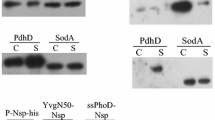
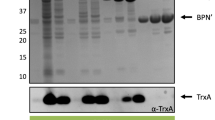
Abstract
Barnase, an extracellular RNAse from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is secreted post-translationally from B. subtilis. The rate of secretion of barnase from B. subtilis was improved by replacement of the barnase signal peptide with a heterologous signal peptide. However, the barnase signal peptide exported Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase faster than mature barnase. Heat shock of B. subtilis cells did not significantly alter the export of barnase using the barnase signal peptide. The slow rate of export of barnase from B. subtilis is due to both the signal peptide and the mature protein sequence rather than either alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman E, Kumamoto CA, Emr SD (1991) Heat shock proteins can substitute for SecB function during protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J 10:239–245
Borchert TV, Nagarajan V (1991) Effect of signal sequence alteration on export of levansucrase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 173:276–282
Collier DN (1993) SecB: A molecular chaperone of the Escherichia coli protein secretion pathway. Adv Protein Chem (in press)
Ferenci T, Silhavy TJ (1987) Sequence information required for protein translocation from the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol 169:5339–5342
Fersht AR, Matouschek A, Serrano L (1992) The folding of an enzyme. 1. Theory of protein engineering analysis of stability and pathway of protein folding. J Mol Biol 224:771–782
Gething M, Sambrook J (1992) Protein folding in the cell. Nature 355:33–45
Gierasch LM (1989) Signal sequences. Biochemistry 28:923–930
Hartley RW (1988) Barnase and barstar. Expression of its cloned inhibitor permits expression of a cloned ribonuclease. J Mol Biol 202:913–915
Hartley R (1989) Barnase and barstar: two small proteins to fold and fit together. Trends Biochem Sci 14:450–544
Lecker S, Lill R, Ziegelhoffer T, Georgopoulos C, Bassford PJ Jr, Kumamoto CA, Wickner W (1989) Three pure chaperone proteins of Escherichia coli-SecB, trigger factor and GroEL-form soluble complexes with precursor proteins in vitro. EMBO J 8:2703–2709
Lee SC, Ollins PO (1992) Effect of overproduction of heat shock chaperones GroELS and DnaK on human procollagenase production in E. coli. J Biol Chem 267:2849–2852
Liu G, Topping TB, Randall LL (1989) Physiological role during export for the retardation of folding by the leader peptide of maltose-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9213–9217
Mossakowska DE, Nyberg K, Fersht AR (1989) Kinetic characterization of the recombinant ribonuclease from B. amyloliquefaciens (barnase) and investigation of key residues in catalysis by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry 28:3843–3850
Nagarajan V (1993) Protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis. In: Hoch JA, Losick R, Sonenshein AL (eds) Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacteria. Physiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics. Amer Soc Microbial, Washington DC (in press)
Nagarajan V, Borchert TV (1991) Levensucrase — A tool to study protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis. Res Microbial 142:787–792
Nagarajan V, Albertson H, Chen M, Ribbe J (1992) Modular vectors for protein expression in Bacillus subtilis. Gene 114:121–126
Paddon CJ, Hartley RW (1986) Cloning, sequencing and transcription of an inactivated copy of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracellular ribonuclease (barnase). Gene 40:231–239
Paddon GJ, Vasantha N, Hartley RW (1989) Translation and processing of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracellular RNase. J Bacteriol 171:1185–1187
Park S, Lui G, Topping TB, Cover WH, Randall LL (1988) Modulation of folding pathways of exported proteins by the leader sequence. Science 239:1033–1035
Phillips GJ, Silhavy T (1990) Heat-shock proteins DnaK and GroEL facilitate export of LacZ hybrid proteins in E. coli Nature 344:882–884
Randall LL, Hardy SJS (1986) Correlation of competence for export with lack of tertiary structure of the mature species: A study in vivo of maltose-binding protein in E. coli. Cell 46:921–928
Streips UN, Polio FW (1985) Heat shock proteins in Bacilli. J Bacteriol 162:434–437
Thom JR, Randall LL (1988) Role of the leader peptide of maltosebinding protein in two of the export process. J Bacteriol 170:5654–5661
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by E. Bautz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Nagarajan, V. The roles of signal peptide and mature protein in RNase (barnase) export from Bacillus subtilis . Molec. Gen. Genet. 239, 409–415 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276939
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276939