Abstract
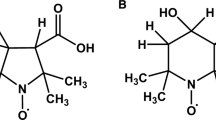
The paramagnetic effect of a spin-labeled sulfonyl fluoride, 4-(2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine-1-oxyl)-p-fluorosulfonylbenzamide (p-V), when bound to the active site serine residue of the proteases, bovine plasma-activated protein C (APC) and des(1–41)-light-chain-activated protein C (GDAPC), on the longitudinal relaxation rate (T1) of Tl+ bound to these same proteins has been examined by 205Tl+-NMR spectroscopy. The substantial shortening by bound p-V of the T1 for Tl+ has been employed to estimate the distances between Tl+ and the unpaired electron on each protein surface. Assuming that a single cation-binding site exists on each enzyme, electron-nuclear distances of 3.4–3.9 Å have been calculated for each protein. This suggests that the removal of 41 amino acid residues and, concomitantly, all γ-carboxyglutamic acid, from the amino-terminal of the light chain of APC, does not significantly affect the protein topography in the region of the molecule probed by this technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bangerter, B. W., and Schwartz, R. N. (1974). J. Chem. Phys. 60, 333–334.
Chase, T., and Shaw, E. (1967). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 29, 508–514.
Drakenberg, T., Fernlund, P., Roepstorff, P., and Stenflo, J. (1983). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 1802–1806.
Esmon, N. L., Owen, W. G., and Esmon, C. T. (1982). J. Biol. Chem. 257, 859–864.
Esmon, N. L., DeBault, L. E., and Esmon, C. T. (1983). J. Biol. Chem. 258, 5548–5553.
Fernlund, P., and Stenflo, J. (1982). J. Biol. Chem. 257, 12170–12179.
Hill, K. A. W. (1986). Ph.D. dissertation, University of Notre Dame.
Hill, K. A. W., and Castellino, F. J. (1986). J. Biol. Chem. 261, 14991–14996.
Hill, K. A. W., and Castellino, F. J. (1987a). J. Biol. Chem. 262, 7098–7104.
Hill, K. A. W., and Castellino, F. J. (1987b), Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 254, 196–202.
Hill, K. A. W., and Castellino, F. J. (1987c). J. Biol. Chem. 262, 7105–7108.
Hill, K. A. W., and Castellino, F. J. (1987d). J. Biol. Chem. 262, 140–146.
Kisiel, W., and Davie, E. W. (1981). Methods Enzymol. 80, 320–332.
Kisiel, W., Ericsson, L. H., and Davie, E. W. (1976). Biochemistry 15, 4893–4900.
Long, G. L., Belagaje, R. M., and MacGillivray, R. T. A. (1984). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 5653–5656.
Steiner, S. A., and Castellino, F. J. (1982). Biochemistry 21, 4609–4614.
Steiner, S. A., and Castellino, F. J. (1985a). Biochemistry 24, 1136–1141.
steiner, S. A., and Castellino, F. J. (1985b). Biochemistry 24, 609–617.
Steiner, S. A., Amphlett, G. W., and Castellino, F. J. (1980). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 94, 340–347.
Stenflo, J. (1976). J. Biol. Chem. 251, 355–363.
Stenflo, J., and Fernlund, P. (1982). J. Biol. Chem. 257, 12180–12190.
vanHinsbergh, V. W. M., Bertina, R. M., vanWijngaarden, A., vanTilburg, N. H., Emeis, J. J., and Haverkate, F. (1985). Blood 65, 444–451.
Vehar, G. A., and Davie, E. W. (1980). Biochemistry 19, 401–410.
Walker, F. J., Sexton, P. W., and Esmon, C. T. (1979). Biochem. Biophys. Acta 571, 333–342.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, K.A.W., Castellino, F.J. Topographical relationships among the monovalent cation binding sites of bovine plasma-activated protein C and des(1–41)-light-chain-activated bovine plasma protein C and a nitroxide spin label bound to their active site serine residues. J Protein Chem 6, 489–495 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276735
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276735