Abstract
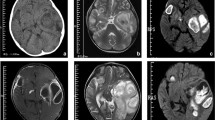
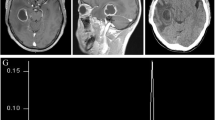
A large traumatic brain abscess in a 9-year-old white boy was successfully treated conservatively with antibiotics, including metronidazole and ampicillin. No neurological or psychological sequelae, except for unilateral loss of the olfactory sense, were revealed at follow-up 5 years later, and on CT two minor hypodense areas remained in the right frontal lobe. Our treatment protocol includes metronidazole (0.5 g 3 times a day) and ampicillin (1 g 6 times a day) for adults. This seems to be the treatment of choice in cases of intracranial brain abscesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boom WH, Tuazon CV (1985) Successful treatment of multiple brain abscesses with antibiotics alone. Rev Infect Dis 7:189–199
Britt RH, Enzmann DR, Placone RC, Obana WG, Yeager AS (1984) Experimental anaerobic brain abscess. Computerized tomographic and neuropathological correlations. J Neurosurg 60:1148–1159
de Tribolet N, Guiguard G, Zander E (1979) Brain abscesses after transnasal intracranial penetration of a paint-brush. Surg Neurol 11:187–189
Dobkin JF, Healton EB, Dickinson PCT, Brust JCM (1984) Nonspecificity of ring enhancement in “medically cured” brain abscess. Neurology (Cleveland) 34:139–144
Everett ED, Strausbaugh LJ (1980) Antimicrobial agents and the central nervous system. Neurosurgery 6:691–714
Hirsch JF, Roux FX, Sainte-Rose C, Renier D, Pierre-Kahn A (1983) Brain abscess in childhood. A study of 34 cases treated by puncture and antibiotics. Child's Brain 10:251–265
Ingham HR, Selkon JB, Roxby CM (1977) Bacteriological study of otogenic cerebral abscesses: chemotherapeutic role of metronidazole. Br Med J 2:991–993
Kawaga M, Takeshita M, Yato S, Kitamura K (1983) Brain abscess in congenital cyanotic heart disease. J Neurosurg 58:913–917
Neuwelt EA, Baker DE, Pagel MA, Blank NK (1984) Cerebrovascular permeability and delivery of gentamycin to normal brain and experimental brain abscess in rats. J Neurosurg 61:430–439
Nielsen H (1983) Cerebral abscess in children. Neuropediatrics 14:76–80
Rousseaux M, Lesoin F, Destee A, Jomin M, Petit H (1985) Developments in the treatment and prognosis of multiple cerebral abscesses. Neurosurgery 16:304–308
Rousseaux M, Lesoin F, Destee A, Jomin M, Petit H (1985) Long term sequelae of hemispheric abscesses as a function of the treatment. Acta Neurochir 74:61–67
Sandermann J, Jensen KT, Bartholdy NJ (1986) Primary nonsurgical treatment of brain abscesses. Proceedings of the 37th Annual Meeting of the Scandinavian Neurosurgical Society, Alborg, 1985 (abstr)
Sandermann J, Jensen KT, Bartholdy NJ (1985) Brain abscesses, nonsurgical treatment (in Danish, English abstract). Ugeskr Læger 147:1323–1327
Whelan MA, Hilal SK (1980) Computed tomography as a guide in the diagnosis and follow-up of brain abscesses. Radiology 135:663–671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandermann, J., Haase, J., Bartholdy, N.J. et al. Nonsurgical treatment of a traumatic brain abscess in a child. Child's Nerv Syst 2, 49–51 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00274036
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00274036