Abstract
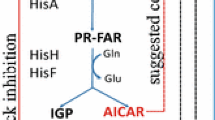
High-level expression of the hisHAFI genes in Escherichia coli, cloned under the control of an IPTG-inducible promoter, caused filamentation, as previously reported in Salmonella typhimurium. We speculated that this filamentation might be produced by an action of the HisH and HisF enzymes on their product AICAR (amino-imidazole carboxamide riboside 5′-phosphate), a histidine by-product and normal purine precursor, possibly by favouring the formation of ZTP, the triphosphate derivative of AICAR. However, filamentation occured even in the absence of carbon flow through the histidine and purine pathways, as observed in a hisG purF strain lacking the first enzyme in each pathway. Filamentation thus does not require either the normal substrate or products of the overproduced histidine enzymes and must reflect another activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antón DN (1978) Genetic control of defective cell shape and osmotic-sensitivity in a mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Mot Gen Genet 160:277–286
Antón DN (1979) Positive selection of mutants with cell envelope defects of a Salmonella typhimurium strain hypersensitive to the products of genes hisF and hisH. J Bacteriol 137:1271–1281
Antón DN, Orce LV (1976) Envelope mutation promoting autolysis in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet 144:97–105
Begg KJ, Spratt BG, Donachie WD (1986) Interaction between membrane proteins PBP3 and RodA is required for normal cell shape and division in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 167:1004–1008
Begg KJ, Takasuga A, Edwards DH, Dewar SJ, Spratt BG, Adachi H, Ohta T, Matsuzawa H, Donachie WD (1990) The balance between different peptidoglycan precursors determines whether Escherichia coli cells will elongate or divide. J Bacteriol 172:6697–6708
Bochner BR, Ames BN (1982) ZTP (5-amino 4-imidazole carboxamide riboside 5′-triphosphate): a proposed alarmone for 10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate deficiency. Cell 29:929–937
Brown EA, D'Ari R, Newman EB (1990) A relationship between L-serine degradation and methionine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol 136:1017–1023
Burton P, Holland IB (1983) Two pathways of division inhibition in UV-irradiated E. coli. Mot Gen Genet 190:309–314
Carlomagno MS, Chiariotti L, Alifano P, Nappo AG, Bruni CB (1988) Structure and function of the Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli K-12 histidine operons. J Mot Biol 203:585–606
D'Ari R, Huisman O (1983) Novel mechanism of cell division inhibition associated with the SOS response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 156:243–250
Flores A, Fox M, Casadesus J (1993) The pleiotropic effects of Salmonella typhimurium his overexpression do not involve AICAR-induced mutagenesis. Mot Gen Genet 240:360–364
Fox M, Frandsen N, D'Ari R (1993) AICAR is not an endogenous mutagen in Escherichia coli. Mot Gen Genet 240:355–359
Geiger JR, Speyer JF (1977) A conditional antimutator in E. coli. Mot Gen Genet 153:87–97
Gibert I, Casadesus J (1990) sulA-independent division inhibition in His-constitutive strains of Salmonella typhimurium. FEMS Microbiol Letters 69:205–210
Grisolia V, Riccio A, Bruni CB (1983) Structure and function of the internal promoter (hisBp) of the Escherichia coli K-12 histidine operon. J Bacteriol 155:1288–1296
Hiraga S, Niki H, Ogura T, Ichinose C, Mori H, Ezaki B, Jaffé A (1989) Chromosome partitioning in Escherichia coli: novel mutants producing anucleate cells. J Bacteriol 171:1496–1505
Hoekstra WPM, Vis HG (1977) Characterization of the E. coli K12 strain AB1157 as impaired in guanine/xanthine metabolism. Antonia Van Leeuwenhoek 43:199–204
Houlberg U, Jensen KF (1983) Role of hypoxanthine and guanine in regulation of Salmonella typhimurium pur gene expression. J Bacteriol 153:837–845
Huisman O, D'Ari R (1981) An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature 290:797–799
Huisman O, D'Ari R, Gottesman S (1984) Cell division control in Escherichia coli: specific induction of the SOS function SfiA protein is sufficient to block septation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:4490–4494
Jaffé A, D'Ari R, Norris V (1986) SOS-independent coupling between DNA replication and cell division in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 165:66–71
Kepes F, D'Ari R (1987) Involvement of FtsZ protein in shift-upinduced division delay in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 169:4036–4040
