Abstract
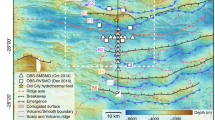
A survey across the western intersection of the mid-Atlantic ridge with Oceanographer fracture zone near 35°N shows this intersection to be different in character from its more typical eastern counterpart. At the western junction the transform valley broadens into a parallelogram shaped deep some 46 by 24 km, which extends well across the trace of the active transform. Within 30 km south of the fracture zone the median valley becomes oblique forming a NE trending ridge which is the SE edge of the deep. Magnetic mapping shows the current spreading centre to be adjacent to this ridge.
A sequence of evolution for this intersection over the past 0.7 Ma is proposed to explain the features mapped. We suggest that the oblique ridge crest trends extended across the transform trace to form the elongated graben-like deep with its associated faults and sediment slumps. Such complex patterns may occur as plate-wide changes in spreading direction become modified by localised shear stress fields at ridge crest-transform intersections, as have been observed in a number of other cases. The absence of significant tranverse ridges across from the spreading centre at this particular fracture zone intersection, may have temporarily allowed these stress patterns to propagate across the fracture zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, J. R.: 1981, ‘The Oceanographer Fracture Zone — A Magnetic Study’, Unpub. M.Sc. thesis Univ. Durham, U.K.
BonattiE. and HonnorezJ.: 1976, ‘Sections of the Earth's Crust in the Equatorial Atlantic’, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 4104–4116.
BirdP. and PhillipsJ. D.: 1975, ‘Oblique Spreading near the Oceanographer Fracture’, J. Geophys. Res. 80, 4021–4027.
ChoukrouneP., FrancheteauJ., and LePichonX.: 1978, ‘In situ Structural Observation along Transform Fault ‘A’ in the FAMOUS Area, Mid-Atlantic Ridge’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bul. 89, 1013–1029.
CraneK.: 1976, ‘The Intersection of the Siquieros Transform Fault and the East Pacific Rise’, Marine Geol. 21, 25–46.
DetrickR. S. and PurdyG. M.: 1980, ‘The Crustal Structure of the Kane Fracture Zone from Seismic Refraction Studies’, J. Geophys. Res. 85, 3759–3777.
DetrickR. S., MudieJ. D., LuyendykB. P., and MacdonaldK. C.: 1973, ‘Near-Bottom Observations of an Active Transform Fault (Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 37°N)’, Nature 246, 59–61.
FedenR. H., FlemingH. S., PerryR. K., and PhillipsJ. D.: 1975, ‘The Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 33°N: The Hayes Fracture Zone’, Earth and Planet. Sci. Letters 26, 292–298.
Fox, P. J. and Gallo, D. G.: (in press) ‘A Tectonic Model for Ridge-Transform-ridge Plate Boundaries: Implications for the Structure of Oceanic Lithosphere’, Tectonophys.
FoxP. J., LowrieA., and HeezenB. C.: 1969, ‘Oceanographer Fracture Zone’, Deep-Sea Res. 16, 59–66.
FoxP. J., SchreiberE., RowlettH., and McCamyK.: 1976, ‘The Geology of the Oceanographer Fracture Zone: A Model for Fracture Zones’, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 4117–4127.
Fox, P. J., Detrick, R. S., and Purdy, S. M.: 1980, ‘Evidence for Crustal Thinning near Fracture Zones: Implications for Ophiolites’, in A. Panayiotou (ed.), Proc. Internat. Ophiolite Symp., Cyprus. Min. Ag. and Nat. Res. Cyprus, Geol. Surv. Dept. 161–168.
LaBrecqueJ. L., KentD. V., and CandieS. C.: 1977, ‘Revised Magnetic Polarity Time-Scale for the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic’, Geology 5, 330–335.
LachenbruchA. H. and ThompsonG. A.: 1972, ‘Ocean Ridges and Transform Faults: Their Intersection Angles and Resistance to Plate Motion’, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters 15, 116–122.
LonsdaleP.: 1978, ‘Near Bottom Reconnaissance of a Fast-Slipping Transform Fault Zone at the Pacific-Nazca Plate Boundary’, J. Geology 8, 451–472.
LonsdaleP. and ShorA.: 1979, ‘The Oblique Intersection of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge with Charlie-Gibbs Transform Fault’, Tectonophys. 54, 195–209.
