Abstract
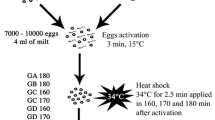
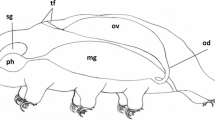
The germ line during the development of the male of the gall midge Heteropeza pygmaea was followed cell generation by cell generation. The development of the male egg begins with two meiotic divisions, followed by fusion of one of the resulting nuclei with (usually) two somatic nuclei (regulation), after which the regulated nucleus passes through 9–10 mitoses, and finally a further two meiotic divisions producing the spermatids. The chromosome numbers (determined by colchicine and air-drying techniques) of the race studied are 55 in the female germ line, very variable with a mean near 47–48 in the male germ line after regulation, 5 or 6 in the sperms, 10 in the female somatic nuclei and 5 in the male somatic nuclei. Statistical techniques for analysis of the different karyotypes are developed and a model explaining the known cytological events in Heteropeza is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camenzind, R.: Die Zytologie der bisexuellen und parthenogenetischen Fortpflanzung von Heteropeza pygmaea Winnertz, einer Gallmücke mit pädogenetischer Vermehrung. Chromosoma (Berl.) 18, 123–152 (1966).
Crozier, R. H.: An acetic acid dissociation, air-drying technique for insect chromosomes, with aceto-lactic orcein staining. Stain Technol. 43, 171–173 (1968).
Defares, J. G., Sneddon, I. N.: An introduction to the mathematics of medicine and biology. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Co. 1960.
Essad, S., Arnoux, J., Maia, N.: Contrôle de validité des caryogrammes. Application au caryotype de Lolium perenne L. Chromosoma (Berl.) 20, 202–220 (1966).
Geyer-Duszyńska, I.: Spindle disappearance and chromosome behavior after partial-embryo irradiation in Cecidomyiidae (Diptera). Chromosoma (Berl.) 12, 233–247 (1961).
—: Genetic factors in oögenesis and spermatogenesis in Cecidomyiidae. In: Chromosomes today (C. D. Darlington and K. R. Lewis, eds.), vol. I, p. 174–178. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd 1966.
Hauschteck, E.: Die Cytologie der Pädogenese und der Geschlechtsbestimmung einer heterogonen Gallmücke. Chromosoma (Berl.) 13, 163–182 (1962).
Kahle, W.: Die Paedogenesis der Cecidomyiden. Zoologica (Stuttg.) 21, 1–80 (1908).
Kraczkiewicz, Z.: Recherches cytologiques sur le cycle évolutif de Miastor metmloas Meinert (Cecidomyidae, Diptera). Cellule 46, 57–74 (1937).
—: La spermatogenèse chez Miastor metraloas (Cecidomyidae, Diptera). C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 127, 1143–1146 (1938).
—: Premiers stades de l'oogenèse de Rhabdophaga saliciperda (Cecidomyiidae, Diptera). Chromosoma (Berl.) 18, 208–229 (1966).
Kunz, W., Trepte, H.-H., Bier, K.: On the function of the germ line chromosomes in the oogenesis of Wachtliella persicariae (Cecidomyiidae). Chromosoma (Berl.) 30, 180–192 (1970).
Moore, R. C., Gregory, G.: Biometrics of the karyotype of Protemnodon bicolor, with reference to the limitations in accuracy of identifying human chromosomes. Nature (Lond.) 200, 234–237 (1963).
Nicklas, R. B.: An experimental and descriptive study of chromosome elimination in Miastor spec. (Cecidomyidae: Diptera). Chromosoma (Berl.) 10, 301–336 (1959).
Ohno, S.: Evolution of sex chromosomes in mammals. Ann. Rev. Genet. 3, 495–524 (1969).
Panelius, S.: Germ line and oogenesis during paedogenetic reproduction in Heteropeza pygmaea Winnertz (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). Chromosoma (Berl.) 23, 333–345 (1968).
Pohlhammer, K.: Zur hormonalen Steuerung der Ovarentwicklung bei den weiblichen Larven der heterogonen Gallmücke Heteropeza pygmaea Winnertz 1846 (Diptera, Cecidomyiidae). Zool. Jb., Physiol. 74, 1–30 (1968).
Snedecor, G. W.: Statistical methods. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State College Press 1956.
White, M. J. D.: The cytology of the Cecidomyidae (Diptera). II. The chromosome cycle and anomalous spermatogenesis of Miastor. J. Morph. 79, 323–369 (1946).
—: Cytological studies on gall midges (Cecidomyidae). Univ. Texas Publ. 5007, 1–80 (1950).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panelius, S. Male germ line, spermatogenesis and karyotypes of Heteropeza pygmaea winnertz (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). Chromosoma 32, 295–331 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284840
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284840