Summary
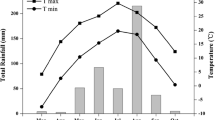
Irrigations scheduled on plant water status ignore the effect of ontogeny on plant water status. Leaf xylem water potential (XWP) of maize sown on three dates in a sandy loam soil was measured under the same environment for evaluating the effect of ontogeny on plant water status. Minimum XWP (measured between 13.00-14.30 h) of the youngest crop was the highest during two crop seasons and the differences in XWP of the youngest and the oldest maize plants ranged from 0.25 to 0.65 MPa during the season. Maximum XWP (measured before dawn) of the youngest crop was nearly 0.1 MPa higher than that of the oldest crop. Diurnal variation in XWP was lowest in the youngest crop. The results highlight the need of ontogeny dependent critical values of plant water status for scheduling irrigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerson RC, Kreig DR (1977) Stomatal and non-stomatal regulation of water use in cotton, corn and sorghum. Plant Physiol 60:850
Fiscus EL (1981) Analysis of components of area growth of bean root systems. Crop Sci 21:909
Frank AB, Power JF, Willis WO (1973) Effect of temperature and plant water status on photosynthesis, diffusion resistance and leaf water potential in spring wheat. Agron J 65:777
Hiler EA, Howell TA (1983) Irrigation options to avoid critical stress. Chapter IIA. In: Taylor HM, Jordan WR, Sinclair TR (eds) Limitations to efficient water use in crop production. Am Soc Agron, Madison, p. 479
Howell TA, Hatfield JL, Yamada H, Davis KR (1984) Evaluation of cotton canopy temperature to detect crop water stress. Trans ASAE 27:84
Hsiao TC, Accevedo E, Ferrers E, Henderson DW (1976) Water stress, growth and osmotic adjustments. Philos Trans R Soc London Series B 273:479
Kramer PJ (1983) Water relations of plants. Academic Press, New York
Prihar SS, Gajri PR, Narang RS (1974) Scheduling irrigation to wheat using pan evaporation. Indian J Agric Sci 44:567
Scholander PF, Hammel HT, Bradstreet ET, Hammingsen EA (1965) Sap pressure in vascular plants. Science 148:339
Singh NT, Tomar VS (1982) Soil-Water-Plant relationships. In: Review of Soil Research in India Part I. 12th International Congress of Soil Science, New Delhi, India
Singh NT, Aggarwal GC, Brar GS (1984) Effect of Soil moisture regime on xylem water potential of some wheat varieties. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 32:14
Teare ID, Sionit N, Kramer PJ (1982) Changes in water status during water stress at various stages of development in wheat. Physiol Plant 55:296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekhon, N., Aggarwal, G.C. Changes in plant water status of Maize (Zea mays L.) with ontogeny. Irrig Sci 9, 227–231 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00275434
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00275434