Summary
Proteins from cultured human fibroblasts and native human hair root cells were investigated using the twodimensional electrophoresis (2DE) technique. Cell material from 35 different healthy persons was examined. Proteins of different sources were separated: total proteins of fibroblasts (12 cell lines), soluble proteins of fibroblasts (12 cell lines), structurebound proteins of fibroblasts (eight cell lines) and soluble proteins of hair root cells (12 subjects). The protein samples of different individuals were run in pairs through the electrophoresis procedure and the two patterns of each pair were compared. All changes in the electrophoretic mobility of polypeptide spots (qualitative variants) and all clearly visible differences in the staining intensity of the spots (quantitative variants) were scored.
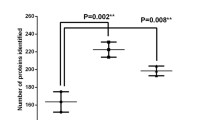
Less than 1% of the qualitative variants per pattern was found in total cell proteins and this percentage was not increased in soluble proteins. No qualitative variation was detected in structure-bound proteins. Quantitative variation occurred to a considerably higher degree in the 2DE patterns than qualitative changes. The incidence of quantitative variants was about three times higher in soluble proteins (11%) than in structure-bound proteins (3.5%); in the total cell proteins it lay in between (7%). Cultured cells (fibroblasts) and native cells (hair root cells) showed a similar degree of variation. A comparison of the data shown here with data obtained by an investigation on inbred strains of the mouse suggest that the major part of the quantitative variants observed in the 2DE patterns of proteins were genetically determined.
The results presented here and the mouse data mentioned above lead us to the conclusion that the genetic variability of proteins may be characterized by quantitative changes rather than by qualitative changes, and that the genetic variability occurs to quite different degrees in different classes of proteins: structure-bound proteins<soluble non-enzymatic proteins<enzymes (certain groups).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Britten RJ, Davidson EH (1976) DNA sequence arrangement and preliminary evidence on its evolution. Fed Proc 35:2151–2157
Brown AJL, Langley CH (1979) Reevaluation of level of genic heterozygosity in natural population of Drosophila melanogaster by twodimensional electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:2381–2384
Comings DE (1982) Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of human brain proteins. III. Genetic and non-genetic variations in 145 brains. Clin Chem 28:798–804
Davidson EH, Britten RJ (1979) Regulation of gene expressions: Possible role of repetitive sequences. Science 204:1052–1059
Edwards Y, Hopkinson DA (1980) Are abundant proteins less variable? Nature 284:511–512
Giometti CS, Anderson NL (1981) A variant of human nonmuscle tropomyosin found in fibroblasts by using two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Biol Chem 256:11840–11846
Goedde HW, Agarwal DP, Harada S (1980) Genetic studies on alcohol metabolizing enzymes. Detection of isoenzymes in human hair roots. Enzyme 25:281
Goldman D, Merril CR (1982) Detection of multiple human lymphocyte polymorphisms with quantitative two-dimensional electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (in press)
Hamaguchi H, Ohta A, Mukai R, Yabe T, Yamada M (1981) Genetic analysis of human lymphocyte proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: I. Detection of genetic variant polypeptides in PHA-stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes. Hum Genet 59:215–220
Harris H, Hopkinson DA, Edwards YH (1977) Polymorphism and the subunit structure of enzymes: A contribution to the neutralist-selectionist controversy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:698–701
King JL (1976) Progress in the neutral mutation—random drift controversy. Fed Proc 35:2087–2091
Klose J (1975a) Protein mapping by combined isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis of mouse tissue. A novel approach to testing for induced point mutations in mammals. Humangenetik 26:231–234
Klose J (1975b) Protein mapping as a tool'for investigating mutagenic and teratogenic effects in mouse embryos. In: Neubert D, Merker HJ (eds) New approaches to the evaluation of abnormal embryonic development. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 375–387
Klose J (1979) Isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis combined as a method for defining new point mutations in the mouse. Genetics [Suppl] 92:13–24
Klose J (1982) Genetic variability of soluble proteins studied by twodimensional electrophoresis on different inbred mouse strains and on different mouse organs. J Mol Evol 18:315–328
Klose J, Feller M (1981a) Genetic variability of proteins from plasma membranes and cytosols of mouse organs. Biochem Genet 19: 859–870
Klose J, Feller M (1981b) Two-dimensional electrophoresis of membrane and cytosol proteins of mouse liver and brain. Electrophoresis 2:12–24
Klose J, Zeindl E, Sperling K (1982) Analysis of protein patterns in two-dimensional gels of cultured human cells with trisomy 21. Clin Chem 28:987–992
McConkey EH, Taylor BJ, Phan D (1979) Human heterozygosity: A new estimate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:6500–6504
O'Farrell PH (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 250:4007–4021
Paigen K (1979) Acid hydrolases as models of genetic control. Ann Rev Genet 13:417–466
Racine RR, Langley CH (1980) Genetic heterozygosity in a natural population of Mus musculus assessed using two-dimensional electrophoresis. Nature 283:855–857
Singh S, Klose, J, Willers I, Goedde HW (1978) Application of protein mapping to human fibroblasts: Aspects of cell culturing, evaluation and studies in mutant cell lines. In: Catsimpoolas N (ed) Electrophoresis '78. Elsevier-North Holland Inc, New York Amsterdam Oxford, pp 297–304
Singh S, Willers I, Klose J, Goedde HW (1980) High-resolution protein mapping of human fibroblasts: Another possibility for the study of genetic defects of known and unknown etiology. Fresenius Z Anal Chem 301:193–194
Singh S, Willers I, Klose J, Goedde HW (1981) High-resolution protein mapping of human fibroblasts and hair root cells: A standardized reproducible procedure considering the effect of cell culture parameters. Biochem Genet 19:871–880
Walton KE, Styer D, Gruenstein EI (1979) Genetic polymorphism in normal human fibroblasts as analyzed by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem 254:7951–7960
Willers I, Singh S, Goedde HW, Klose J (1981) High-resolution protein mapping in fibroblast cell lines and hair roots from patients with genetic disease. Clin Genet 20:217–221
Zuckerkandl E (1976) Evolutionary processes and evolutionary noise at the molecular level. J Mol Evol 7:167–183
Zuckerkandl E (1978) Multilocus enzymes, gene regulation, and genetic sufficiency. J Mol Evol 12:57–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klose, J., Willers, I., Singh, S. et al. Two-dimensional electrophoresis of soluble and structure-bound proteins from cultured human fibroblasts and hair root cells: Qualitative and quantitative variation. Hum Genet 63, 262–267 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284661
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284661