Summary
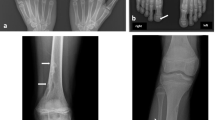
A 15-year-old girl affected by autosomal recessive 3-M slender boned nanism (3-MSBN) was studied. The clinically normal parents, two other obligate and two probable heterozygotes for the 3-MSBN gene from an unrelated family were radiologically investigated. All except one probable heterozygote showed mild features of the 3-MSBN, mainly bone slenderness and prominent talus. These findings are interpreted as demonstrative of the heterozygotic expression of the 3-MSBN gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantú, J. M., García-Cruz, D., Sánchez-Corona, J., Fragoso, R., Hernández, A., Nazará-Cazorla, A.: 3-M Slender boned nanism. A distinct autosomal recessive intrauterine growth retardation syndrome. Am. J. Dis. Child. (in press, 1979)
Miller, J. D., McKusick, V. A., Malvaux, P., Temtamy, S., Salinas, C.: The 3-M syndrome: a heritable low birthweight dwarfism. In: New chromosomal and malformation syndromes, Vol. XI/5, Bergsma, D. (ed.), pp. 39–47. Miami: Symposia Specialists for The National Foundation 1975
Spranger, J., Opitz, J. M., Nourmand, J.: A new familial intrauterine growth retardation syndrome. The 3-M syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 123, 115–124 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Cruz, D., Cantú, J.M. Heterozygous expression in 3-M slender-boned nanism. Hum Genet 52, 221–226 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271577
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271577