Summary
It is uncertain how the hypoglycaemic effect of sulphonylureas varies with drug concentration in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The interrelationship of tolbutamide dosage and concentration, and glucose and insulin concentrations were therefore examined in 54 out-patients (the observational group) and in 20 patients studied under controlled conditions (the experimental group).
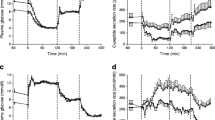
In the observational group, tolbutamide concentration depended significantly on the daily dose, time from dose to sampling, body weight, and age. Blood glucose and insulin concentration were related, but were independent of tolbutamide concentration.
In the experimental group, peak, but not pre-dose, tolbutamide concentration, depended on dose and on body mass index. Fasting and maximum post-prandial blood glucose concentration were positively correlated with maximum tolbutamide concentration, probably because tolbutamide dosage was highest in those with the poorest response.
In the subset with a fasting blood glucose concentration of less than 8 mmol·l−1, neither glucose nor insulin concentrations depended significantly on tolbutamide concentrations. Tolbutamide concentration does not directly determine hypoglycaemic response in outpatients, and therapeutic monitoring of drug concentrations would not improve the management of such patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferner RE, Alberti KGMM (1989) Sulphonylureas in the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Q J Med 73: 987–995
Sonksen PH, Lowy C, Perkins JR, Lims HS (1984) Non-insulindependent diabetes: 10-year outcome in relation to initial response to diet and subsequent sulphonylurea therapy. Diabetes Care 7 [Suppl 1]: 59–66
Groop LC, Pelkonen R, Koskimies S, Bottazzo GF, Doniach D (1986) Secondary failure to treatment with oral antidiabetic agents in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes Care 9: 129–133
De Fronzo RA. Lilly Lecture 1987 (1988) The triumvirate: betacell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes 37: 105–108
Krall LP, Bradley RF (1962) ‘Secondary failures’ in the treatment of diabetes mellitus with tolbutamide and with phenformin. Diabetes 11 [Suppl]: 88–93
Karam JH, Sanz N, Salamon E, Nolte MS (1986) Selective unresponsiveness of pancreatic B-cells to acute sulfonylurea stimulation during sulfonylurea therapy in NIDDM. Diabetes 35: 1314–1320
Scott J, Poffenbarger PI (1979) Pharmacogenetics of tolbutamide metabolism in humans. Diabetes 28: 41–51
Peart GF, Boutagy J, Shenfield GM (1987) Lack of relationship between tolbutamide metabolism and debrisoquine oxidation phenotype. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33: 397–402
Hermansen K (1982) Tolbutamide, glucose, calcium, and somatostatin concentration. Acta Endocrinol 99: 86–93
Deingott D, Mirsky IA (1956) Relation to quantity of sulfonylurea by mouth to the hypoglycemic response in normal human subjects. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 118: 168–173
McMahon FG, Upjohn HL, Carpenter OS, et al (1962) The comparative pharmacology of a variety of hypoglycemic drugs. Curr Res Ther 4: 330–343
Heine P, Kewitz H, Schnapperelle U (1974) Dose-response relationships of tolbutamide and glibenclamide in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 7: 321–330
Melander A, Sartor G, Wahlin-Boll E, Schersten B, Bitzen P-O (1978) Serum tolbutamide and chlorpropamide concentrations in patients with diabetes mellitus. Br Med J 1: 142–144
Soeldner JS, Slone D (1965) Critical variables in the radio-immunoassay of insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes 14: 771–779
Heding LG (1975) Radioimmunological determination of human C-peptide in serum. Diabetologia 11: 541–548
Nation RL, Peng GW, Chiou WL (1978) Simple, rapid and micro high-pressure liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of tolbutamide and hydroxytolbutamide in plasma. J Chromatogr 146: 121–131
Hoaglin DC, Mosteller F, Tukey JW (1983) Understanding robust and exploratory data analysis. Wiley and Sons, New York
Belsey DA, Kuh E, Welsch RE (1980) Regression diagnostics. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Alberti KGMM, Gries FA (1988) Management of non-insulindependent diabetes mellitus in Europe: a concensus view. Diabetic Med 5: 275–281
Olson SC, Ayres JW, Antal EJ, Albert KS (1985) Effect of food and tablet age on relative bioavailibility and pharmacodynamics of two tolbutamide products. J Pharm Sci 74: 735–739
Antal EJ, Gillespie WR, Phillips JP, Albert KS (1982) The effect of food on the bioavailability and pharmacodynamics of tolbutamide in diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22: 459–462
Adir J, Miller AK, Vestal RE (1982) Effects of total plasma concentration and age on tolbutamide plasma protein binding. Clin Pharmacol Ther 31: 488–493
Wahlin-Boll E, Sartor G, Melander A, Schersten B (1980) Influence of food intake on the absorption and effect of glipizide in diabetics and in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18: 279–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferner, R.E., Antsiferov, M.L., Kelman, A.W. et al. The relationships between dose and concentration of tolbutamide and insulin and glucose responses in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40, 163–168 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280071
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280071