Abstract
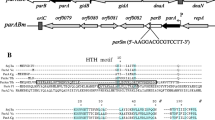
The DNA sequence of the 5.7 kb plasmid pHH9 containing the replicon region of the 150 kb plasmid pHH1 from Halobacterium salinarium was determined. The minimal region necessary for stable plasmid maintenance lies within a 2.9 kb fragment, as defined by transformation experiments. The DNA sequence contained two open reading frames arranged in opposite orientations, separated by an unusually high AT-rich (60–70% A + T) sequence of 350 bp. All H. salinarium strains (H. halobium, H. cutirubrum) investigated harbour endogenous plasmids containing the pHH1 replicon; however, these pHH1-type plasmids differ by insertions and deletions. Adjacent to the replicon, and separated by a copy of each of the insertion elements ISH27 and ISH26, is the 9 kb p-vac region required for gas vesicle synthesis. Analysis of these and other ISH element copies in pHH1 revealed that most of them lack the target DNA duplication usually found with recently transposed ISH elements. These results underline the plasticity of plasmid pHH1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaseio U, Pfeifer F (1990) Transformation of Halobacterium halobium: Development of vectors and investigation of gas vesicle synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6772–6776
Bramhill D, Kornberg A (1988) A model for initiation at origins of DNA replication. Cell 54:915–918
Charlebois RL, Lam WL, Cline SW, Doolittle WF (1987) Characterization of pHV2 from Halobacterium volcanii and its use in demonstrating transformation of an archaebacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8530–8534
Charlebois RL, Schalkwyk L, Holman J, Doolittle WF (1991) Detailed physical map and set of overlapping cosmid clones covering the genome of the archaebacterium Haloferax volcanii DS2. Mol Biol 222:509–524
Cline SW, Doolittle WF (1992) Transformation of members of the genus Haloarcula with shuttle vectors based on Halobacterium halobium and Haloferax volcanii plasmid replicons. J Bacteriol 174:1076–1080
Cline SW, Schalkwyk L, Doolittle WF (1989) Transformation of the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii with genomic DNA. J Bacteriol 171:4987–4991
DasSarma S (1989) Mechanisms of genetic variability in Halobacterium halobium: the purple membrane and gas vesicle mutations. Can J Microbiol 35:65–72
DasSarma S, RajBhandari U, Khorana HG (1983) High-frequency spontaneous mutation in the bacterio-opsin gene in Halobacterium halobium is mediated by transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2201–2205
DasSarma S. Damerval T, Jones JG, Tandeau de Marsac N (1987) A plasmid-encoded gas vesicle protein gene in a halophilic archaebacterium. Mol Microbiol 1:365–370
Devereux J, Häberli P, Smithies O (1984) A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res 12:387–395
Ebert K, Goebel W (1985) Conserved and variable regions in the chromosomal and extrachromosomal DNA of halobacteria. Mol Gen Genet 200:96–102
Ebert K, Hanke C, Delius H, Goebel W, Pfeifer F (1987) A new insertion element, ISH26, from Halobacterium halobium. Mol Gen Genet 206:81–87
Englert C, Krüger K, Offner S, Pfeifer F (1992) Three different but related gene clusters involved in gas vesicle synthesis in halophilic Archaea. J Mol Biol 227:586–592
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Hofman JD, Schalkwyk L, Doolittle WF (1986) ISH51: a large, degenerate family of insertion sequence-like elements in the genome of the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6983–7000
Holmes M, Nuttall S, Dyall-Smith M (1991) Construction and use of halobacterial shuttle vectors and further studies on Haloferax DNA gyrase. J Bacteriol 173:3807–3813
Horne M, Englert C, Pfeifer F (1988) Two genes encoding gas vacuole proteins in Halobacterium halobium. Mol Gen Genet 213:459–464
Horne M, Englert C, Wimmer C, Pfeifer F (1991) A DNA region of 9 kb contains all genes necessary for gas vesicle synthesis in halophilic archaebacteria. Mol Microbiol 5:1159–1174
Jones JG, Hackett N, Halladay J, Scothorn D, Yang C, Ng W, DasSarma S (1989) Analysis of insertion mutants reveals two new genes in the gas vesicle gene cluster of Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7785–7793
