Summary
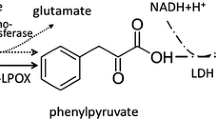
The production of l-phenylalanine from the racemate d,l-phenyllactate in an enzyme membrane reactor has been examined. In a first step the racemate is dehydrogenated to the prochiral intermediate phenylpyruvate by the enzymes d-and l-hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase. In a second step phenylpyruvate is reductively aminated to l-phenylalanine by l-phenylalanine dehydrogenase. Both steps are dependent on coenzyme, the first one requires NAD, the second one NADH in stoichiometric amounts; in this way the coenzyme is regenerated and only required catalytically. The coenzyme is covalently bound to polyethylene glyco-20 000 and can thus be retained in the reactor analogously to the three enzymes. In order to optimize the continuous production of l-phenylalanine from d,l-phenyllactate, models of the reaction kinetics and of the reactor system have been set up. By means of the reactor model, we can calculate the optimum ratio of the three enzymes, the optimum coenzyme concentration and the optimum phenylpyruvate concentration in the feed.
In this process, at a substrate concentration of 50 mM d,l-phenyllactate we reached a spacetime-yield of 28 g l-Phe/(l*d).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PEG:
-
polyethylene glycol
- d-HicDH:
-
d-hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase
- l-HicDH:
-
l-hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase
- PheDH:
-
l-phenylalanine dehydrogenase
- V max :
-
maximum velocity
- K M :
-
Michaelis-Menten constant
- K l :
-
inhibition constant
- R1 :
-
reaction rate of the d-HicDH forward reaction
- R2 :
-
reaction rate of the d-HicDH reverse reaction
- R3 :
-
reaction rate of the l-HicDH forward reaction
- R4 :
-
reaction rate of the l-HicDH reverse reaction
- R5 :
-
reaction rate of the PheDH forward reaction
- R6 :
-
reaction rate of the PheDH reverse reaction
- d-PLac:
-
d-phenyllactate
- l-PLac:
-
l-phenyllactate
- PPy:
-
phenylpyruvate
- l-Phe:
-
l-phenylalanine
- NH4 :
-
ammonium
- τ:
-
residence time
References
Boehringer Mannheim GmbH (1973) l-Amino acid oxidase (l-AOD). Biochemica Information I, p 41
Bückmann AF, Kula M-R, Wichmann R, Wandrey C (1981) An Efficient Synthesis of High Molecular Weight NAD(H)-Derivatives suitable for Continuous Operating with Coenzyme Depending Enzyme Systems. J Appl Biochem 3:301–315
Hoffmann U, Hofmann H (1971) Einführung in die Optimierung mit Anwendungsbeispielen aus dem Chemie-Ingenieur-Wesen, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, FRG
Hummel W, Schütte H, Kula M-R (1985) d-2-hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus casei—A new enzyme suitable for stereospecific reduction of 2-keto-carboxylic acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 21:7–15
Hummel W, Schmidt E, Wandrey C, Kula M-R (1986) l-Phenylalanine dehydrogenase from Brevibacterium sp. for production of l-phenylalanine by reductive amination of phenylpyruvate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 25:175–185
Jandel L (1981) Rechnerunterstützte Optimierung eines Enzym-Membran-Reaktors zur kontinuierlichen Producktion von l-Aminosäuren. Dissertation, TU Clausthal, FRG
Klausner A (1985) Bullding for success in phenylalanine. Bio Technology, Vol 3, pp 301–307
Rozzell JD (1986) Coupled Two-Enzyme-Systems for Producting l-Amino Acids. Enzyme Engineering 8 (in press)
Schmidt E, Fiolitakis E, Wandrey C (1986) Multiple Steady States in a Coupled Enzyme System-represented by the enzymatically catalyzed production of l-phenylalanine. Enzyme Engineering 8 (in press)
Schmidt E, Bossow B, Wichmann R, Wandrey C (1986) The Enzyme Membrane Reactor—An Alternative Approach for Continuous Operation with Enzymes. Kem Ind 35 2:71–77
Schütte H, Hummel W, Kula M-R (1984) l-2-hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase—A new enzyme from Lactobacillus confusus for the stereospecific reduction of 2-keto-carboxylic acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 19:167–176
Wandrey C, Fiolitakis E, Wichmann U, Kula M-R (1984) l-Amino acids from a racemic mixture of α-hydroxy-acids. Enzyme Engineering 7, Ann N Y Acad Sci 434:91–94
Wood LL, Calton GJ (1986) Commercial production of phenylalanine by an immobilized cell process. Enzyme Engineering 8 (in press)
Ziehr H, Schmidt E, Stock J, Wandrey C, Klein J, Kula M-R (1986) Continuous Production of l-Phenylalanine by Transamination. Biotech Bioeng (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, E., Vasić-Rački, Đ. & Wandrey, C. Enzymatic production of l-phenylalanine from the racemic mixture of d,l-phenyllactate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 42–48 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282147
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282147