Abstract
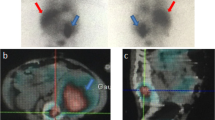
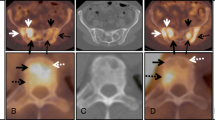
Fourteen children with histopathologically confirmed neuroblastoma underwent 38 studies using 99mTc-methylene-diphosphonate (MDP) and galliumcitrate Ga67 whole-body scintigraphy during various stages of the disease. Ten patients (71%) showed 99mTc-MDP accumulation in the primary tumoral site, whereas 11 patients (78.6%) showed 67Ga concentration. In 12 patients (86%), at least one of these two radiopharmaceuticals concentrated in the primary tumor. Nine patients had osseous or extraosseous metastases. All of these metastases (100%) were positive on 99mTc-MDP sctintigraphy. No 67Ga-citrate uptake was demonstrable in osseous metastases; only one extraosseous lung metastasis concentrated this radiopharmaceutical. 67Ga-citrate was superior to 99mTc-MDP with regard to accurately demonstrating the extent of primary tumors. Only 99mTc-MDP indicated the relationship of the tumor to the kidneys and neighbouring osseous structures, prividing early screening of kidney compression and possible damage caused by the tumor. From these results, we found these two methods to be complementary for the diagnosis and follow-up of neuroblastoma; their combined use resulted in high diagnostic accuracy and a considerable gain of information. We therefore recommend sequential 99mTc-MDP and 67Ga-citrate scans for the diagnosis and evaluation of the primary tumor; periodic 99mTc-MDP wholebody scans should be used in the follow-up of treatment, and for discovering disease exacerbations and metastases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anghileri LJ, Miller ES (1971) Calcium metabolism in tumor: its relationship with chromium complex accumulation. I. Uptake of calcium and phosphorus by experimental tumors. Oncology 25:119–136
Baker M, Siddiqui AR, Provisor A, Cohen MD (1983) Radiographic and scintigraphic skeletal imaging in patients with neuroblastoma: concise communication. J Nucl Med 24:467–469
Bekerman C, Post RB, Pang E, Moohr JW, Kranzler JK (1973) Scintigraphic evaluation of childhood malignancies by 67Ga-citrate. Radiology 127:719–725
Bidani N, Kirchner PT, Moohr J, Radkowski MA, Pang E, Cooper M (1980) Gallium scan as a prognostic indicator in neuroblastoma. Clin Nucl Med 5:450–453
Buja LM, Tofe AJ, Kulkarni PV, Mukherjee A, Parkey RW, Francis MD, Boute FJ, Willerson JT (1977) Sites and mechanisms of localization of technetium-99m phosphorus radiopharmaceuticals in acute myocardial infarcts and other tissues. J Clin Invest 60:724–740
Chew FS, Hudson TM, Enneking WF (1983) Radionuclide imaging of soft tissue neoplasms. Semin Nucl Med 4:266–276
Edeling CJ (1978) Tumor visualization using 67gallium scintigraphy in children. Radiology 127:727–731
Fawcett HD, McDougall IR (1983) Bone scan in extraskeletal neuroblastoma with hot primary and cold skeletal metastases. Clin Nucl Med 5:49–50
Feldman JA, Morales JO (1975) Gallium scanning for neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg 10:553–554
Fitzer PM (1974) 99mTc-Polyphosphate concentration in a neuroblastoma. J Nucl Med 15:904–906
Garty I, Koren A (1985) Simultaneous demonstration of photopenic (“cold”) and osteoblastic (“hot”) skull metastases in a patient with neuroblastoma. Clin Nucl Med 10:529
Garty I, Koren A, Mougilner G, Dharan M, Siplovich L (1985a) Nearly total absence of pulmonary perfusion with corresponding 99mTc-MDP and Ga-67 uptake in a patient with mediastinal neuroblastoma. Clin Nucl Med 10:579–582
Garty I, Risescu J, Rosen G, Bar-Ilan I (1985b) Unusual extraosseous accumulation of Tc-99m-MDP. Eur J Nucl Med 10:362–365
Handmaker H, O'Mara RE (1977) Gallium imaging in pediatrics. J Nucl Med 18:1057–1063
Heisel MA, Miller JH, Reid BS, Siegel SE (1983) Radionuclide bone scan in neuroblastoma. Pediatrics 71:206–209
Helson L (1974) Neurobolastoma: early diagnosis, a key to successful treatment. Pediatr Ann 5:46–52
Holland T, Donohue JP, Baehner RL (1980) The current management of neuroblastoma. J Urol 124:579–582
Howman-Giles RB, Gilday DL, Ash JM (1979) Radionuclide skeletal survey in neuroblastoma. Radiology 131:497–502
King RL, Storaasli JP, Bolande RP (1961) Neuroblastoma: review of 28 cases and presentation of two cases with metastases and long survival. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 85:733–747
Larson SM (1978) Mechanisms of localization of gallium-67 in tumors. Semin Nucl Med 8:193–203
Makinen J (1972) Microcopic patterns as a guide to prognosis of neuroblastoma in children. Cancer 29:1637–1646
Martin-Simmerman P, Cohen MD, Siddiqui A, Mirkin D, Privisor A (1984) Calcification and uptake of Tc-99m diphosphonate in neuroblastomas: concise communication. J Nucl Med 25:656–660
McCartney W, Nusynowitz ML, Reismann EF, Prother J, Mazat B (1976) 99mTc-Diphosphonate uptake in neuroblastoma. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 126:1077–1081
Poulose KP, Reba RC, Eckelman WC, Goodyear BS (1975) Extraosseous localization of 99mTc-Sn pyrophosphate. Br J Radiol 48:724–726
Rosenfield N, Treves S (1974) Osseous and extraosseous uptake of fluorine-18 and technetium-99m polyphosphate in children with neuroblastoma. Radiology 111:127–133
Shih WJ, DeLand FH, Domstad PA, Johnston EH (1982) Extraosseous localization of 99mTc-MDP in ganglioneuroblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med 7:336–338
Sty JR, Babbitt MD, Casper J, Boedecker RA (1979) 99mTc-Methylene disphosphonate imaging in neural crest tumors. Clin Nucl Med 4:12–17
Sty JR, Kun IE, Casper JS (1980) Bone imaging as a diagnostic aid in evaluating neuroblastoma. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2:15–18
Sty JR, Starshak RJ, Casper JT (1983a) Extraosseous accumulation of 99mTc-MDP metastatic intracranial neuroblastoma. Clin Nucl Med 8:26–27
Sty JR, Starshak RJ, Miller JH (1983b) Bone scintigraphy. In: Pediatric nuclear medicine. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, pp 1–25
Wilson LMK, Draper GJ (1974) Neuroblastoma, its natural history and prognosis: a study of 487 cases. Br Med J 3:301–307
Yand SL, Alderson PO, Kaizer HA, Nayner HN Jr. (1979) Serial Ga-67 citrate imaging in children with neoplastic disease: concise communication. J Nucl Med 20:210–214
Young LW, Rubin P, Hanson RE (1970) The extra-adrenal neuroblastoma: high radiocurability and diagnostic accuracy. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 108:75–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Presented in part in the European Congress of Nuclear Medicine, London, England, September 1985
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garty, I., Koren, A., Goshen, Y. et al. The complementary role of sequential 99mTc-MDP and 67Ga-citrate scanning in the diagnosis and follow-up of neuroblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med 11, 224–229 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279074
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279074