JU, Rattazzi MC, Desnick RJ (1975) Characterisation of Hex S, the major residual β-hexosaminidase activity in type 0 GM2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff-Jatzkewitz disease). Am J Hum Genet 27:639–650
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Michael CA, Hahnel R, Hockey A, Wysocki S (1974) Pitfalls in the prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Aust Paediatr J 10:23–24
Milunsky A (1973) Prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Lancet 22:1442
Minami R, Nakumura F, Oyanagi K, Nakao T (1981) Hexosaminidase C in brain affected by Tay-Sachs disease. Tohoku J Exp Med 133:175–185
O'Brien JS, Okada S, Fillerup, DL, Veath ML, Adornato B, Brenner PH, Leroy JG (1971) Tay-Sachs disease: Prenatal diagnosis. Science 172:61–64
Okada S, O'Brien JS (1969) Tay-Sachs disease: generalized absence of a β-D-N-acetylhexosaminidase component. Science 165:698–700
Penton E, Poenaru L, Dreyfus JC (1975) Hexosaminidase C in Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 391:162–169
Potier M, Boire G, Dallaire L, Melancon SB (1977) N-acetyl-β-hexosaminidase isoenzymes of amniotic fluid and maternal serum. Their relevance to prenatal diagnosis of the GM2 gangliosidoses. Clin Chim Acta 76:309–315
Saifer A, Schneck L, Perle G, Valenti C, Volk BW (1973) Caveats of antenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol 115:553–555
Sandhoff K, Andrease U, Jatzkewitz H (1968) Deficient hexosaminidase activity in an exceptional case of Tay-Sachs disease with additional storage of kidney globoside in visceral organs. Life Sci 7:278–285
Swallow DM, Evans L, Saha N, Harris H (1976) Characterization and tissue distribution of N-acetyl-hexosaminidase C: suggestive evidence for a separate hexosaminidase locus. Ann Hum Genet 40:55–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kustermann-Kuhn, B., Harzer, K. Prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Reflectometry of hexosaminidase A, B, and C/S bands on zymograms. Hum Genet 65, 172–175 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286657
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286657