Abstract
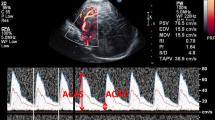
Doppler ultrasound investigation of cerebral blood flow velocity was performed in hydrocephalic infants through the anterior fontanelle. Systolic (S) and end-diastolic (D) frequency values recorded on the anterior cerebral artery were used to define the pulsatility index (PI) calculated from the equation PI=S-D/S. Comparison between systolic, end-diastolic and pulsatility index values of 50 normal infants and 10 hydrocephalic infants showed a statistically significant difference (P<0.05) for systolic and pulsatility index values. However, no significant difference was found for end-diastolic values. The authors believe that the phenomenon could be explained as an increase of the cerebrovascular compliance which counteracts the increase of the perivascular pressure in an attempt to maintain a normal cerebral blood flow. Therefore, the transfontanelle Doppler ultrasound technique may provide a useful and early tool in diagnosing cerebral blood-flow changesin hydrocephalic infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmann PA, Dykes FD, Lazzara A, Holt PJ, Giddens DP, Carrigan TA (1983) Relationship between pressure passivity and subependymal/intraventricular hemorrhage as assessed by pulsed Doppler ultrasound. Pediatrics 72:665–669
Auer LM, Samaya I (1983) Intracranial pressure oscillations (B-waves) caused by oscillations in cerebrovascular volume. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 68:93–100
Bada HS, Sumner DS (1984) Transcutaneous Doppler ultrasound: pulsatility index, mean flow velocity, end diastolic flow velocity, and cerebral blood flow. J Pediatr 104:395–397
Bada HS, Miller JE, Menke JA, Menten TG, Bashiru M, Binstadt D, Sumner DS, Khanna NN (1982) Intracranial pressure and cerebral arterial pulsatile flow measurements in neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. J Pediatr 100:291–296
Batton DG, Hellemann J, Hernandez MJ, Maisels MJ (1983) Regional cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood velocity, and pulsatility index in newborn dogs. Pediatr Res 17:908–912
Ellison P, Eichorst D, Rouse M, Heimler R, Denny J (1983) Changes in cerebral hemodynamics in preterm infants with and without patent ductus arteriosus. Acta Paediatr Scand [Suppl] 311:23–27
Greisen G, Johansen K, Ellison PH, Fredriksen PS, Mali J, Friis-Hansen B (1984) Cerebral blood flow in the newborn infant: comparison of Doppler ultrasound and 133 xenon clearance. J Pediatr 104:411–418
Hansen NB, Stonestreet BS, Rosenkrantz TS, Oh W (1983) Validity of Doppler measurements of anterior cerebral artery blood flow velocity: correlation with brain blood flow in piglets. Pediatrics 72:526–531
Hill A, Volpe JJ (1982) Decrease in pulsatile flow in the anterior cerebral arteries in infantile hydrocephalus. Pediatrics 69:4–7
Hochwald GM, Bolad RD, Marlin A, Kumar AJ (1975) Changes in regional blood flow and water content of brain and spinal cord in acute and chronic experimental hydrocephalus. Dev Med Child Neurol [Suppl] 35:42–50
Johnston KW, Maruzzo BC, Cobbold RSC (1977) Errors and artifacts of Doppler flowmeters and their solution. Arch Surg 112:1335–1342
Lipman B, Serwer GA, Brazy JE (1982) Abnormal cerebral hemodynamics in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatrics 69:778–781
Lunt MJ (1975) Accuracy and limitations of the ultrasonic Doppler blood velocimeter and zero crossing detector. Ultrasound Med Biol 2:1–10
McMenamin JB, Volpe JJ (1984) Bacterial meningitis in infancy: effects on intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow velocity. Neurology 34:500–504
Methew NT, Hartmann A, Meyer JS (1975) The importance of CSF pressure-regional cerebral blood flow dysautoregulation in the pathogenesis of normal pressure hydrocephalus. In: Lundberg N, Ponten V, Brock M (eds) Intracranial pressure, II. Springer, New York, pp 145–149
Perlman JM, Volpe JJ (1983) Seizures in the preterm infant: effects on cerebral blood flow velocity, intracranial pressure, and arterial blood pressure. J Pediatr 102:288–293
Perlman JM, Hill A, Volpe JJ (1981) The effect of patent ductus arteriosus on flow velocity in the anterior cerebral arteries: ductal steal in the premature newborn infant. J Pediatr 99:767–771
Perlman JM, McMenamin JB, Volpe JJ (1983) Fluctuating cerebral blood-flow velocity in respiratory-distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 309:204–209
Pourcelot L (1974) Applications clinique de l'examen Doppler transcutanée. In: Perroneau P (ed) Velocimetrie ultrasonore Doppler. INSERM, Paris, p 213
Strassburg H-M, Niederhoff H, Sauer M (1982) Die Dopplersonographische Registrierung der Durchblutung intracranieller Gefäße beim Säugling. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 130:608–612
Van Bel F, Grimberg MThTh (1982) Intracranial bleeding in asphyxia of newborn infant studied with the Doppler Ultrasound method (in Dutch). Tijdschr Kindergeneeskd 50:1–10
Van Bel F, Hirasing RA, Grimberg MThTh (1984) Can perinatal asphyxia cause cerebral edema and affect cerebral blood flow velocity? Eur J Pediatr 142:29–32
Volpe JJ, Perlman JM, Hill A, McMenamin JB (1982) Cerebral blood flow velocity in the human newborn: the value of its determination. Pediatrics 70:147–152
Wilcox WD, Carrigan TA, Dooley KJ, Giddens DP, Dykes FD, Lazzara A, Ray JL, Ahmann PA (1983) Range-gated pulsed Doppler ultrasonographic evaluation of carotid arterial blood flow in small preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus. J Pediatr 102:294–298
Wozniak M, McLone DG, Raimondi AJ (1975) Micro- and macrovascular changes as the direct cause of parenchymal destruction in congenital murine hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 43:535–545
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvisi, C., Cerisoli, M., Giulioni, M. et al. Evaluation of cerebral blood flow changes by transfontanelle Doppler ultrasound in infantile hydrocephalus. Child's Nerv Syst 1, 244–247 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272019