Abstract
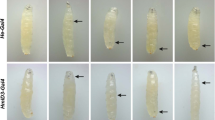
The Drosophila Tumorous-lethal (Tum-l) mutation acts as an activated oncogene, causing hematopoietic neoplasms, overproliferation, and premature differentiation. Tum-l is a dominant mutation in the hopscotch (hop) locus, which is required for cell division and for proper embryonic segmentation. The Tum-l temperature-sensitive period for melanotic tumor formation includes most of larval and pupal development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker BS, Smith DA (1979) The effects of mutagen-sensitive mutants of Drosophila melanogaster in non-mutagenized cells. Genetics 92:833–847
Corwin HO, Hanratty WP (1976) Characterization of a unique lethal tumorous mutation in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet 14:345–347
Craymer L, Roy E (1980) New mutants. Dros Inf Serv 55:200–204
Gateff EA, Mechler BM (1989) Tumor-suppressor gene of Drosophila melanogaster. CRC Crit Rev Oncogenesis 1:221–245
Geer BW, Lischwe TD, Murphy KG (1983) Male fertility in Drosophila melanogaster: Genetics of the vermilion region. J Exp Zool 225:107–118
Hanratty WP, Ryerse JS (1981) A genetic melanotic neoplasm of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol 83:238–249
Lefevre G (1971) Salivary chromosome bands and frequency of crossing-over in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 67:497–513
Lefevre G (1981) The distribution of randomly recovered X-ray induced sex-linked genetic effects in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 99:461–480
Lefevre G, Watkins W (1986) The question of the total gene number in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 113:869–895
Lindsley DL, Zimm GG (1992) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Academic Press, San Diego
Nappi AS, Kmiecik J, Silvers M (1984) Cellular immune competence of a Drosophila mutant with neoplastie hematopoietic organs. J Invert Pathol 44:220–227
Nappi AJ, Silvers M (1984) Cell surface changes associated with cellular immune reactions in Drosophila. Science 225: 1166–1168
Perrimon N, Mahowald AP (1986) l(l)hopscotch, a larval-pupal zygotic lethal with a specific maternal effect_ on segmentation in Drosophila. Dev Biol 118:28–41
Rizki TM (1978) The circulatory system and associated cells and tissues. In: Ashburner M, Wright TRF (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, Vol 2B. Academic Press, New York, pp 398–452
Rosengard AM, Krutzsch HC, Shearn A, Biggs JR, Barker E, Margulies IM, King CR, Liotta LA, Steeg PS (1989) Reduced Nm23/awd protein in tumour metastasis and aberrant Drosophila development. Nature 342:177–180
Shilo B-Z (1987) Proto-oncogenes in Drosophila melanogaster. Trends Genet 3:69–72
Silvers M, Hanratty WP (1984) Alterations in the production of hemocytes due to a neoplastic mutation of Drosophila melanogaster. J Invert Pat. 44:324–328
Sparrow JC (1978) Melanotic tumours. In: Ashburner M, Wright TRF (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, Vol 2B. Academic Press, New York, pp 277–313
Stewart M, Murphy C, Fristrom J (1972) The recovery and preliminary characterization of X chromosome mutants affecting imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol 27:71–83
Watson KL, Johnson TK, Denell RE (1991) Lethal(l) aberrant immune response mutations leading to melanotic tumor formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genetics 12:173–187
Zhimulev IF, Semeshin VF, Belyaeva ES (1981a) Fine cytological analysis of the band 10A1-2 and the adjoining regions in the Drosophila melanogaster X chromosome. I. Cytology of the region and mapping of chromosome rearrangements. Chromosoma 82:9–23
Zhimulev IF, Pokholkova GV, Bgatov AV, Semeshin VF, Belyaeve ES (1981b) Fine cytological analysis of the band 10A1-2 and the adjoining regions in the Drosophila melanogaster X chromosome. II. Genetical analysis. Chromosoma 82:25–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by B.H. Judd
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanratty, W.P., Dearolf, C.R. The Drosophila Tumorous lethal hematopoietic oncogene is a dominant mutation in the hopscotch locus. Molec. Gen. Genet. 238, 33–37 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279527
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279527