Abstract
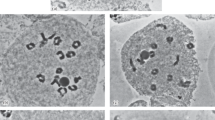
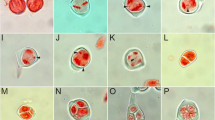
Eighteen plants displaying varying degrees of asynapsis ranging from weak to very strong were found among four out of six populations of Lolium perenne L. (2n=14) which had been subjected to three cycles of directional phenotypic selection for productivity of green material. No plants were found displaying univalents in the original generation but the incidence increased with cycles of selection, indicating the genetic control and differential distribution of asynaptic genes among these populations. — The analysis of univalents and chiasma frequency of pollen mother cells (PMC) of six partially asynaptic plants chosen for detailed study revealed that univalents occurred throughout all PMC chiasma classes irrespective of chiasma frequency, but the higher the chiasma frequency of any PMC the less the likelihood of univalents occurring. The relationship between chiasma frequency and univalent frequency per PMC per plant was negative. — Mean chiasma frequency per bivalent increased for the asynaptic cells in comparison with the normal in both the weak and medium asynaptic groups which was explained by the availability of additional chiasmata for redistribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beadle, G.W.: Further studies of asynaptic maize. Cytologia (Tokyo) 4, 269–286 (1933)
Cooper, J.P., Thomas, P.T.: Cytological unbalance resulting from intensive selection in Lolium. Rep. Welsh Pl. Breed. Stn for 1961 115–118 (1962)
Gottschalk, W.. Klein, H.D.: The influence of mutated genes on sporogenesis. A survey on the genetic control of meiosis in Pisum sativum. Theor. Appl. Genetics 48, 23–34 (1976)
Gottschalk, W., Pietrini, R.V.: The influence of mutant genes on chiasma formation in Pisum sativum. Cytologia (Tokyo) 30, 88–97 (1965)
Koller, P.C.: Asynapsis in Pisum sativum. J. Genet. 36, 275–306 (1938)
Mather, K.: Competition between bivalents during chiasma formation. Proc. roy. Soc. (Lond.) B 120, 208–277 (1936)
Parker, J.S.: Chromosome specific control of chiasma formation. Chromosoma (Berl.) 49, 391–406 (1975)
Prakken, R.: Studies of asynapsis in rye. Hereditas (Lund) 29, 475–495 (1943)
Riley, R., Law, C.N.: Genetic variation in chromosome pairing. Advanc. Genet. 13, 51–114 (1965)
Shaw, D.D.: Genetic and environmental components of chiasma control. III. Genetic analysis of chiasma frequency variation in two selected lines of Schistocerca gregaria Forsk. Chromosoma (Berl.) 46, 365–375 (1974)
Sjödin, J.: Induced asynaptic mutants in Vicia faba L. Hereditas (Lund) 66, 215–232 (1970)
Snow, R.: Alcoholic hydrochloric acid-carmine as a stain for chromosomes in squash preparations. Stain Technol. 38, 9–13 (1963)
Tease, C., Jones, G.H.: Chromosome-specific control of chiasma formation in Crepis capillaris. Chromosoma (Berl.) 57, 33–49 (1976)
Thomas, H., Rajhathy, T.: A gene for desynapsis and aneuploidy in tetraploid Avena. Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 8, 506–515 (1966)
Vivero, J.L.: Phenotypic selection in Lolium perenne L. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. of Wales (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omara, M.K., Hayward, M.D. Asynapsis in Lolium perenne . Chromosoma 67, 87–96 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285651
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285651