Summary
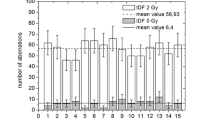
The G-band pattern in 445 metaphases obtained seven weeks after irradiation (600 rad gamma-ray) was analysed. Approximately 37% of these cells had one or more structural aberrations. The majority of the aberrant events was reciprocal translocation followed by inversion and deletion in the proportion of 9:1:1 respectively. Statistical analyses (Chi-square tests) on the distribution of breakpoints among chromosomes showed an excess number of breaks in chromosomes 1,7,and 12. Chromosomes 1 and 12 were particularly involved in cells carrying multiple aberrations while chromosome 7 was preferentially involved in deletion. Within chromosomes a significantly large number of breaks were located in(a) the light bands and (b) the terminal segments. The significance of these findings is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aurias A, Prieur M, Dutrillaux B, Lejeune J (1978) Systematic analysis of 95 reciprocal translocations of autosomes. Hum Genet 45: 259–282
Benn PA (1977) Specific breakpoints in chromosomally abnormal human fibroblasts. Cytogenet Cell Genet 19:118–135
Buckton KE (1976) Identification with G and R banding of the position of breakpoints induced in human chromosomes by in-vitro X-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol 29:475–488
Caspersson T, Haglund U, Lindell B, Zech L (1972) Radiation-induced non-random chromosome breakage. Expt Cell Res 75: 541–543
Cook P, Seabright M, Wheeler M (1975) The differential distribution of X-ray-induced chromosome lesions in trypsin-banded preparations from human subjects. Hum Genet 28:221–231
Cruciger QVJ, Pathak S, Cailleau R (1976) Human breast carcinomas: marker chromosomes involving 1q in seven cases. Cytogenet Cell Genet 17:231–235
Dubos C, Pequignot EV, Dutrillaux B (1978) Localization of gammaray induced chromatid breaks using a three consecutive staining technique. Mutat Res 49:127–131
Franke U (1972) Quinacrine mustard fluorescence of human chromosomes: characterization of unusual translocations. Am J Hum Genet 24:189–231
Holmberg M, Jonasson J (1973) Chromosome breakage in the R-bands of human chromosomes. Hereditas 74:57–68
Jacobs PA, Buckton KE, Cunningham C, Newton M (1964) An analysis of the breakpoints of structural rearrangements in man. J Med Genet 11:50–64
Kakati S, Oshimura M, Sandberg AA (1976) The chromosomes and causation of human cancer and leukaemia. XIX. Common markers in various tumours. Cancer 38:770–777
Lee CLY, Lee SHS, Kamra OP (1979) Studies on isolated cloned populations from irradiated human embryonic cell cultures. Cytogenet Cell Genet 24:150–159
Lee CLY, Welch JP, Winsor EJT (1972) Banding pattern in human chromosomes: production by proteolytic enzymes. J Hered 63: 296–297
Oshimura M, Hayata MS, Kakati S, Sandberg AA (1976) Chromosomes and causation of human cancer and leukemia XVII. Banding studies in acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML). Cancer 38:748–761
Rowley JD (1975) Abnormalities of chromosome 1 in myeloproliferative disorders. Cancer 36:1748–1757
San Roman C, Bobrow M (1973) The sites of radiation-induced breakage in human lymphocyte chromosomes, determined by quinicrine fluorescence. Mutat Res 18:325–331
Savage JRK, Watson GE, Bigger TRL (1973) The participation of human chromosome arms in radiation-induced chromatid exchange. In: Wahrman J, Lewis KR (eds) Chromosome today, Vol 4. Longman, London, p 267
Seabright M (1973) High resolution studies on the pattern of induced exchanges in human karyotype. Chromosoma 40:333–346
Seman G, Hunter SJ, Muller RC, Dmochowski L (1976) Characterization of an established cell line (SH-3) derived from pleural effusion of a patient with breast tumour. Cancer 37:1814–1824
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.L.Y., Kamra, O.P. The pattern of radiation-induced transmissible aberrations in a human cell culture. Hum Genet 57, 380–384 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00281689
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00281689