LoudenK. E. and ForsythD. W.: 1982, ‘Crustal Structure and Isostatic Compensation near the Kane Fracture Zone from Topography and Gravity Measurements: I Spectral Analysis Approach’, Geophys. J. Roy Astr. Soc. 68, 725–750.
MacdonaldK. C.: 1977, ‘Near-Bottom Magnetic Anomalies, Asymmetric Spreading Oblique Spreading and Tectonics of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge near Lat. 37°N’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 88, 541–555.
MacdonaldK. C. and LuyendykB.: 1977, ‘Deep-Tow Studies of the Structure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge near 37°N (FAMOUS)’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 88, 621–636.
MacdonaldK. C., KastensK., SpiessF. N., and MillerS. P.: 1979, ‘Deep-Tow Studies of the Tamayo Transform Fault’, Mar. Geophys. Res. 4, 37–70.
NelsonK. D.: 1981, ‘A Simple Thermal-Mechanical Model for Mid-Ocean Ridge Topographic Variation’, Geophys. J. Roy. Astr. Soc. 65, 19–30.
OlivetJ. L., LePichonX., MontiS., and SichlerB.: 1974, ‘Charlie-Gibbs Fracture Zone’, J. Geophys. Res. 79, 2059–2072.
OTTER: (1984), ‘The Geology of the Oceanographer Transform: The Ridge-Transform Intersection’, Mar. Geophys. Res. 6, 109–141 (this issue).
PhillipsJ. D., FlemingH. S., FedenR., KingW. E., and PerryR.: 1975, ‘Aeromagnetic Study of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge near the Oceanographer Fracture Zone’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 86, 1348–1357.
PitmanW. C. and TalwaniM.: 1972, ‘Sea-Floor Spreading in the North Atlantic’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 83, 619–645.
RambergI. B., GrayD. F., and RaynoldsR. G. H.: 1977, ‘Tectonic Evolution of the FAMOUS Area of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Lat. 35° 50′ to 37° 20′N’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 88, 609–620.
RonaP. A.: 1976, ‘Asymmetric Fracture Zones and Seafloor Spreading’, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters 30, 109–116.
RonaP. A. and GrayD. F.: 1980, ‘Structural Behaviour of Fracture Zones Symmetric and Asymmetric about a Spreading Axis: Mid-Atlantic Ridge (Lat. 23°N to 27°N)’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 91, 485–494.
RowlettH.: 1981, ‘Seismicity at Intersections of Spreading Centres and Transform Faults’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 3815–3820.
Rowlett, H. and Forsyth, D. W.: ‘Recent Faulting and Microearthquakes at the Intersection of the Vema Fracture Zone and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge’, J. Geophys. Res. (in press)
Scales, J. P.: 1982, ‘Interpretation of an Aeromagnetic Survey over Oceanographer Fracture Zone’ Unpub. M.Sc. thesis Univ. Durham, U.K.
SearleR. C.: 1979, ‘Side-Scan Sonar Studies of North Atlantic Fracture Zones’, J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 136, 283–292.
SearleR. C. and LaughtonA. S.: 1977, ‘Sonar Studies of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Kurchatov Fracture Zone’, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 5313–5328.
Sinha, M. C. and Louden, K. E.: ‘The Oceanographer Fracture Zone: I Crustal Structure from Seismic Refraction Studies’, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. (in press)
SleepN. H. and BiehlerS.: 1970, ‘Topography and Tectonics at the Intersection of Fracture Zones with Central Rifts’, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 2748–2752.
TAMAYO TECTONIC TEAM: 1984, ‘Tectonics at the Intersection of the East Pacific Rise with the Tamayo Transform Fault’, Mar. Geophys. Res. 6, 159–185 (this issue).
VanAndelT. H., VonHerzenR. P., and PhillipsJ. D.: 1971, ‘The Vema Fracture Zone and the Tectonics of Shear Zones in Oceanic Crustal Plates’, Mar. Geophys. Res. 1, 261–283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, C.A., Louden, K.E. & Tanner, S.J. The western intersection of Oceanographer fracture zone with the mid-Atlantic ridge. Mar Geophys Res 6, 143–158 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285957
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285957