Summary
Some of the strains containing mutations in the genes for the acetolactate synthase isoenzymes are temperature sensitive (ts). Suppression of the acetolactate synthase defect due to one of these mutations suppresses also the ts phenotype; moreover, a genetic cross shows that the two phenotypes cannot be dissociated.
The ts phenotype is accompanied by a decreased efficiency of transduction with Pl phage. Observations at the light microscope show formation of abnormal cells. Under specific conditions diaminopimelate stimulates growth and restores normal transduction efficiency. The rate of diaminopimelate formed and excreted by non-growing cells decreases when an acetolactate synthase mutation is present.
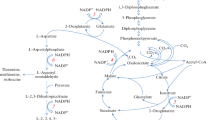
We give evidence that the ts phenotype is due to an increased formation of lysine from diaminopimelate; this causes a starvation for the latter and therefore cell wall abnormalities. In fact, even at the permissive temperature, the lysine pool is 8x increased in a strain with an acetolactate synthase defect, while a slight decrease in the diaminopimelate pool is observed. Moreover, introduction into a ts strain of a mutation in lysA (the gene coding for diaminopimelate decarboxylase) cures the ts phenotype. Finally among the temperature resistant revertants we found some lysine auxotrophs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann, B.J.: Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bact. Rev. 36, 525–557 (1972)
Bukhari, A.I., Taylor, A.L.: Mutants of Escherichia coli with a growth requirement for either lysine or pyridoxine. J. Bact. 105, 988–998 (1971)
De Felice, M., Guardiola, J., Esposito, B., Iaccarino, M.: Structural genes for a newly recognized acetolactate synthase in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bact. 120, 1068–1077 (1974)
De Felice, M., Guardiola, J., Malorni, M.C., Klopotowski, T., Iaccarino, M.: Regulation of the pool size of valine in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bact. 120, 1058–1067 (1974)
De Felice, M., Squires, C., Levinthal, M., Guardiola, J., Lamberti, A., Iaccarino, M.: Growth inhibition of Escherichia coli K-12 by L-valine: a consequence of a regulatory pattern. Molec. gen. Genet. 156, 1–7 (1977)
Favre, R., Wiater, A., Puppo, S., Iaccarino, M., Noelle, R., Freundlich, M.: Expression of a valine-resistant acetolactate synthase activity mediated by the ilvO and ilvG genes of Escherichia coli K-12. Molec. gen. Genet. 143, 243–252 (1976)
Gilvarg, C.: The enzymatic synthesis of diaminopimelic acid. J. biol. Chem. 233, 1501–1504 (1958)
Guardiola, J., De Felice, M., Iaccarino, M.: Mutant of Escherichia coli K-12 missing acetolactate synthase activity. J. Bact. 120, 536–538 (1974)
Guardiola, J., De Felice, M., Lamberti, A., Iaccarino, M.: The acetolactate synthase isoenzymes of Escherichia coli K-12. Molec. gen. Genet. 156, 17–25 (1977)
Hirshfield, I.N., Buklad, N.E.: Effect of alanine, leucine and fructose on lysyl-transfer ribonucleic acid ligase activity in a mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bact. 113, 167–177 (1973)
Iaccarino, M., Berg, P.: Isoleucine auxotrophy as a consequence of a mutationally altered isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J. Bact. 105, 527–537 (1971)
Lee, N.M., Lansford, E.M., Jr., Shive, W.: A study of the mechanism of lysine-sensitive aspartokinase control by lysine. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 24, 315–318 (1966)
McQuillen, K.: Bacterial protoplasts. In: The bacteria. Vol. I (I.C. Gunsalus and R.Y. Stanier, eds.), pp. 250–359. New York: Acad. Press 1960
Patte, J.C., Loviny, T., Cohen, G.N.: Effects inhibiteurs cooperatifs de la L-lysine avec d'autres amino acides sur une aspartokinase de Escherichia coli. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 99, 523–530 (1965)
Ramakrishnan, T., Adelberg, E.A.: Regulatory mechanisms in the biosynthesis of isoleucine and valine. I. Genetic derepression of enzyme formation. J. Bact. 87, 566–573 (1964)
Rebello, J.L., Jensen, R.A.: Metabolic interlock. The multimetabolite control of prephenate dehydratase activity in Bacillus subtilis. J. biol. Chem. 245, 3738–3744 (1970)
Ryter, A., Hirota, Y., Schwarz, U.: Process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. Growth pattern of E. coli murein. J. molec. Biol. 78, 185–195 (1973)
Vogel, H.J., Bonner, D.M.: Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J. biol. Chem. 218, 97–106 (1956)
Wilska, A.: Mikroskopie (Wien) 9, 1 (1954); cited in: Gabler, F., Positiver oder negativer Phasenkontrast? Mikroskopie (Wien) 10, 119–124 (1955)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by F. Gros
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Felice, M., Guardiola, J., Schreil, W. et al. Metabolic interlock between the acetolactate synthase isoenzymes and lysine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. Molec. Gen. Genet. 156, 9–16 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272246
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272246