Abstract
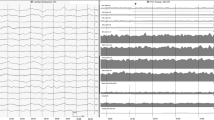
EEG and CT scans of 280 cases of minor head injury in children under 15 years of age were studied. Abnormality on initial EEG was shown in 42.5%. Those who lost consciousness had a higher incidence of abnormality than those who did not, and it was higher between 4 and 13 years of age. The sleep state has much influence on the finding. The patients should be awake or in a light sleep stage. The most frequent abnormality was slow waves, seen predominantly in the occipital regions, and which tended to disappear more easily than the paroxysmal ones. The EEGs became or remained normal in 95%, excluding incompletely followed-up cases. There was no case of post-traumatic epilepsy in our series, but 4 cases of post-traumatic early convulsions, in which the EEGs were variable. CT scan disclosed abnormality in 6%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH, Mitchell DF, Graham DI, Doyle D (1977) Diffuse brain damage of immediate impact type. Brain 100:489–502
Aird RB, Gastaut Y (1959) Occipital and posteriorelectroence-phalographic rhythms. EEG Clin Neurophysiol 11:637–656
Dawson RE, Webster JE, Gurdjian ES (1951) Serial electroencephalography in acute head injuries. J Neurosurg 8:613–630
Denny-Brown D, Russell WR (1941) Experimental cerebral concussion. Brain 64:93–165
Dollinskas CA, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1978) A sign of subarachnoid bleeding on cranial computed tomograms of pediatric head trauma patients. Radiology 126:409–411
Dow RS, Ulett G, Tunturi A (1945) Electroencephalographic changes following head injuries in dogs. J Neurophysiol 8:161–172
Fukushima Y, Kawaguchi S, Ohsawa T, Onuma T (1973) A study of EEG abnormality in normal children. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn 27:106–115
Gennarelli TA, Thibault LE, Adams JH, Graham DI, Thompson CJ, Marcincin RP (1982) Diffuse axonal injury and traumatic coma in the primate. Ann Neurol 12:564–574
Groat RA, Windle WE, Magoun HW (1945) Functional and structural changes in the monkey's brain during and after concussion. J Neurosurg 2:26–35
Hayes RL, Pechura CM, Katayama Y, Povlishock J-T, Giebel ML (1984) Activation of pontine cholinergic sites implicated in unconsciousness following cerevral concussion in the cat. Science 223:301–303
Holbourn AHS (1943) The mechanics of head injuries. Lancet II:438–411
Landau-Ferey J, Bour F (1980) Interet pronostique de l'EEG dans les jours qui suivent certains traumatismes craniens de l'enfant et de l'adolescent. EEG Clin Neurophysiol 49:173–180
Mizrahi EM, Kellaway P (1984) Cerebral concussion in children: assessment of injury by electroencephalography. Pediatrics 73:419–425
Nevin NC (1967) Neuropathological changes in the white matter following head injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 26:77–84
Oppenheimer DR (1968) Microscopic lesions in the brain following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 31:299–306
Povlishock JT, Becker DP, Cheng LY, Vaughan GW (1983) Axonal change in minor head injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 42:225–242
Rand CW, Courville CB (1934) Histologic changes in the brain in cases of fatal injury to the head. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 31:527–555
Sekino H, Nakamura N, Yuki K, Satoh J, Kikuchi K, Sanada S (1981) Brain lesions detected by CT scans in cases if minor head injuries. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 21:677–683
Silverman D (1962) Electroencephalographic study of acute head injury in children. Neurology 12:273–281
Strich S (1956) Diffuse degeneration of the cerebral white matter in sever dementia following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 19:163–185
Strich S (1961) Shearing of nerve fibres as a cause of brain damage due to head injury. Lancet II:443–448
Sugiura M, Mori N, Yokosuka R, Yamamoto A, Imamizu H, Sugimori T, Jinbo M, Kitamura K, Kohno H (1981) Head injury in children. Neurol Surg (Tokyo) 9:697–704
Walker AE, Kollros JJ, Case TJ (1944) The physiological basis of concussion. J Neurosurg 1:103–116
Ward JW, Clark SL (1948) The electroencephalogram in experimental concussion and related conditions. J Neurophysiol 11:59–74
Wei EP, Dietrich WD, Povlishock JT, Navari RM, Kontos HA (1980) Functional, morphological, and metabolic abnormalities of the cerebral microcirculation after concussive brain injury in cats. Circ Res 46:37–47
Williams D, Denny-Brown D (1941) Cerebral electrical changes in experimental concussion. Brain 64:223–238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enomoto, T., Ono, Y., Nose, T. et al. Electroencephalography in minor head injury in children. Child's Nerv Syst 2, 72–79 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286224
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286224