Lin RT, D'Ari R, Newman EB (1990) The leucine regulon of Escherichia coli K-12: a mutation in rblA alters expression of L-leucine-dependent metabolic operons. J Bacteriol 172:4529–4535
Markiewicz Z, Broome-Smith JK, Schwarz U, Spratt BG (1982) Spherical E. coli due to elevated levels of D-alanine carboxypeptidase. Nature 297:702–704
Matsuhashi M, Wachi M, Ishino F (1990) Machinery for cell growth and division: penicillin-binding proteins and other proteins. Res Microbiol 141:89–103
Meng LM, Nygaard P (1990) Identification of hypoxanthine and guanine as the corepressors for the purine regulon genes of Escherichia coli. Mot Microbiol 4:2187–2192
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Murray ML, Hartman PE (1972) Overproduction of hisH and hisF gene products leads to inhibition of cell division in Salmonella. Can J Microbiol 18:671–681
Murray V (1987) 5-Amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide is a mutagen in E. coli. Mutat Res 190:89–94
Neuhard J, Nygaard P (1987) Purines and Pyrimidines. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Low KB, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular Biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 445–473
Niki H, Jaffé A, Imamura R, Ogura T, Hiraga S (1991) The new gene mukB-codes for a 177 kd protein with coiled-coil domains involved in chromosome partitioning of E. coli. EMBO J 10:183–193
Patzer J (1973) Suppression of the defect in the histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. Acta Microbiol Polonica, 5:3–14
Patzer J (1974) Defective cell separation in the smoA mutant. Acta Microbiol Polonica 6:173–182
Pisabarro AG, Prats R, Vázquez D, Rodríguez-Tébar A (1986) Activity of penicillin-binding protein 3 from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 168:199–206
Pochet S, D'Ari R (1990) Synthesis and enzymatic polymerisation of 5-amino-1-(2′-deoxy-β-d-ribofuranosyl)imidazole-4-carbox-amide-5′-triphosphate. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7127–7131
Rieder G, Kleiner D (1993) Clarification of the last blind spot in the histidine biosynthesis — function of hisF and hisH gene products. Bioengineering 9:30
Rohlman CE, Matthews RG (1990) Role of purine biosynthetic intermediates in response to folate stress in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 172:7200–7210
Rolfes RJ, Zalkin H (1991) Purification of the Escherichia coli purine regulon repressor and identification of corepressors. J Bacteriol 172:5637–5642
Roth JR, Hartman PE (1965) Heterogeneity in P22 transducing particles. Virology 27:297–307
Sabina RL, Holmes EW, Becker MA (1984) The enzymatic synthesis of 5-amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide riboside triphosphate (ZTP). Science 223:1193–1195
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sloan JB, Urban JE (1976) Growth response of Escherichia coli to nutritional shift up. J Bacteriol 128:302–308
Spratt BG (1975) Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:2999–3003
Taschner PEM, Huls PG, Pas E, Woldringh CL (1988) Division behavior and shape changes in isogenic ftsZ, ftsQ, ftsA, pbpB, and ftsE cell division mutants of Escherichia coli during temperature shift experiments. J Bacteriol 170:1533–1540
Tsui H-CT, Arps PJ, Connolly DM, Winkler ME (1991) Absence of hisT-mediated tRNA pseudouridylation results in a uracil requirement that interferes with Escherichia coli K-12 cell division. J Bacteriol 173:7395–7400
Wachi M, Matsuhashi M (1989) Negative control of cell division by mreB, a gene that functions in determining the rod shape of Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol 171:3123–3127
Wachi M, Doi M, Tamaki S, Park W, Nakajima-Iijima S, Matsuhashi M (1987) Mutant isolation and molecular cloning of mre genes, which determine cell shape, sensitivity to mecillinam, and amount of penicillin-binding proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 169:4935–4940
Wientjes FB, Nanninga N (1989) Rate and topography of peptidoglycan synthesis during cell division in Escherichia coli: concept of a leading edge. J Bacteriol 171:3412–3419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. Devoret
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frandsen, N., D'Ari, R. Excess histidine enzymes cause AICAR-independent filamentation in Escherichia coli . Molec. Gen. Genet. 240, 348–354 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280385
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280385