Abstract
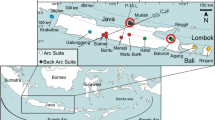
The rate earth element chemistry of a large suite of samples from the Central American volcanic front has been determined to understand their petrogenesis. Different segments of the volcanic front are compared on the basis of their calculated source rare earth patterns as deduced from inverse modeling. The results yield a range in the extent of light rare earth enrichment of the source, as well as in source mineralogy. Moderateto-strong LREE enrichment and high modal garnet contents are observed for the sources of both Guatemala and central Costa Rica, whereas slight LREE depletion and little or no garnet occurs in the Nicaraguan source region. Although distinct source regions beneath each Central American segment are permitted by the modeling, it is more likely that the mantle wedge is broadly homogeneous but locally heterogeneous. Small volume, relatively enriched, garnet-bearing veins surrounded by a matrix of isotopically depleted mantle periodotite could exist throughout the mantle wedge. Apparently distinct sources occur due to the variation in partial melting beneath the different segments, controlled by the amount of subduction-generated flux per unit wedge volume, which in turn is a function of the dip of the subducted lithosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarède F, Tamagnan V (1988) Modelling the recent geochemical evolution of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcano, Reunion Island. J Petrol 29:997–1030
Anderson DL (1989) Theory of the earth. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Arculus RJ, Powell R, (1986) Source component mixing in the regions of arc magma generation. J Geophys Res 91:5913–5926
Bryan WB, Finger LW, Chayes F (1969) Estimating proportions in petrographic mixing equations by least-squares approximation. Science 163:926–927
Carr MJ (1984) Symmetrical and segmented variation of physical and geochemical characteristics of the Central American volcanic front. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 20:231–252
Carr MJ, Stoiber RE (1990) Volcanism. In: Dengo G, Case JE (eds) The geology of North America, vol H, The Caribbean region. Geol Soc of America, Boulder, Colorado, pp 375–391
Carr MJ, Feigenson MD, Bennett EA (1990) Incompatible element and isotopic evidence for tectonic control of source mixing and melt extraction along the Central American arc. Contrib Mineral Petrol 105:369–380
Feigenson MD, Carr MJ (1985) Determination of major, trace and rare earth elements in rocks by DCP-AES. Chem Geol 51:19–27
Feigenson MD, Carr MJ (1986) Positively correlated Nd and Sr isotope ratios of lavas from the Central American volcanic front. Geology 14:79–82
Feigenson MD, Hofmann AW, Spera FJ (1983) Case studies on the origin of basalt, II. The transition from tholeiitic to alkalic volcanism on Kohala volcano, Hawaii. Contrib Mineral Petrol 84:390–405
Frey FA, Garcia MO, Wise WS, Kennedy A, Gurriet P, Albarède F (1991) The evolution of Mauna Kea volcano, Hawaii: Petrogenesis of tholeiitic and alkalic basalts: J Geophys Res 96:14,347–14,375
Hofmann AW, Feigenson MD (1983) Case studies on the origin of basalt. I. Theory and reassessment of Grenada basalts. Contrib Mineral Petrol 84:382–389
Hofmann AW, Feigenson MD, Raczek I (1984) Case studies on the origin of basalt, III. Petrogenesis of the Mauna Ulu eruption, Kilauea, 1969–1971. Contrib Mineral Petrol 88:24–35
Kay SM, Maksaev V, Moscoso R, Mpodozis C, Nasi C (1987) Probing the evolving Andean lithosphere: Mid-late tertiary magmatism in Chile (29°–30°30′ S) over the modern zone of subhorizontal subduction. J Geophys Res 92:6173–6189
McKenzie D, O'Nions RK (1991) Partial melt distributions from inversion of rare earth element concentrations. J Petrol 32:1021–1091
Minster JF, Allègre CJ (1978) Systematic use of trace elements in igneous processes, part III. Inverse problem of batch partial melting in volcanic suites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 68:37–52
O'Hara MJ (1968) The bearing of phase equilibria studies on the origin and evolution of basic and ultrabasic rocks. Earth Sci Rev 4:69–133
Shaw DM (1970) Trace element fractionation during anatexis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 34:237–243
Shimizu N, Kushiro I (1975) The partitioning of rare earth elements between garnet and liquid at high pressures: preliminary experiments. Geophys Res Lett 2:413–416
Spiegelman M, McKenzie D (1987) Simple 2-D models for melt extraction at mid-ocean ridges and island arcs. Earth Planet Sci Lett 83:137–152
Stack CA, Feigenson MD, Carr MJ (1991) Inverse modeling of alkaline lavas from Guayacan, Costa Rica. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 72:294–295
Walker JA, Carr MJ, Feigenson MD, Kalamarides RI (1990) The petrogenetic significance of interstratified high- and low-Ti basalts in central Nicaragua. J Petrol 31:1141–1164
Watson S, McKenzie D (1991) Melt generation by plumes: A study of Hawaiian volcanism. J Petrol 32:501–537
Wilson M (1989) Igneous petrogenesis. Unwin Hyman, London
Wood SA (1990) The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium. 2. Theoretical predictions of speciation in hydrothermal solutions to 350° C at saturation water vapor pressure. Chem Geol 88:99–125
Yoder HS Jr (1976) Generation of basaltic magma. National Academy of Sciences, Washington
Zindler A, Hart S (1986) Chemical geodynamics. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 14:493–571
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feigenson, M.D., Carr, M.J. The source of Central American lavas: inferences from geochemical inverse modeling. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 113, 226–235 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00283230
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00283230