Jones JG, Young DC, DasSarma S (1991) Structure and organization of the gas vesicle gene cluster on the Halobacterium halobium plasmid pNRC100. Gene 102:117–122
Krebs M, RajBhandari U, Khorana HG (1990) Nucleotide sequence of ISH11, a new Halobacterium halobium insertion element isolated from the plasmid pGRB1. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6699
Lam W, Doolittle WF (1989) Shuttle vectors for the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5478–82
Manen D, Caro L (1991) The replication of plasmid pSC101. Mol Microbiol 5:233–237
Moore R, McCarthy B (1969) Characterization of the deoxyribonucleic acid of various strains of halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 99:248–254
Ng WL, Kothakota S, DasSarma S (1991) Structure of the gas vesicle plasmid in Halobacterium halobium: inversion isomers, inverted repeats, and insertion sequences. J Bacteriol 173:1958–1964
Pfeifer F (1985) Insertion elements and genome organization of Halobacterium halobium. Syst Appl Microbiol 7:36–40
Pfeifer F (1988) Genetics of halobacteria. In: F Rodriguez-Valera (ed) Halophilic bacteria. Vol 2, CRC Press, Boca Raton Florida, pp 105–133
Pfeifer F, Betlach M (1985) Genome organization in Halobacterium halobium: a 70 kb island of more AT-rich DNA in the chromosome. Mol Gen Genet 198:449–455
Pfeifer F, Blaseio U (1989) Insertion elements and deletion formation in a halophilic archaebacterium. J Bacteriol 171:5135–5140
Pfeifer F, Blaseio U (1990) Transposition burst of the ISH27 insertion element family in Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6921–6952
Pfeifer F, Ghahraman P (1991) The halobacterial insertion element ISH28. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5788
Pfeifer F, Weidinger G, Goebel W (1981 a) Characterization of plasmids in halobacteria. J Bacteriol 145:369–374
Pfeifer F, Weidinger G, Goebel W (1981 b) Genetic variability in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol 145:375–381
Pfeifer F, Ebert K, Weidinger G, Goebel W (1982) Structure and functions of chromosomal and extrachromosomal DNA in halobacteria. Zbl Bakt Hyg I Abt Orig. C3 110–119
Pfeifer F, Betlach M, Martienssen R, Friedman J, Boyer HW (1983) Transposable elements of Halobacterium halobium. Mol Gen Genet 191:182–188
Pfeifer F, Boyer HW, Betlach M (1985) Restoration of bacterioopsin gene expression in a revertant of Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 164:414–420
Pfeifer F, Blaseio U, Ghahraman P (1988) Dynamic plasmid populations in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol 170:3718–42
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Simon RD (1978) Halobacterium strain 5 contains a plasmid which is correlated with the presence of gas vacuoles. Nature, London 273:314–317
Simsek M, DasSarma S, RajBhandari U, Khorana HG (1981) A transposable element from Halobacterium halobium which inactivates the bacteriorhodopsin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:7268–7272
Staley J, Marvin P. Pfennig N, Holt J (1989) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. Vol. 3, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland, pp 2216–2228
Weidinger G, Klotz G, Goebel W (1979) A large plasmid from Halobacterium halobium carrying genetic information for gas vacuole formation. Plasmid 2:377–386
Weidinger G, Pfeifer F, Goebel W (1981) Plasmids in halobacteria: restriction maps. Methods Enzymol 88:374–379
Xu WL, Doolittle WF (1983) Structure of the archaebacterial transposable element ISH50. Nucleic Acids Res 11:4195–4199
Zvyaga TA, Zozulya SA, Guriev SO (1987) The nucleotide sequence of the archaebacterial transposable genetic element ISH S1. Bioorg Chem 13:1351–1357
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Goebel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfeifer, F., Ghahraman, P. Plasmid pHH1 of Halobacterium salinarium: characterization of the replicon region, the gas vesicle gene cluster and insertion elements. Molec. Gen. Genet. 238, 193–200 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279547
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279547