Abstract
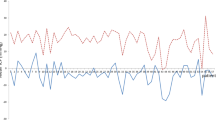
Measurement of intracranial pressure (ICP) is important in patients at risk of raised ICP, as in hydrocephalus. Ideally, it should be non-invasive, thus avoiding the risk of infection and other complications. Such is provided by measurement of ICP through the anterior fontanelle. There are several methods of measuring anterior fontanelle pressure (AFP); those most frequently used are based on the applanation principle. An evaluation of AFP measurement devices resulted in the choice of the Rotterdam Teletransducer (RTT) to be used in our study of children with hydrocephalus. The literature contains little information on the accuracy or validation of the AFP measurements using the RTT. Therefore, the physical qualities of the RTT were reassessed, using a specially developed calibration device. The results of this study demonstrate that membrane temperature does not have any effect on the measured pressure. The thermal stabilization time of the RTT was found to be 3 h after switching on . Insufficient thermal stabilization results in a pressure underestimation of up to 3 mmHg. Furthermore, a maximum inaccuracy of 2.6 mmHg, after calibration and readjustment of the transducer, was calculated. Validation of the equipment was achieved by simultaneous AFP/ICP measurements in hydrocephalic patients showing high correlations (r=0.96–0.98). The discusion suggests a measurement protocol as a means of increasing the reliability of RTT measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bunegin L, Albin MS, Rauschhuber R, Marlin AE (1987) Intracranial pressure measurement from the anterior fontanelle utilizing a pneumoelectronic switch. Neurosurgery 20:726–730
Hayashi T, Kuramoto S, Honda E, Anegawa S (1987) A new instrument for non-invasive measurement of intracranial pressure through the anterior fontanel. I. Preliminary report. Child's Nerv Syst 3:151–155
Honda E (1984) Measurement of fontanelle pressure. I. A new instrument for noninvasive measurement of intracranial pressure via the anterior fontanelle. Kurume Med J 31:235–247
Horbar JD, Yeager S, Philip AGS, Lucey JF (1980) Effect of application force on non-invasive measurement of intracranial pressure. Pediatrics 66:455–457
Jong DA de, Berfelo MW, Lange SA de, Maas AIR (1979) Epidural pressure monitoring with the so-called Rotterdam Transducer. Further in vivo results. Acta Neurochir 45:301–309
Jong DA de, Maas AIR, Berfelo MW, Ouden AH den, Lange SA de (1982) The Rotterdam Teletransducer. A telemetric device for measuring epidural pressure. Biotelemetry Patient Monit 9:154–165
Jong DA de, Maas AIR, Voort E van de (1984) Non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring. A technique for reproducible fontanelle pressure measurements. Z Kinderchir 39:274–276
Jong DA de, Maas AIR, Ouden AH den, Lange SA de (1984) Long-term intracranial pressure monitoring. Med Prog Technol 10:89–96
Jørgensen PB, Riishede J (1972) Comparative clinical studies of epidural and ventricular pressure. In: Brock M, Dietz H (eds) Intracranial pressure I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 41–45
Lacey L, John E, McDevitt M, Cassady G, Philips J (1986) Effect of application force and gestational age on transfontanel pressure in healthy neonates. Biol Neonate 50:136–140
Leggate JRS, Minns RA (1991) Intracranial pressure monitoring — current methods. In: Minns RA (ed) Problems of intracranial pressure in childhood. McKeith, Oxford New York, pp 123–140
Maas AIR (1985) The Rotterdam Teletransducer: state of the device. Z Kinderchir 40 [Suppl I]:19–23
Maas AIR, Jong DA de (1986) The Rotterdam Teletransducer: state of the device. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 79:5–12
Mehta A, Wright BM, Shore C (1988) Clinical fontanometry in the newborn. Lancet: 754–756
Neter J, Wasserman W, Whitmore GA (1988) Applied statistics, 3rd edn. Allyn and Bacon, Boston London Sydney, pp 273–301
Overweg-Plandsoen WCG (1990) The Rotterdam Teletransducer. Anterior fontanelle pressure monitoring in infants. Thesis, Rotterdam, pp 28–37
Plandsoen WCG, Jong DA de, Maas AIR, Stroink H, Eijndhoven JHM van (1986) The pressure-depth curve in anterior fontanelle pressure monitoring. In: Miller JD, Teasdale GM, Rowan JO, Galbraith SL, Mendelow AD (eds) Intracranial pressure VI. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 193–196
Schettini A, McKay L, Majors R, Mahig J, Nevis A (1971) Experimental approach for monitoring surface brain pressure. J Neurosurg 34:38–47
Sundbärg G, Nornes H (1972) Simultaneous recording of the epidural and ventricular fluid pressure. In: Brock M, Dietz H (eds) Intracranial pressure I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 46–50
Vidyasagar D, Raju TNK (1977) A simple non-invasive technique of measuring intracranial pressure in the newborn. Pediatrics 59:957–961
Wealthall SR, Smallwood R (1974) Methods of measuring intracranial pressure via the fontanelle without puncture. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 37:88–96
Whitelaw AGL, Wright BM (1982) A pneumatic applanimeter for intracranial pressure measurement. J Physiol 336:3–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, R.J.A., Hanlo, P.W., Gooskens, R.H.J.M. et al. Non-invasive ICP monitoring in infants: the Rotterdam Teletransducer revisited. Child's Nerv Syst 11, 207–213 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00277655
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00277655