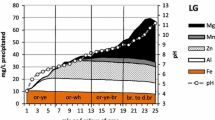
Abstract
In this study we report on the effect of sediment, from an acidified lake, on the neutralization of the acidified water column. The results of this experimental study show that organic acids (presumably humic or fulvic acids) can dissolve from the sediment and destroy alkalinity as measured by a Gran plot analysis. Alkalinity destruction by organic acid dissolution was shown to be a function of pH. Some Na ion exchange for sediment H+ was also observed. This ion exchange was shown to be a function of pH and Na concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA: 1985, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 16th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington D.C.
ASA: 1982, Methods of Soil Analysis Part 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties, Amer. Sec. of Agronomy, Madison, WI.
Baker, L. A., Brezonik, P. L., Edgerton, E. S., and Ogburn, R. W., III: 1985, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 25, 215.
Barnard, T. E.: 1985, ‘The Development of Analytical Procedures and Methods for Quantification of Parameters of and Acid-Base Model of Dilute Acidified Waters’, Ph. D. Dissertation, Cornell U., Ithaca, NY.
Barnard, T. E. and Bisogni, J. J., Jr.: 1985, Water Res. 19, 393.
Benes, P., Gjessing, E. T., and Steinnes, E.: 1976, Water Res. 10, 711.
Cook, R. B., Kelly, C. A., Schindler, D. W., and Turner, M. A.: 1986, Limnol. Oceanogr. 31, 134.
Crandell, C. M.: 1979, ‘The Effect of Sediment on Dilute Acidified Adirondack Surface Waters’, M. S. thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY.
Fraser, J. M. and Britt, D. L.: 1982, Liming of Acidified Waters: A Review of Methods and Effects on Aquatic Ecosystems, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Division of Biological Services, Eastern Energy and Land Use Team, FWS/OBS-80/40.13.
Loughnan, F.C.: 1969, Chemical Weathering of the Silicate Minerals, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Molot, L. A.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 27, 297.
Oliver, B. G., Thurman, E. M., and Malcolm, R. L.: 1983, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 47, 2031.
Scheffe, R. D., Booty, W. G., and DePinto, J. V.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 31, 857.
Schindler, D. W. and Turner, M. A.: 1982, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 18, 259.
Schnitzer, M. and Khan, S. U.: 1978, Soil Organic Matter, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Thurman, E. M. and Malcolm, R. L.: 1981, Env. Sci. Tech. 15, 463.
Visser, S. A.: 1982, J. Environ. Sci. Health A17, 767.
Wright, J. R. and Schnitzer, M.: 1963, Soil Sci. Amer. Proc. 27, 171.
Young, T. C., Rhea, J. R., and McLaughlin, G.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 31, 839.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bisogni, J.J., Kishbaugh, S.A. Alkalinity destruction by sediment organic matter dissolution during neutralization of acidified lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut 38, 85–95 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279587
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279587