Summary
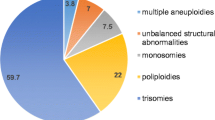
Spontaneous abortions were studied by analyzing chromosomes directly from chorionic villi. The frequency and the type of anomalies detected among 140 abortuses are in good agreement with those observed by others using conventional tissue cultures. Abnormal karyotypes were found in 48.6% of the cases. Trisomy predominated (66.2%), followed by polyploidy (22.1%), monosomy X (7.4%), and structural anomalies (4.4%). Among the trisomies, the most prevalent were of chromosome 22 (22.2%), 16(22.2%), and 13 (9.5%). The relative frequencies of trisomies, monosomy X, and the different chromosomes involved in trisomies seem to differ between our study and those in which tissue cultures were analyzed. Our low frequency of 45,XO karyotypes and the shift to trisomies of chromosomes whose involvement increases steeply with maternal age are considered due to the approximately 3 year higher mean maternal age in our sample. The sex ratio (male to female) in chromosomally abnormal abortuses was 1.28, which is nearly identical to the 1.2 found in earlier studies. Surprisingly, in chromosomally normal abortions males were significantly outnumbered by females (sex ratio 0.76). Since maternal cell contamination cannot have influenced the sex ratio in our study, we consider it worthwhile to investigate whether failures associated with X inactivation are responsible for pregnancy wastage of some euploid female conceptuses. Knowledge of the karyotypes may serve as a prerequisite for the investigation of non-chromosomal genetic causes of pregnancy wastage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberman E, Elliott M, Creasy M, Dhadial R (1975) Previous reproductive history in mothers presenting with spontaneous abortions. Br J Obstet Gynecol 82:366–373
Boué A, Boué J, Gropp A (1985) Cytogenetics of pregnancy wastage. In: Harris H, Hirschborn K (eds) Advances in human genetics 14. Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–57
Brandriff B, Gordon L, Ashworth L, Watchmaker G, Moore D, Wyrobek AJ, Carrano AV (1985) Chromosomes of human sperm: variability among normal individuals. Hum Genet 70:18–24
Cattanach BM (1986) Parental origin effects in mice. J Embryol Exp Morphol [Suppl] 97:137–150
Eiben B, Schübbe I, Borgmann S, Hansmann I (1986) Rapid cytogenetic diagnosis of early spontaneous abortions. Lancet I:1273–1274
Engel E (1980) A new genetic concept: uniparental disomy and its potential effect, isodisomy. Am J Med Genet 6:137–143
Flori E, Nisand I, Flori J, Dellenbach P, Ruch JV (1985) Direct fetal chromosome studies from chorionic villi. Prenat Diagn 5:287–289
Ford CE (1981) Nondisjunction. In: Burgio GR, Fraccaro M, Tiepolo L, Wolf U (eds) Trisomy 21. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 103–143
Hansmann I (1983) Factors and mechanisms involved in nondisjunction and X-chromosome loss. In: Sandberg AA (ed) Cytogenetics of the mammalian X-chromosome, part A. Basic mechanisms of X chromosome behaviour. Liss, New York, pp 131–170
Hansmann I, Bartels I, Schübbe I (1986) Cytogenetic analysis of early human abortuses after preparation of chromosomes directly from chorionic villi. Hum Genet 72:189
Hassold TJ, Jacobs PA (1984) Trisomy in man. Annu Rev Genet 18: 69–97
Hassold T, Chen N, Funkhouser J, Jooss T, Manuel B, Matsuura J, Matsuyama A, Wilson C, Yamane JA, Jacobs PA (1980) A cytogenetic study of 1000 abortions. Ann Hum Genet 44:151–164
Hummler E, Theuring F, Hansmann I (1987) Meiotic nondisjunction in oocytes from aged Djungarian hamsters correlates with an alteration in meiosis rate but not in univalent formation. Hum Genet 76:357–364
Kajii T, Ohama K (1979) Inverse maternal age effect in monosomy X. Hum Genet 51:147–151
Kajii T, Ferrier A, Niikawa N, Takahara H, Ohama K, Avirachan S (1980) Anatomic and chromosomal anomalies in 639 spontaneous abortuses. Hum Genet 55:87–98
Kamiguchi Y, Mikamo K (1986) An improved efficient method for analyzing human sperm chromosomes using zona-free hamster ova. Am J Hum Genet 38:724–740
Martin RH, Lin CC, Balkan W, Burns K (1982) Direct chromosomal analysis of human spermatozoa: preliminary results from 18 normal men. Am J Hum Genet 34:459–468
Mikkelsen M (1985) Cytogenetic findings in first-trimester chorionic villi biopsies: a collaborative study. In: Fraccaro M, Simoni G, Brambati B (eds) First trimester fetal diagnosis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 109–120
Rudak E, Jacobs PA, Yanagimachi R (1978) Direct analysis of the chromosome constitution of human spermatozoa. Nature 274: 911–913
Searle AG, Beechey CV (1985) Noncomplementation phenomena and their bearing on non-disjunctional effects. In: Dellarco VL, Voytek PE, Hollaender A (eds) Aneuploidy. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 363–376
Shapiro LJ, Mohandas T (1983) Noninactivation of X-chromosome loci in man. In: Sandberg AA (ed) Cytogenetics of the mammalian X-chromosome, part A. Basic mechanisms of X chromosome behaviour. Liss, New York, pp 299–314
Simoni G, Brambati SB, Danesino C, Rosella F, Terzoli GL, Ferrari M, Fraccaro M (1983) Efficient direct chromosome analysis and enzyme determinations from chorionic villi samples in the first trimester of pregnancy. Hum Genet 63:349–357
Solter D (1987) Inertia of the embryonic genome in mammals. Trends Genet 3:23–27
Warburton D (1985) Genetic factors influencing aneuploidy frequency. In: Dellarco VL, Voytek PE, Hollaender A (eds) Aneuploidy. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 133–148
Warburton D, Kline J, Stein Z, Susser M (1980a) Monosomy X: a chromosomal anomaly associated with young maternal age. Lancet I:167
Warburton D, Stein Z, Kline J, Susser M (1980b) Chromosome abnormalities in spontaneous abortion: data from the New York city study. In: Porter IH, Hook EB (eds) Human embryonic and fetal death. Academic Press, New York London, pp 261–287
Yamamoto M, Ito T, Watanabe M, Watanabe G (1982) Causes of chromosome anomalies suggested by cytogenetic epidemiology of induced abortions. Hum Genet 60:360–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eiben, B., Borgmann, S., Schübbe, I. et al. A cytogenetic study directly from chorionic villi of 140 spontaneous abortions. Hum Genet 77, 137–141 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272380
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272380